Planting shrubs in spring. Planting seedlings of fruit trees - how to do it right
What month to plant on your personal plot bushes and trees, depends on a number of factors. It is necessary to take into account the climatic features of the region, the characteristics of the variety, the weather, the time of arrival of frosts. Planting trees in autumn is preferable for southern cities and the middle zone, where winters are not very snowy, colds do not come until the end of October. However, planting new crops on the site is also permissible in the spring, which is most often practiced in the northern regions.
- Decent choice of material. At the end of the fruiting phase (in summer), it is possible to evaluate not only the characteristics of the seedling, but also the volume and taste of the fruit in a particular variety.
- If you do not miss the deadlines, the plants have time to get stronger before winter, take root and take root on the site. New roots appear on them, which are already actively growing with the onset of spring.
- Rainfall is more frequent in autumn than in summer, which reduces the amount necessary irrigation. Loose breathable soil contributes to good rooting of the seedling, which allows you to prepare the plants for winter.
Planting shrubs in the fall has its drawbacks:
- Planting material is immature seedlings of a bush or tree. With the onset of early frosts, sudden changes in temperature, too heavy rains, they may not take root and die in a cold snowy winter.
- A variety of pests in the absence of food can eat the bark of fruit trees and shrubs, which significantly reduces the chances of plant rooting.
It is necessary to take into account the amount of snow that falls in a particular region. If the nast is too large and heavy, thin stems and branches may break under its weight.
What fruit bushes and trees are planted in autumn
In autumn, you can plant the following fruit trees:
- cherry;
- peach;
- almond;
- apple trees;
- cherries;
- apricot;
- plum.
Almost any fruit bushes, with the exception of sea buckthorn, it is optimal to plant in autumn period. Winter-hardy varieties are:
- nut;
- currant;
- coniferous;
- some types of pear;
- honeysuckle;
- gooseberry;
- aronia.
After the autumn planting, seedlings brought from the southern regions do not take root. They are unable to bear sub-zero temperatures and a large number of snow.
Terms of landing works
Autumn planting of trees must be carried out at the following times:
- in the cities of the middle zone - from the end of September to the end of October;
- in the warm parts of the country - from the last decade of September to mid-November.
Plants can be planted later, depending on the weather. In southern latitudes, winter generally occurs in late November or early December. If the above-zero temperature is maintained until this period, there are no heavy rains, snow and night frosts, you can do planting work.
tree planting technology
Planting fruit trees in the fall has certain nuances. It is important to choose the side of the site where there is more light and low (at least 1.5 m) groundwater occurrence. Some crops, such as peach, cherry, raspberry, without proper lighting will not give a good harvest.
Site and soil preparation
Before choosing a place, consider the size of the future plant, namely the roots and crown of the bush / tree. It is also necessary to make indents from the house, communications and outbuildings.
The distance is calculated based on the height of the tree:
- tall ones, reaching 20–25 m, are placed at least 35 m from the building;
- undersized species - from 4.5 m.
Some crops in the neighborhood give a poor harvest and interfere with each other, depriving them of light. The neighborhood of an apple tree with cherry plum, peach, apricot with cherry, walnut with many fruit crops is not recommended.
Pit preparation is as follows:
- The size is determined based on the diameter of the roots. Stone fruits require a hole of at least 40 cm in diameter up to 60 seconds deep, for pome fruits the hole should be up to 80 cm in diameter and a similar depth.
- Root cutting is not recommended. If the seedling does not fit in the hole, its diameter must be increased.
- At the bottom of the pit, a drainage layer of crushed stone 20-40 mm, sand and gravel mixture or river pebbles is arranged.
- The top layer is removed carefully; in the future, supplements of mineral or organic origin will be added to it.
Two years after planting, the seedling will fully feed on the substances that are in the soil of the planting pit. That is why the initial feeding is so important.

How to prepare seedlings
When choosing planting material pay attention to appearance plants:
- the roots should be straightened and not bent up;
- on the root system there should be a clod of moist earth;
- too many leaves on a seedling may indicate that there is not enough moisture in the tissues;
- if unripened shoots are visible, then the seedling was dug up before the leaves fell;
- there should be no visible cracks, rot or other damage on the bark.
A good seedling is even, with at least 5-6 shoots, without curved sections of the trunk and branches.
Landing scheme
Technique for planting seedlings of fruit trees in autumn:
- Place seedlings on the south side of the site. Most fruit crops are thermophilic, need good lighting. On the north side, it is better to plant tall trees.
- Prepare the seedling - remove the dried parts of the root system with secateurs, moisten with a wet piece of cloth or a spray bottle.
- Place a wooden peg in the center of the dug hole, make a mound at the bottom.
- Place a seedling in the center of this mound so that it is at least 5 cm from the peg. The inoculation should be located 3 cm above the ground.
- Fill the hole with earth, gently pressing it with your hands. Do some mulching.
Pre-remove upper layer soil, place it in a large container. Here it is necessary to make top dressing and fill up the place around the seedling.

Subtleties of planting shrubs
It is better to plant shrubs on the site in the first decade of September, so that before the winter cold they have time to take root and not be damaged by frost. The planting technique depends on whether you want to get free-standing bushes or a hedge.
Site and soil preparation
The dimensions of the planting holes must correspond to the parameters of the root system. Lateral roots - to be able to receive nutrients and water from all layers of the soil due to growth to the sides.
Pits for bushes are prepared as follows:
- To create a natural fence from the bushes, you need to dig a long trench. At the lowest point of the dug hole, drain the water. If there is no slope of the site, an artificial slope is created by removing the top layer of soil.
- Some shrubs, such as thuja, are suitable for creating hedges. In this case, it is also possible to make a trench, the depth of which will be 50-60 cm.
- Medium-sized plants require trenches up to 50 cm deep.
- From the smallest shrubs, you can create low borders. In this case, the trench will not exceed 35 cm in depth.

The width of the pit also varies depending on the size of the seedlings:
- single row landing - 50 cm;
- medium shrubs - up to 40 cm;
- small seedlings - the width of a shovel.
As in the case of planting trees, the top layer of soil about 12 cm thick is removed and deposited in a separate container for top dressing.
Planting material processing
When seedlings are purchased in advance, they must be protected from drying out by wrapping the root system with a wet cloth and transfer the plants to a cool place. If the seedling is bought too late, it is better to bury it before the next planting period. Preparatory steps:
- the roots are pruned until healthy tissues appear, dried roots are removed with pruners;
- 1.5 hours before being transferred to the pits, the root system is watered abundantly;
- the plant is transferred to a pit with adhering earthy clod;
- some cultures require pruning of shoots before planting.
It is necessary to remove all dried shoots and roots, as well as broken, with signs of disease, cracks. Use a sharp tool so as not to hurt the healthy tissue of the plant.
Landing technology
Bush planting scheme:
- It is necessary to drive a pointed peg made of wood into the dug hole to a depth of about 20 cm. The height of the peg should be about 1-1.5 m. It is necessary for further tying plants (standard varieties) and strengthening on the ground.
- Before planting about 15 minutes, the roots of the seedlings should be in the open air. To do this, remove the packaging or a damp cloth, lay out the planting material near the dug holes.
- Pour into the bottom of the hole vegetable land and form a mound in the form of a cone at least half the depth high. Consider the nature of the branching and the shape of the root system.
- Place the seedling and straighten the roots along the cone with your hands. It should be strictly vertical and at a distance of 5 cm from the peg.
- Please note that with subsequent watering the soil will settle. Therefore, the seedling should be 5 cm higher normal surface garden plot, the root neck does not go deep into the hole.
- Pour the soil in layers, compact with your feet to the outside of the hole. This will help to avoid the appearance of voids and too much shrinkage when watering.
- Completely cover the entire root system, gently tamp. Center the position of the seedling and tie it with a soft rope to a peg at a height of about 1.5 mots of soil.

For non-standard forms of shrubs, as a fortification, you can use not a peg, but a rounded hole, which is organized according to the diameter of the landing pit.
Immediately after planting shrubs and fruit trees seedlings need to be watered. Mulching is carried out with peat chips, the layer thickness should be about 2 cm. This will reduce the evaporation of moisture. In addition to peat, you can use a mixture of earth and sand, crushed tree bark and others. natural materials.
As a top dressing, a ready-made or self-made growth stimulator is used. It is added to the water used for irrigation. This will promote the rapid rooting of plants.
When working with shrubs or trees, consider the climatic conditions. The low temperatures of the Urals or Siberia are suitable for growing acclimatized or zoned varieties that can endure early frosts and snowy windy winters. Early digging of seedlings, if it is carried out before the foliage has flown, can cause bushes with unripened shoots to freeze and die. Choose planting material without leaves, not overdried, without broken or dry roots.
The best time for planting fruit seedlings in spring is the month of April, the period of which is a little earlier than mid-April and until mid-May.
At the end of the article, be sure to watch a video on the topic of proper tree planting, in the video everything is said and shown in more detail, clearly and clearly practical example planting seedlings in the soil, a specialist gardener.
Beginning gardeners, just summer residents and gardeners ask themselves the question: “Is it possible to plant a seedling in the spring and how effective will the tree take root in this case? We understand the rules for successful spring planting of trees.
When thinking about which trees are best to plant in the spring, you need to consider the region in which you live. For example, for the southern regions, the optimal time for planting is autumn, because trees planted in spring may not have time to take root before the onset of hot days, which means they risk getting burned or dying. 
But in central regions tree planting dates can fall both in autumn and in spring - thanks to temperate climate seedlings have every chance to take root equally. For the northern regions, spring planting of seedlings - the best way, since trees planted in autumn often do not have time to acclimatize and die from hypothermia.
Spring tree planting: pros and cons
Let's start with the benefits of planting trees in the spring:
1. In the spring there is an opportunity to observe the process of plant survival, and the likelihood that it will freeze out, as often happens in winter, is practically reduced to zero.
2. You will have enough time to prepare everything related to planting fruit trees: fertilize the soil, think over a planting plan, get a tool, which means that the procedure itself will be better.
The disadvantages of spring planting are as follows:
1. Seedlings should be bought in autumn, because in spring the choice on the market will not be so wide (although in spring it is not small).
2. If the summer is hot, young trees will have to be watered almost every day.
Preparing a seedling for planting
 It is better to buy tree seedlings in the fall, when the plants are already at rest. And before planting seedlings in the spring, they need to be prepared.
It is better to buy tree seedlings in the fall, when the plants are already at rest. And before planting seedlings in the spring, they need to be prepared.
Carefully inspect the root system and cut off dead, rotten or damaged roots with a sharp pruner. Remove growths, shorten too long roots.
To improve root formation, before planting, dip the roots of the seedling into a growth stimulant solution (Kornevin, Heteroauxin, Kornerost, Root, etc.) for at least a couple of hours, or overnight.
Preparing a hole for planting
Since most trees are photophilous plants, best location garden on the site - south and south-west side. When planning to plant trees on the site, remember that it is important to observe right neighborhood. So, cherries and apple trees feel great next to each other, but they do not recommend planting a pear next to cherries, cherry plums and plums.
Depending on the species, the distance between trees when planting
should be from 1.5 to 6 m.
| culture | Distance between rows (m) | Distance between plants in a row (m) |
| Apricot | 5-6 | 3-4 |
| Cherry tall | 4-5 | 3-4 |
| Cherry stunted | 3-4 | 2,5-3 |
| Pear on a vigorous rootstock | 6-8 | 4-6 |
| Pear on a stunted rootstock | 4-5 | 1,5-2,5 |
| Peach | 5-6 | 3-4 |
| Plum tall | 4-5 | 3-4 |
| Plum stunted | 3-4 | 2,5-3 |
| Apple tree on a vigorous rootstock | 6-8 | 4-6 |
| Apple tree on a stunted rootstock | 4-5 | 1,5-2,5 |
For the spring planting of trees, the soil must be prepared since summer-autumn, so that in a few months a favorable environment for the seedling will form in it. In extreme cases, work is carried out in the spring after thawing the soil, 1-2 weeks before planting.
At the first autumn digging you need to select large weeds from the soil, during the second - apply fertilizer at the rate of: 6-8 kg of compost and 8-10 kg of a mixture of peat with superphosphate (80-100 g), potassium salt (30-50 g) and potassium sulfate (30 -40 d) per 1 sq.m of land selected for planting trees.
In the spring, before digging the planting holes, mark their contours with a shovel (for convenience, put a stake in the chosen place and use it as the center of the circle).
 For pears and apples standard size the landing pit is 80 -100 cm in diameter and 60 - 70 cm deep. Plum and cherry seedlings will feel good in a hole with a diameter of 70 - 80 cm and a depth of 50 - 60 cm. If the seedlings are more than 2 years old, then the size of the hole needs to be increased.
For pears and apples standard size the landing pit is 80 -100 cm in diameter and 60 - 70 cm deep. Plum and cherry seedlings will feel good in a hole with a diameter of 70 - 80 cm and a depth of 50 - 60 cm. If the seedlings are more than 2 years old, then the size of the hole needs to be increased.
You can be guided by this rule: the diameter of the planting pit should be 1.5 times the diameter of the seedling's earthen coma.

How to plant a seedling
When digging, on one side of the pit, fold the top (turf, 15-20 cm deep) layer, on the other - the bottom (it has more dark color). Make the pit round and make the walls vertical (sheer). Insert into the bottom of the hole in the center strong stake 1.5-2 m long, to later tie a seedling to it. Lay the excavated sod layer at the bottom, then fill the pit with a part of the fertile substrate to a height of 15-20 cm (mix equal amounts of peat, compost and soil removed from the pit).
 At the bottom of the pit, form a mound and place the seedling in it (close to the stake), evenly distributing the roots.
At the bottom of the pit, form a mound and place the seedling in it (close to the stake), evenly distributing the roots.
Make sure that when planting, the roots of the seedling do not bend upwards: bent roots develop worse and “slow down” the engraftment of the tree.
When installing a seedling in a pit, deepen it into the soil strictly along the root collar, ideally it should be located 3-5 cm above ground level. Later, the soil will settle a little, and the root collar will drop. If the seedling is too deep, the plant may later begin to rot. While holding the seedling (you will need someone's help for this), fill the hole with the remaining substrate.
The root collar is where the stem of the plant meets the roots. Usually it is 2-3 above the topmost spine.
Gradually compact the ground with your feet, pressing on it from the edge to the center of the near-stem circle. Tie the trunk of the seedling not very tightly to the stake in two places, so that when the soil “shrinks”, the tree also falls.
 Form a roller around the tree along the perimeter of the circle (you will get a watering “pool”).
Form a roller around the tree along the perimeter of the circle (you will get a watering “pool”).
Watering trees after planting
Immediately after the tree is planted, it is necessary to water it under the root. The water pressure should not be too strong so that the soil does not erode, so use a watering can with a bell or a hose with a sprinkler nozzle. After filling the “pool”, wait until the water is absorbed, then fill it again. The first watering will require 1-2 buckets of water.

In the first year after planting, seedlings are watered quite often - as the soil dries up (during the drought period - 1-2 times a day). Then the frequency of watering is gradually reduced, and completely stopped for 2-3 years.
Experienced gardeners recommend mulching trunk circle tree - pour a layer (8-10 cm) of mulching material (wood chips, sawdust, mowed grass, etc.), leaving the root neck uncovered. This will improve the structure of the soil, protect it from freezing.
Primary care of planted seedlings
 During the first year of the life of a planted tree, it is necessary to monitor how it develops and, if possible, correct deficiencies. It is not necessary to feed the seedling in the first year, since all the main fertilizers were applied during planting. The trunk circle should be loose and free of weeds.
During the first year of the life of a planted tree, it is necessary to monitor how it develops and, if possible, correct deficiencies. It is not necessary to feed the seedling in the first year, since all the main fertilizers were applied during planting. The trunk circle should be loose and free of weeds.
Carefully inspect a young tree and collect leaf-eating caterpillars, which can cause great harm to the plant. Also, do not allow the formation of overgrowth on the trunk and near the roots, if necessary, cut it off at the very base.
 The tree should not be tightly tied to the peg, check if the garter does not rub the bark of the seedling and if it cuts into it. If damage is visible, loosen the garter.
The tree should not be tightly tied to the peg, check if the garter does not rub the bark of the seedling and if it cuts into it. If damage is visible, loosen the garter.
Planting young trees is a serious matter, but observing simple rules, after a while you will get beautiful blooming garden and a great harvest.
Video: How to plant fruit trees
Video: Spring planting of fruit trees

Other category content:

Orange peels from ants, aphids and cats in the garden, bird feeder

Most owners of cottages, gardens and plots buy seedlings on the market, where the seller can immediately give a lot of advice on their proper fit. Often, sellers understand this business well, but there are often cases when the seller is just hired by a horticultural business to sell seedlings, and in this case, he is asked to write recommendations that he memorizes by heart and tells you whether it is correct or not.
Well, if you have your own personal experience in planting and laying out a garden and growing this tree, and if not, and the recommendations turn out to be incorrect, then goodbye to a young fruit tree - at best it will not bear fruit for a very long time, at worst it will die before our eyes , right after landing.
Therefore, it is always important to know what, when and how to plant correctly - a fruit tree, especially a young one, a seedling is not a field for experiments - believe me.
So, how to plant a tree in the garden.
In the beginning, consider the very structure of a young fruit tree - a seedling in photo 1.

Rice. 1 The structure of the seedling
As many know, its roots are separated from the trunk by the root collar.
Before planting a seedling, be sure to find a root collar (usually this is the branching point of the first large root of the root system).
This is important because grafting can be done both in the trunk of a rootstock (the so-called vaccination for stem), but it can also be made into the root neck - therefore, it is impossible to navigate when planting a seedling for grafting - it will be more accurate to rely on the root neck.
Landing site - preparation
To plant a seedling, dig a hole approximately 80 centimeters in diameter, and a little less than a meter deep (80-90 centimeters in Figure 2).
Now it is important to fill it, for which take manure (necessarily completely rotted) and peat (two garden carts each), as well as complex fertilizers and sand.
At the same stage of planting a young tree, you can drive a stake into the bottom of the pit, to which you later tie the seedling so that it grows straight.
It is better to fill a hole for a seedling in layers - soil, humus, peat and mineral fertilizers, then mix, and repeat again in the same order. Backfill the planting pit until a small mound about 20 centimeters in height appears around the seedling above the ground. This mound subsequently compensates for the shrinkage of the soil around the seedling, so it should be about 7-10% of the depth (this is approximately how much the backfill soil mixture settles).
If you fill the planting hole flush with the soil, the soil will settle and after the first rain there will be a puddle around the young seedling, which means it will start to rot (not necessary, but it is quite possible, at least the risk of bark rotting in rainy weather is very high ).
However, it is also impossible without moisture at all, and the fight against it should be reasonable, so make a kind of rim around the seedling that will allow water to soak into the depth and not spread over the site. (Figure 2).

Rice. 2 Planting hole preparation
Rice. 3 Correct and incorrect filling of the pit
a) shrinkage of the soil with proper filling of the pit
b) soil shrinkage due to improper filling of the pit
Proper planting of a seedling (Photo 5)
Now we start planting a seedling. To do this, we make a recess on top of the poured mound, which should slightly exceed the size of the roots of the seedling in size.
Now carefully straighten all the roots, spread them apart and in depth as evenly as possible, and sprinkle with soil so that the root neck rises 6-7 centimeters above the ground.
Before watering the seedling, you need to compact the soil, you can do this with your foot - in photo 4 you can see that in this case the toe of the shoe should be located towards the seedling.
It is not necessary to tie a seedling to a stake tightly, with a figure eight - the task of a rope or twine is not to pull the tree seedling to the peg as tightly as possible, but only to hold it in vertical position so that it grows straight.
Some gardeners believe that if the upper roots of the seedling are visible during planting, then this is not scary and they will still be drawn into the depths a few days after the start of growth, but I try to cover them completely - after all, the young seedling is still very tender and weak.

Rice. 4 Trampling the soil around the seedling
Rice. 5 Planting a seedling on a hill
How to water a seedling
Pour a freshly planted tree with four buckets of water (by volume). You can do this with a garden watering can and a hose. In most cases, I do not pour water from - but before planting I try to heat the water in the sun or take it from a garden barrel, you can rain it.
Still, the water from the well is cold.
Water slowly - letting the water go deep into the roots, make sure that the mound around the seedling does not wash out.
If a seedlings are planted in the spring, then you need to water it every 7-10 days until autumn, if the summer is not rainy enough, then even more often, there is not enough ground moisture for a young tree.
If planting in autumn, then you can water less often.
Pruning a seedling
The tops of seedlings can often dry out by 6-7 centimeters, because the tree is still young and growth by winter may simply not have time to form. This is especially often manifested in those seedlings that were planted in the fall.
Therefore, in autumn seedlings, you can cut off the top to the very border with mature wood (dense lignification of the shoot is usually clearly visible - the bark is glossy there, and in the immature part the bark is pubescent, the internodes are located very close to each other).
If it is not possible to determine this by the color of the bark or leaves, then you can simply trim the seedling to 2-3 upper buds after planting - this will be enough. At the same time, trim the side branches so that they do not outstrip the central trunk in height.
If the seedling is planted too deep, can it be transplanted?
Most often, seedlings die in winter - there are many death factors here - and poor winter hardiness (it happens that they deceive our brother in the summer resident, in fact, we buy a pig in a poke). The second no less common reason is improper planting of a seedling.
If the root collar was deeply buried and hidden by the ground, the tree, instead of immediately entering active growth and vegetation, which will allow him to easily endure the winter, will take a long time to settle down in a new place, or, as they say, “grow”. Also, as a result of the deepening of the root collar, the tree may not start producing crops for a very long time.
In this case, it will be necessary to carefully dig the seedling, rake the ground and find the root collar. In the event that it is below ground level, then the seedling or young tree will need to be dug deeper (without damaging the root system) and, together with the earthen clod, raised to the required height. As a rule, after such a procedure, the tree begins to bear fruit in due time.
Advice for summer residents and gardeners
Even seedlings of winter-hardy fruit varieties, if grown in southern nurseries, are poorly adapted to the climate of the middle zone. Therefore, choose nurseries located close to your site for the purchase of planting material. Try to buy seedlings from the manufacturer, and not from a reseller.
Expert comments:
Amateur gardeners ask themselves many questions: When to plant? How to plant?". What gardeners do not come up with, for example, they lay rusty iron, stones, branches, etc. in a pit, with such a planting, the tree does not grow well and, as a result, dies.
In almost all gardening literature, it is recommended to plant fruit trees in the spring, because in the fall they do not have time to take root, and they are recommended to simply dig in until spring. I had the unfortunate experience of planting fruit trees in the spring, as many horticultural scientists recommend, namely planting apple trees in pits prepared in the fall. At first, the plants grew and developed well, as soon as the time of flowering came, they bloomed, and then the flowers and ovaries dropped and dried up.
After that, I started planting fruit trees only in autumn, and they grow very well. See what happens in nature in autumn: the trees sow themselves, drop bones, seeds, etc. on the ground.
And I do so. I plant the purchased seedlings of fruit trees only in the fall. I prepare a hole depending on the size of the root system, if it is large, I make a hole 60 × 60 cm, if it is small, I make a smaller hole. I put 2-3 buckets of rotted manure in the pits, mix it with the ground, you can replace the manure with mature compost, add 4-5 glasses of wood ash and 1.5 - phosphorus- potash fertilizers.
Before planting, I soak the roots in a clay mash for a day, because almost all seedlings have a dried up root system, and then I plant them. We plant a seedling together. I put the sapling in the center, I drive a stake near it, I tie the sapling to it. We throw earth on the roots. I shake the plant so as not to deepen the root neck, then I compact the soil with my feet along the radius from the trunk. The root neck should be 5-6 cm above the soil. Then I sprinkle mounds of earth to the trunk, which I rake from the trunk to the edges, it turns out a round earthen roller. I pour 1.5-2 buckets of water to the trunk (see fig.). I do watering to supply moisture to the roots and for better contact with the soil. The next day, I correct and sprinkle the sagging soil, then mulch with compost.
Trees planted in autumn before the onset of spring take root well, as they grow even when the above-ground part is resting. When cold weather sets in, I mulch around the trunk with compost and dry leaves with a layer of 20 cm, and above-ground part I wrap the trees with burlap.
How to transplant a tree seedling

Sometimes only after some time it becomes obvious that the place on the site for the tree was chosen unsuccessfully. It's not worth it to grab a saw! Plants that were planted no more than 5 years ago can usually still be transplanted (ideally in October and April in dry weather).
So that the tree (in our case, hawthorn (Crataegus) "Carrierei") does not lose too many young roots, it must be relocated along with an earthen clod.
First (2) form a hemisphere with a shovel upper part earthen clod, removing the earth in layers, starting from the trunk. Then (3), cutting off the lateral roots, separate the lump.
(4) Pry it up with a shovel, cutting off the roots going deep into the ground. (5) Carefully trim all protruding roots with secateurs. If some roots are not completely chopped off, 6 lumps will begin to crack and may even fall apart. To prevent this from happening, be sure to complete the work and only then take out the tree. Then (7) place it on top of a piece of burlap and (8) tie off the ends of the fabric. For reliability, tie a lump (9) with another piece of burlap.
Then (10) shorten the branches to reduce the diameter of the crown, then the plant will need less nutrients and water (in this case, the chances of good rooting in a new place will increase). Move the tree to a new location and plant at the same depth as before transplanting.
You can not remove the burlap, it is enough to untie the knots. Fill the planting hole with soil and water the plant well.
Preparing a planting hole for planting a seedling
No one will argue that when planting seedlings, the planting hole must be filled fertile soil. But where can I get it? Yes, of course, if you decide to plant your garden at once and at the same time are going to plant, say, a dozen fruit trees, then the total volume of the required fertile soil will be several cubic meters. In this case, the best option is to bring land to the site by car. What if there is only one landing hole? Where to get soil? Cut off the beds? It is possible, of course, to do so. But just who will benefit from this? Well this is how much you have to cut the beds! And did you really work for this, poring over your garden and carefully planning plantings? That's really true: we treat one thing, we cripple another.
Some will notice to me that you can buy land in a store. Okay, but let's do the math first. The volume of an ordinary landing pit measuring 80x80x80 cm is about 500 liters (half a cube). In other words, you will need 10 fifty-liter packages of a pound, the retail price of which is from 200 rubles and more. It turns out that the total cost of this pleasure will be 2000 rubles. Yes, it's tricky.
And therefore, for several years now, when planting fruit seedlings, I have been using a technology that allows several times to reduce the cost of purchasing soil and at the same time significantly increase the fertility of the soil in the pit. The technology is based on the use of green manure.
I dig a landing hole of the above dimensions. I try to make the walls somewhat inclined (wait a minute to accuse me of excessive luxury, then you will see why this is necessary). At the same time, I lay the surface layer of soil with sod in a separate place, and store the rest of the soil next to the dug hole.
If I intend to use seedlings with an open root system (their sale usually ends in June-July), then I prepare the pit as early as the thawed soil allows.
And if the seedlings are with closed roots, then you can start preparing the pit until the beginning of August, but not later, otherwise you may not have time to prepare everything for planting. The fact is that the duration of the preparation of the pit according to my technology is two and a half, or even all three months.
Slowly but surely

I buy green manure grass seeds in advance at the rate of one package for each hole. I mainly use lupins and vetch-oat mixture, but I think other green manures are also possible. You also need a package of complex fertilizer, for example, azofoski (70-80 rubles), and a package of 40-50 kg of peat soil (about 150 rubles). Total expenses for 320-330 rubles.
When the hole is dug, I pour a handful of green manure seeds to the bottom of it and put it into the ground. With the help of a cultivator or a rake, I try to close up the seeds on the side walls of the pit - it is for the convenience of this operation that I make them inclined. Then I water with a solution of complex fertilizer and wait two weeks.
During this time, siderats give abundant seedlings, first at the bottom, and then on the walls of the pit (photos 1 and 2). Then I cut off the fresh shoots only at the bottom with a sharp chopper, sprinkle with a layer of excavated soil (12-15 cm, primarily with turf, laid
blowing its roots up) and again plant the seeds of green manure. I compact the poured soil. I do not touch the growth on the walls. Again I water with a solution of fertilizers.
At this stage, I install a landing stake, which I make from two connected U-shaped galvanized profiles 1.5 m long. It turns out a square pipe, in the lower part I drill a dozen holes for water to exit. This design allows further delivery of water and fertilizer solutions directly to the root layer, leaving surface weeds without nutrition.
So, after two weeks, I repeat all the steps, while adding a small amount of peat-sand mixture and wood ash to the soil taken out of the pit to improve the soil structure. Notify if necessary. I repeat the procedure 4-6 times.
Grow beautiful garden not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. It is enough to choose the right seedlings and correctly place them on the site. Planting fruit trees and shrubs is carried out not only in spring, but also in autumn. Seedlings need not only to be properly planted in open ground, but also to choose the most suitable for them. appropriate place with good soil, sufficient lighting and protection from drafts.
This article describes in detail the features of planting fruit trees and shrubs, the rules for choosing and preparing a site, and photos and videos will help to carry out this procedure correctly.
Planting fruit trees
well maintained orchard- this is not only a wonderful decoration for your summer cottage, but also a rich source of vitamins.
It will take a lot of effort and time to grow it like this. And our article will also equip you with the necessary baggage of knowledge and rules that will help in cultivating an orchard.
rules
Sometimes it happens that the seedlings were High Quality, and the pits were prepared in time and appropriately, and the garden still does not start to grow. Most often this comes from ignorance by novice gardeners of the rules for placing seedlings. It is their strict observance that ensures that all your efforts and costs invested in the future garden will not be in vain.
Landing fruit and berry trees and bushes are held so(picture 1):
- The soil is prepared in advance, for example, for spring planting - in the fall, and provides for loosening the soil and fertilizing.
- Immediately before being transferred to the ground, the seedlings must be put in water for several hours so that the root system has the opportunity to make some moisture.
- Damaged or too long roots should be trimmed smoothly.
- The roots of the seedling should be freely placed in the hole.
- It's not enough just to dig a hole right size: it is also necessary to loosen its bottom and lay a layer of compost seasoned with fertilizer on it.
- It is necessary to drive a support stake into the dug hole from the leeward side.
- The soil that remains from digging the hole is mixed with compost, mineral and organic fertilizers, sand. This substrate is used to fill the hole after planting the tree.
- Seedlings are placed in the hole strictly vertically. If a tree is grafted, then the grafting site should be located above ground level at a height of 10 cm.
- During planting, the pit is filled with prepared soil evenly, compacting it and conducting intermediate watering.
 Figure 1. Rules for planting seedlings
Figure 1. Rules for planting seedlings After planting the tree, it is necessary to form a watering circle. To do this, around the entire circumference of the hole, an embankment is made in the form of a roller 5-7 cm high, and the trunk circle itself is mulched with organic matter (rotted manure, straw, raw compost). The planted tree must be watered abundantly and tied to a peg.
Peculiarities
If you are going to lay a garden, you should start with tilling the soil in the selected area: carry out deep loosening of the soil and remove weeds, because in loose earth seedlings quickly grow and begin to bear fruit much earlier. Then you need to decide on the size of the holes.
Note: For annual plants, holes are dug with a depth and width of 50-60 cm, for two-year-olds you will need a hole 110-120 cm wide and 60-70 cm deep. If the soil is heavy, then 15-20 cm are added to all sizes.
If the soil has elevated level acidity, it must be limed. For fertilizer, organic and ash top dressings are used. It is not recommended to use fresh or half-rotted manure, because with a lack of air in the soil, it decomposes and releases harmful substances that poison the entire plant.
Where to plant fruit trees
When choosing a place for fruit crops, they pay attention to the relief, the nature of the soil, the depth of groundwater, and the possibility of protection from the wind. In your summer cottage, give preference to a place with good illumination, which is not flooded by groundwater. So, the maximum standing height groundwater for apple and pear trees is 1.5 m, for cherries and plums - 1 m. If the groundwater is high, drainage will have to be done (Figure 2).
 Figure 2. Placement of fruit trees and shrubs on the site
Figure 2. Placement of fruit trees and shrubs on the site It is known that gardens grow best on gentle slopes, but flat laying is not so effective. It is not recommended to plant a garden in hollows due to stagnation of cold air and excess water in them.
Which side of the world to plant fruit trees
An important role is played not only by the fact when to plant seedlings of fruit trees in spring or autumn, but also the side of the world where the garden will be located.
Experienced gardeners advise planting fruit trees on the south, southeast and southwest side of the site.
Fit Types
The correct arrangement of plants in the garden, that is, the type of planting, most directly affects the survival rate of seedlings. Therefore, it is so important to imagine it in all details before starting the laying of the garden. It is also necessary to calculate the distances between seedlings. The interval between them should not be less than the height of mature trees. It is in such conditions that plants will more efficiently pollinate and bear fruit. It is also known that more fruits are formed on the side branches, so the crowns of fruit trees should be formed so that they grow in width (Figure 3).
 Figure 3. The main types of planting fruit trees: 1 - groups, 2 - central placement of bouquets, 3 - checkerboard, 4 - row planting, 5 - row planting different breeds, 6 - central planting of shrubs
Figure 3. The main types of planting fruit trees: 1 - groups, 2 - central placement of bouquets, 3 - checkerboard, 4 - row planting, 5 - row planting different breeds, 6 - central planting of shrubs However, you should be aware that in an arrangement that is too sparse, fruit trees are more susceptible to sunburn and freezers, so they grow much worse. In this case, the so-called "seals" are planted between tall fruit trees, that is, undersized fruit crops such as cherries or plums. They are not as durable as apple and pear trees, and therefore cease fruiting after 20 years of life and can be removed, since the crowns of tall trees will have had time to fully form and grow by that time.
When to plant seedlings of fruit trees in spring
Timely planting of seedlings of fruit trees in the spring is important not only for their survival, but also for the subsequent growth and development of plants. The question arises when it is better to plant fruit trees and shrubs in the spring.
Since changes in nature occur very quickly, the air temperature rises, the soil dries quickly, so the best time for the procedure is early spring, although in the southern regions it can be produced in the fall. However, a culture such as cherries often freezes during autumn planting, so it should be planted only in spring. At the same time, the sooner a tree is planted, the better and faster it will take root.
How to choose a place to land
When choosing a place to place fruit crops, you should pay attention to several factors: the depth of groundwater, illumination and the presence of drafts. So, groundwater must lie at a depth of at least 1 m. Otherwise, trees will have to be placed on mounds 60-120 cm high.
It is known that fruit trees need a lot of sunlight and heat, so it would be wise to choose a site that is well lit by the sun, preferably on the south side of the site. In addition, it should be noted that young trees are afraid of drafts, so you should try to place a young garden under the protection of buildings. Experienced gardeners recommend not planting seedlings in the same place where fruit trees used to grow. The wasteland area left after uprooting the garden must be sown with meadow or legume grasses for several years or completely change the soil in the pits.
Planting seedlings of fruit trees in spring time
Spring planting should be carried out as early as possible, the determination of which depends specifically on the seedling and weather conditions.
In any case, the work should be completed before the buds bloom on the trees (seedlings). The survival and development of culture in the future depends on this.
Planting fruit trees in spring: video
When to plant seedlings of fruit trees in the spring and how to do it correctly, you can see in the video clip. Its author will give valuable practical advice on landing, which are sure to be useful for beginners and experienced gardeners.
Planting seedlings of fruit trees in autumn
Although spring planting is most commonly practiced, autumn planting also has its advantages (Figure 4). For example, in autumn it is much more profitable to purchase seedlings, since it is possible to see the fruits that a certain variety produces. In addition, seedlings planted in the fall do not require much trouble; watering in dry weather will be enough. Their roots will continue to grow until the onset of stable frosts, which means that such a tree will grow earlier in the spring.
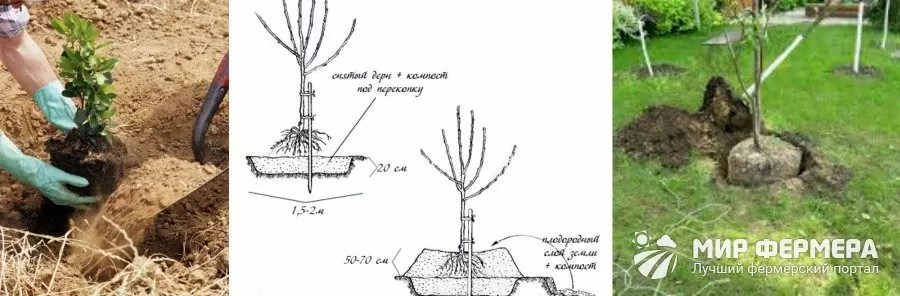 Figure 4. Rules for planting fruit crops in autumn
Figure 4. Rules for planting fruit crops in autumn Most often, autumn procedures are practiced in the southern regions, where young plants are not in danger of hypothermia due to mild winters. However, one should be aware of the vagaries of nature and understand the risk to the growth of autumn plantings. Severe frosts and wind, ice and snowfalls can not only lead to damage to seedlings, but also completely destroy them. Therefore, experts advise against planting fruit crops such as pear, apple, plum, apricot, peach, cherry, almond and cherry in the fall.
Timing
The optimal time for autumn planting is called the end of September - the month of October, and in the southern regions - from October to mid-November. However, you should be aware that these dates are rather arbitrary, since they depend on weather conditions.
Therefore, it is still better to focus on the condition of the seedlings. best time for planting is a period of rest, which occurs after the end of leaf fall.
Gardens are laid in areas with different topography, groundwater levels and illumination. However, there are certain rules that must be followed when planting a garden, regardless of its location.
It must be remembered that improperly planted trees take root and grow poorly, which can lead to their death.
rules
Planting fruit trees is carried out in accordance with certain rules, which not only ensure the survival of plants, but also improve the volume of fruiting in the future.
The basic rules for planting fruit and berry crops include several important points (picture 5):
- Pits must be prepared two weeks before the planned planting. At the same time, their size depends on the quality of the soil, but should not be less than 50-60 cm in depth and width.
- When digging holes, the soil is laid out in two parts: the upper fertile layer and the lower, less fertile, separately. The bottom layer is enriched with nutrients by adding compost to it. The use of manure for this purpose is not recommended, since even in a rotted state it can damage the bare roots of plants.
- The bottom of the pit must be loosened to improve air access to the roots of the plant. If the soil is sandy, then a layer of clay 15 cm thick is laid out at the bottom of the pit, which will retain the necessary moisture.
- A few days before planting, the pits are filled with fertilizers (2-4 buckets of humus, phosphorus - 200 g, potassium chloride - 100 g, wood ash- 1 kg per pit measuring 60-100 cm). All fertilizers are mixed with the soil, which is intended for backfilling the pit. If the pit was dug and filled in the fall, then this work is not carried out in the spring.
- Before placing the seedling in the center of the pit, it is necessary to drive a stake 5-6 cm thick and 1.3-1.5 m high from the leeward side.
- Planting material must be carefully examined, cut off all damaged or diseased branches and roots.
- You can keep the seedling in a container with water for 1-2 days, so that its root system accumulates enough moisture for quick engraftment. It is also recommended to dip the root in a mash of clay and manure (clay, mullein, water in a ratio of 1:2:5), which will ensure good contact of the roots with the soil.
 Figure 5. Features of planting fruit trees
Figure 5. Features of planting fruit trees Immediately before planting, a mound of soil filled with fertilizer is poured into the bottom of the pit, then a seedling is placed on it from the north side of the stake and the roots are straightened. The pit is covered with a fertile layer of earth removed when digging the pit, compacting it and regularly shaking the seedling. This is done so that voids do not form between the roots. Ultimately, the root collar of the seedling should be slightly above the level of the soil in the garden in order to catch up with it after watering.
After planting along the diameter of the pit, the soil is poured with a roller of small height, and the circle itself is watered with 5-6 buckets of water. The tree itself must be tied to a stake.
The trunk circle must be mulched with organic material to prevent the formation of a surface crust and help retain moisture.
Peculiarities
When choosing seedlings, it would be useful to know their age, because this significantly affects the survival rate of trees. For example, apple and pear seedlings should be 2-3 years old, while cherry and plum seedlings should be 2 years old. When deciding on varieties, heed the advice of experienced gardeners.
Note: Arrange the plants in the garden in rows at a certain distance from each other. So, pears and apple trees are planted at a distance of 6-8 meters, and cherries and plums - at a distance of 3 meters between tall fruit trees and 3-4 meters between rows. You can also take aisles with currant or gooseberry bushes. It will be great if the rows of the garden are located from east to west. So they are better illuminated by the sun in the morning.
To mark out a plot for a garden, you first need to draw its plan, where to provide for the boundaries and arrangement of rows, paths and flower beds (Figure 6). On the ground, stakeout is carried out using a rope, tape measure and pegs. The rope is needed to determine and indicate the distances that will be respected during landing. It is stretched along the future row, and with the help of knots or scraps of fabric, you mark the landing sites. Here it is necessary to ensure that the rows are even. It is not only beautiful, but also easy to care for.
 Figure 6. Scheme for placing trees and shrubs
Figure 6. Scheme for placing trees and shrubs Planted trees are recommended to be tied to stakes to protect them from excessive swinging. To do this, use the usual bast, which must be fixed on a support in the form of a figure eight, so that the seedling does not damage its tender young bark on the stake.
In addition, after planting a tree, you need to cut its branches. At the same time, strong shoots must be shortened by half, and weak ones - a little less. As a result of pruning, the ends of the skeletal branches should end in the same horizontal plane. The central shoot is cut so that it is 20-30 cm higher than all the others. Both the lateral and central branches are cut above the outer bud.
Planting shrubs can be done both in spring and autumn. All work in the spring begins after the snow melts and the soil thaws, and in the fall - before the start of frost.
rules
Planting shrubs, as well as planting trees, is carried out according to certain rules (Figure 7). First of all, they begin with the preparation of the soil and planting material, and also determine the compatibility of the soil and the selected plants. If the soil does not meet the requirements of a particular shrub, it is necessary to carry out a set of agrotechnical measures to improve the soil.
Shrubs are planted in specially prepared pits, the depth of which should correspond to the height of the plant's root system. In this case, attention should be paid to the level of occurrence of groundwater. If they come too close to the ground surface, the planting hole should be 15-20 cm deeper than the standard one in order to be able to arrange drainage. A layer of soil is poured at the bottom of the pit, then a bush is planted.
Note: It is necessary to ensure that during planting the roots of the plant are straightened and sprinkled with earth. It is recommended to fill up a hole with a seedling 5-10 cm higher general level soil, however, the root neck should not be buried in the ground.
The planted plant must be watered, it is possible with the addition of growth stimulants. Further care consists in feeding, watering and trimming the branches.
Peculiarities
Planting shrubs in the fall is carried out taking into account the characteristics of certain species. So, for raspberries there is no need to prepare special holes, since its annual seedlings are planted in fertilized soil under a shovel. But for currants and gooseberries, shallow pits are needed. These plants are best planted at the age of two.
Shrub branches before moving into the ground must be cut so that their length from the roots is from 25 to 30 cm. This procedure will help reduce evaporation, and in currants and gooseberries it stimulates the branching of the bush. Before planting, it is recommended to dip the root system of bushes in a soil or clay mash to protect it from drying out.
 Figure 7. Features of planting shrubs
Figure 7. Features of planting shrubs Rows of shrubs are marked with a rope, placing them parallel to the rows of trees between the rows. If the planting of shrubs is located separately, then the distance between the rows and in them is one and a half meters. The exception is raspberries, which can be planted at intervals of 70-80 cm. The earth around the planted plants must be tamped and watered at the rate of 1 bucket of water for 4-5 seedlings. After absorbing moisture, the planting circle can be mulched with peat or humus.
Note: It is important to know that raspberry bushes should not be planted deeper than on the uterine plot. But currant and gooseberry seedlings, on the contrary, must be planted deeper than before. This way they can develop additional roots and grow better.
As for strawberries and strawberries, these plants are planted in a slightly different way, since they are herbaceous. So, strawberries are best planted from late July to early September, because late planting will not allow the plant to take root well before the onset of winter. Strawberries are planted between rows of fruit trees or in a separate area. In this case, strawberries are planted in rows, observing an interval of 20-25 cm between bushes and rows. After every three rows, it is recommended to leave a passage half a meter wide. If there is not enough space, you can plant strawberries in the aisles of fruit trees or berry bushes at a distance of one and a half meters from them. With such a planting, the plants are arranged in a row with an interval of 25-30 cm. It is important to ensure that the apical bud of the strawberry is not covered with earth. Irrigation rate - 1 bucket for 15-20 plants. To keep the moisture longer, and the surface layer of the soil is not covered with a crust, it is recommended to mulch the plantings with fine manure or peat.
Where to plant shrubs on the site
The indisputable advantage of shrubs is the fact that they not only give tasty and healthy berries, but can also serve as a wonderful hedge. The choice of a place on the site for planting shrubs is carried out specifically for each species. For example, currant prefers moist and well-lit places (between two fruit trees, near a fence or wall of a house). But the wild rose does not tolerate too moist and saline soil, it loves light and heat.
Gooseberries are also afraid of excess moisture, but they tolerate short-term drought well. So, to the choice permanent place planting berry bushes should be taken seriously, as bushes grow quickly, and transplanting a large plant is much more difficult.
Fit Types
There are several types of planting shrubs:
- tree-shrub group;
- Alley;
- Hedge.
The tree-shrub group combines several types of plants (both trees and shrubs) located separately on the site. For this type of planting, plants are selected with similar agrotechnical conditions and according to their compatibility with each other, crown shape, flowering time, etc.
An alley is a group of tall shrubs arranged in a row at the same distance from each other, for example, along a garden path.
If you plant shrubs in one line so that their crowns close together, you can get a hedge that looks much more aesthetically pleasing than any fence.
Planting shrubs in autumn
Most often, autumn planting of shrubs is practiced in middle lane our country, including the Moscow region. At this time, you can plant such berry bushes: white, red and black currants, chokeberry, gooseberries, raspberries, honeysuckle, sea buckthorn.
As a rule, autumn planting begins in mid-September, when the life processes of the plant slow down.
Landing dates
In central Russia, the autumn planting of shrubs takes place from mid-September to almost the end of October. In the northern regions, the planting period ends in the first days of October, and in the southern regions, on the contrary, the terms are extended - until the second decade of November.
 Figure 8. Compatibility of fruit trees and shrubs
Figure 8. Compatibility of fruit trees and shrubs However, the main indicator of the most optimal time for autumn planting is the onset of the dormant period of the plant. It is possible to determine it at the end of leaf fall. It is important to know that seedlings dug out before the start of the period of biological dormancy are frozen in winter, primarily due to unripened shoots.
Compatibility of fruit trees and shrubs when planting
Experienced gardeners have long noticed that some fruit trees and shrubs feel uncomfortable next to other plants or, on the contrary, successfully coexist with them. In the first case, the roots of plants can be at the same depth and interfere with each other. There is a situation when one of the plants releases substances into the soil that inhibit the development of others. Therefore, when planning the planting of fruit- berry plants, do not be too lazy to look into the table of their compatibility (Figure 8).
For example, apple trees can get along with almost any horticultural crops, except for mountain ash. Red and black currants do not tolerate neighborhood with each other and with raspberries, since its root system inhibits the neighboring plant. For this reason, it is recommended to plant raspberries on separate area. Gooseberries cannot coexist with black currants, and they are not friendly with raspberries either.
You will find more information about the compatibility of fruit and berry crops in the video.
Distance to the border when planting fruit trees
When planting fruit trees on your site, it would be useful to familiarize yourself with the legislative acts of planting trees in order to maintain good neighborly relations. So, the rules state that the distance from perennial plant to the border of the site should be at least 3 meters for low trees.
The larger the diameter of the crown, the greater this distance becomes, because the branches and roots of the tree that go beyond your site, the neighbors can rightfully remove without your consent. Bushes can be planted at a distance of 1 meter from the border, and plums, peaches, cherries - 2 meters.
If it becomes necessary to plant trees and shrubs in the garden, then you need to follow certain rules. This is where I ran into some problems. From my grandfather got a house in the village, where there was a fairly large garden. I would like to save valuable trees, as well as plant new ones, so that children and grandchildren have a place to relax and live.
Ennobling the territory, it is necessary to remove old plantings, plant new plants. The main principles that guide me, I decided to reflect in this article.
Planning helps to distribute the territory for different purposes. In conditions countryside(sometimes in cities) plots are allocated for individual housing construction. On them, in addition to a residential building, part of the land is allocated for green spaces.
Plantings of shrubs and trees are distributed on the plan. Recreation areas are defined that cannot be imagined without trees. Usually in gardens they try to have:
- 1…2 apple trees early varieties maturation;
- 3…4 apple trees of late ripening varieties with long-term storage of the crop;
- 1 ... 2 pears of different varieties, selection is needed for reliable pollination;
- 1 ... 3 cherry and cherry trees;
- 1…3 apricots early term maturation;
- 2 ... 5 currant bushes (black, red, white, yellow);
- 2 ... 3 gooseberry bushes (green, black);
- 3 ... 5 raspberry and blackberry bushes;
- 2 ... 3 bushes of honeysuckle;
In addition to fruit and berry plants, perennial flowers are planted and ornamental plants. They are pleasing to the eye, decorate the site.

|
Table 1 |
||
|
culture |
Distance between rows, m |
Distance between plants in a row, m |
| Apricot | 5,0…5,5 | 3,0…4,0 |
| Quince | 5,0…5,5 | 3,0…4,0 |
| Cherry tall | 4,0…4,5 | 3,0…4,0 |
| Cherry stunted | 3,0…3,5 | 2,5…3,0 |
| Pear on a vigorous rootstock | 6,0…6,5 | 4,0…6,0 |
| Pear on a stunted rootstock | 4,0…4,5 | 1,5…2,5 |
| Sea buckthorn | 2,5…3,0 | 2,0…2,5 |
| Walnut | 6,0…7,0 | 4,0…5,0 |
| Peach | 5,0…5,5 | 3,0…4,0 |
| Plum tall | 4,0…5,0 | 3,0…4,0 |
| Plum stunted | 3,0…4,0 | 2,5…3,0 |
| Apple tree on a vigorous rootstock | 6,0…6,5 | 4,0…6,0 |
| Apple tree on a stunted rootstock | 4,0…5,0 | 1,5…2,5 |

When to plant trees and shrubs in the garden
Autumn plantings
Residents of the Central and Southern regions try to plant in the autumn. They explain their preferences with a number of advantages:
- available in autumn big choice a wide variety of varieties. Zoned plants are selected, they take root better in the autumn-winter period;
- stone fruit crops are planted less frequently during autumn acquisition, they are added dropwise for spring planting, covered with a layer of non-woven fabric, and snow on top;
- you need to perform one or two irrigations, the rest of the irrigations are organized by nature, in the fall it rains torrentially;
- in the autumn, the gardener has more free time that he can devote to seedlings.

Disadvantages of autumn planting seedlings:
- autumn colds may suddenly come, then all work will have to be postponed in anticipation of warm days;
- at high location groundwater requires additional measures to overcome the freezing of the roots. Mounds are poured and plants are planted on them;
- with a small amount of rain (dry autumn), you will often have to water the plantings;
- prices in autumn are slightly higher than in spring;
- need protection from hares and other winter garden pests.

Based on long-term observations, the main proposals for planting seedlings for the regions of the Russian Federation were formulated (Table 2).
|
table 2 |
|
| Planting trees and shrubs by regions of the Russian Federation | |
|
Time of planting (transplanting) trees |
|
| Southern regions | The survival rate of trees in the autumn period is much higher than when planting in spring period. During the winter, seedlings form a strong root system, which, with the advent of heat, begins to nourish the entire plant. When planting in spring, the soil quickly dehydrates, planted plants take root worse. Therefore, the probability of survival of trees and bushes is low. Often seedlings dry up during the summer. A number of varieties on undersized rootstocks come into fruition in the first two years. Palmette tree plantings are used. |
| Central regions | In spring and autumn, planted trees and shrubs have time to build up a sufficient root system to survive the warm and cold periods. The survival rate is high. When planted in autumn with the advent of spring, flowering is possible even in the first year. Such examples are distinguished by cherries and sweet cherries, as well as apple trees on undersized rootstocks. Apple trees, pears on tall rootstocks are best planted in the fall. |
| Northern regions | Spring planting ensures root development. With low summer temperatures, trees and shrubs will be able to adapt. With the onset of autumn, and then winter, the seedlings will have time to accumulate required amount nutrients to overwinter, and then develop with renewed vigor. |
Spring planting of trees and shrubs
With the onset of spring, gardeners try to make use of the special conditions that occur after the snow melts. The soil is saturated with moisture to the maximum. When planting, plants actively develop, form roots, without fear of freezing.
In the south, plantings are organized in March, in the central regions the snow finally melts only in April. It's landing time. In the Northern regions, planting is carried out in the first decade of May.
In the spring, stone fruits (cherries, sweet cherries, honeysuckle and others) take root quite easily. Within a week after planting, the root system grows quite intensively.
When planting trees, the root neck should be left above the soil level. If it is deepened, then the plant develops slowly. Sometimes you can observe the fading of the development of a tree.
In apple trees, pears, apricots, when the root neck is deepened, you can never wait for flowering and the appearance of fruits.

Benefits of planting in the spring
- on the trading floors the choice of planting plants is quite extensive;
- prices are usually lower than in autumn, and the quality is higher;
- easier to check the quality of the roots in plastic container, plants can be lifted and see the state;
- the soil is sufficiently moist, bushes and trees take root easier;
- you need to have time to plant seedlings before bud break;
- spring for the gardener is created comfortable temperature, high spirits.
- many plants begin to bloom leaves, you may not have time to plant before the leaves appear. Plants in this case may die;
- during spring planting, it is necessary to treat near-stem areas for pests;
- in the spring, the seedlings need to pull the wire or support pegs.

Rules for planting trees on tall rootstocks
- Planting large trees requires extracting deep holes 0.8 ... 0.9 (length) x 0.8 ... 0.9 (width) x 0.6 ... 0.8 (depth) m.
- More often they dig rectangular holes (tradition).
- A small mound of fertile soil is poured in the lower part. Can be filled with humus or high peat.
- Install the seedling vertically. A support peg is placed nearby.
- Sprinkle a hole, holding a tree. It is necessary to trample down the earth around the root.
- An irrigation circle is formed around the trunk.
- After planting, pour at least two buckets of water.

Rules for planting trees on dwarf and low-growing rootstocks, as well as shrubs
- Need landing pits 0.4…0.6 (length)x0.4…0.6 (width)x0.4…0.6 (depth) m.
- Complex fertilizer, for example, nitrophoska, is poured at the bottom. Norm 40 ... 50 g.
- Spread the roots over the existing pit.
- The seedling is kept upright, sprinkled with humus, fertile soil or peat mixture.
- Be sure to compact the soil around the trunk.
- Form an irrigation circle.
- More often, several plants are planted.
- Install supporting pillars, a wire is stretched between them.
- The branches are further stretched along the wire.
 2>
2>
Plant care in the first year after planting
During the first year of life, plants need constant care. While the tree or bush is young, formative pruning should be performed.
Top dressing is carried out at intervals of 18 ... 25 days. At the same time, part of the fertilizer is sprinkled in the trunk part. Foliar top dressing is useful, which is performed by spraying a solution that contains:
- 15…25 g nitrogen fertilizers(mainly urea);
- 20…25 g phosphate fertilizers(superphosphate);
- 12 ... 15 g of potash fertilizers (potassium salt).
All mineral fertilizers are dissolved in 10 liters of water, then applied to a bush or tree using a garden sprayer.
- From the first decade of June to mid-July, feeding with chicken manure is useful.
- 200 g of chicken manure is placed in a bucket of 20 liters.
- Insist at least five days.
- Filter the liquid. Solid inclusions can be buried at some distance from the root (1 ... 2 m).
- The liquid is diluted in a ratio of 1: 20.
- She watered the near-trunk circle. Approximately 10 liters per large tree and 5 liters per bush.

Green fertilizers for seedlings
From June to mid-September, "green" fertilizers are used.
- Grass is accumulated in the barrel, they try to fill it to the top.
- They pour water. Close the lid, and in its absence, cover with plastic wrap.
- Insist at least 10 days. The liquid ferments vigorously.
- At the end of fermentation, the lid is removed.
- Solid inclusions are taken out and used as mulch.
- The solution is diluted 1 to 10. They are watered with young trees and seedlings. Under the trees, you can pour 7 ... 10 liters of solution. 3 ... 5 liters of "green" fertilizer are poured under the bushes.
Conclusion
- Trees and shrubs are planted in early spring or late autumn.
- They try to plant pome crops in the fall, and stone fruits in the spring.
- Care and feeding are organized for young plants.
