What are the components of an internal combustion engine? What is DVS
Any motorist has encountered an engine internal combustion. This element is installed on all old and modern cars. Of course, in terms of design features, they may differ from each other, but almost all work on the same principle - fuel and compression.
The article will tell you everything you need to know about the internal combustion engine, characteristics, design features, as well as tell about some of the nuances of operation and Maintenance.
What is DVS
ICE is an internal combustion engine. That is how, and no other way, this abbreviation is deciphered. It can often be found on various automotive sites, as well as forums, but as practice shows, not all people know this decoding.
What is an internal combustion engine in a car? - This is power unit which drives the wheels. The internal combustion engine is the heart of any car. Without this structural detail, the car cannot be called a car. It is this unit that drives everything, all other mechanisms, as well as electronics.
The motor consists of structural elements, which may differ depending on the number of cylinders, injection system and other important elements. Each manufacturer has its own norms and standards of the power unit, but they are all similar to each other.
Origin story
The history of the creation of an internal combustion engine began more than 300 years ago, when the first primitive drawing was made by Leonardo DaVinci. It was his development that laid the foundation for the creation of an internal combustion engine, the device of which can be observed on any road.
In 1861, according to the drawing of DaVinci, the first draft of a two-stroke motor was made. At that time, there was no talk of installing a power unit for an automobile project, although steam ICEs were already actively used on the railway.
The first to develop a car device, and introduce internal combustion engines on a massive scale, was the legendary Henry Ford, whose cars up to this time have been very popular. He was the first to publish the book "Engine: its device and scheme of work."

Henry Ford was the first to calculate such a useful coefficient as the efficiency of an internal combustion engine. This legendary man is considered the progenitor of the automotive industry, as well as part of the aviation industry.
AT modern world, ICE was widely used. They are equipped not only in cars, but also in aviation, and due to the simplicity of design and maintenance, they are installed on many types of vehicles and as alternating current generators.
The principle of the engine
How does a car engine work? - This question is asked by many motorists. We will try to give the most complete and concise answer to this question. The principle of operation of an internal combustion engine is based on two factors: injection and compression torque. It is based on these actions that the motor drives everything.
If we consider how an internal combustion engine works, then it is worth understanding that there are cycles that divide the units into single-stroke, two-stroke and four-stroke. Depending on where the internal combustion engine is installed, the cycles are distinguished.
Modern car engines are equipped with four-stroke "hearts" that are perfectly balanced and work perfectly. But single-stroke and two-stroke motors are usually installed on mopeds, motorcycles and other equipment.
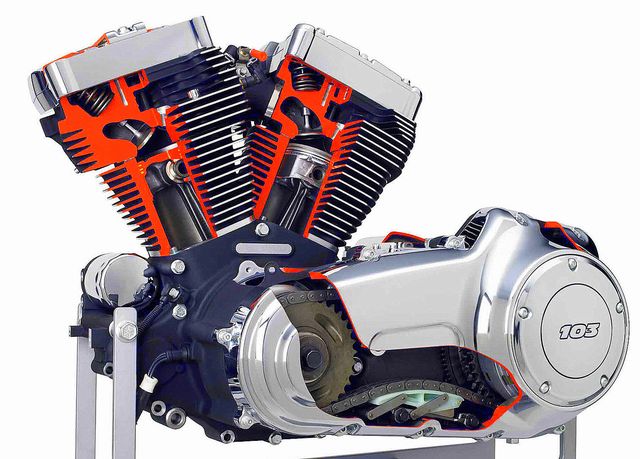
So, consider the internal combustion engine and its principle of operation, using the example of a gasoline engine:
- Fuel enters the combustion chamber through the injection system.
- The spark plugs spark and the air/fuel mixture ignites.
- The piston, which is located in the cylinder, goes down under pressure, which drives the crankshaft.
- The crankshaft transmits power through the clutch and gearbox to the drive shafts, which in turn drive the wheels.
How is the internal combustion engine
The device of a car engine can be considered according to the cycles of operation of the main power unit. Tacts are a kind of cycles of internal combustion engines, without which it is impossible to do. Consider the principle of operation of a car engine from the side of cycles:
- Injection. The piston makes a downward movement, while the intake valve of the block head of the corresponding cylinder opens and the combustion chamber is filled with an air-fuel mixture.
- Compression. The piston moves in the TMV and a spark occurs at the highest point, which entails the ignition of the mixture, which is under pressure.
- Working move. The piston moves in the NTM under the pressure of the ignited mixture and the resulting exhaust gases.
- Release. The piston moves up, the exhaust valve opens and pushes the exhaust gases out of the combustion chamber.
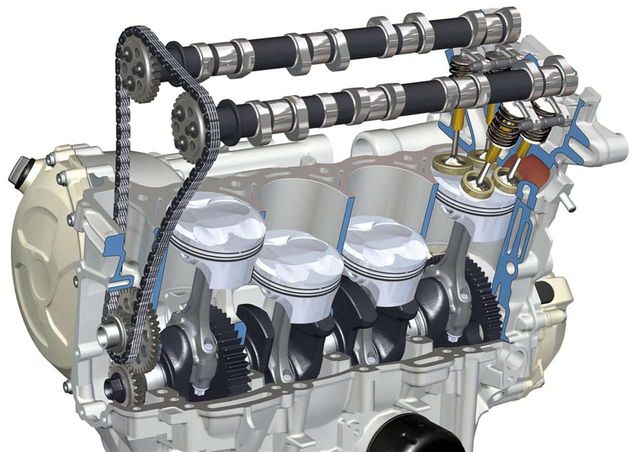

All four cycles are also called - the actual cycles of the internal combustion engine. Thus, a standard four-stroke gasoline engine works. There is also a five-stroke rotary engine and a new generation of six-stroke power units, but the technical characteristics and operating modes of an engine of this design will be discussed in other articles of our portal.
General ICE device
The device of the internal combustion engine is quite simple, for those who have already encountered their repair, and quite heavy for those who do not yet have an idea about this unit. The power unit includes in its structure several important systems. Consider, general device engine:
- injection system.
- Cylinder block.
- Block head.
- Gas distribution mechanism.
- Lubrication system.
- Cooling system.
- Exhaust mechanism.
- The electronic part of the engine.

All these elements determine the structure and principle of operation of the internal combustion engine. Next, it is worth considering what the car engine consists of, namely the power unit assembly itself:
- Crankshaft - rotates at the heart of the cylinder block. Brings to work piston system. It bathes in oil, so it is located closer to the oil pan.
- Piston system (pistons, connecting rods, pins, bushings, liners, yokes and oil scraper rings).
- Cylinder head (valves, oil seals, camshaft and other timing elements).
- Oil pump - circulates lubricating fluid through the system.
- Water pump (pump) - provides circulation of the coolant.
- Timing mechanism kit (belt, rollers, pulleys) - ensures the correct timing. Not a single internal combustion engine, the principle of which is based on cycles, can do without this element.
- Spark plugs ignite the mixture in the combustion chamber.
- inlet and exhaust manifold- the principle of their operation is based on the inlet of the fuel mixture and the release of exhaust gases.
The general arrangement and operation of an internal combustion engine is quite simple and interconnected. If one of the elements is out of order or missing, then the operation of automobile engines will be impossible.

Classification of internal combustion engines
Automobile motors are divided into several types and classifications, depending on the design and operation of the internal combustion engine. ICE classification according to international standards:
- For the type of injection of the fuel mixture:
- Those that run on liquid fuels (gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel).
- Those that run on gaseous fuels.
- Those who work for alternative sources(electricity).
- Consisting behind the work cycles:
- 2 stroke
- 4 stroke
- According to the method of mixing:
- with external mixing (carburetor and gas power units),
- with internal mixture formation (diesel, turbodiesel, direct injection)
- According to the method of ignition of the working mixture:
- with forced ignition of the mixture (carburetor, engines with direct injection of light fuels);
- compression ignition (diesels).
- According to the number and arrangement of cylinders:
- one, two, three, etc. cylinder;
- single row, double row
- According to the method of cooling the cylinders:
- with liquid cooling;
- air cooled.

Operating principles
Automobile engines are operated with different resource. The simplest engines can have a technical life of 150,000 km with proper maintenance. But some modern diesel engines that are equipped on trucks can nurse up to 2 million.
When arranging the design of the motor, automakers usually focus on reliability and specifications power units. Considering current trend, many car engines are designed for a short but reliable life.
Thus, the average operation of the power unit of a passenger vehicle is 250,000 km. And then, there are several options: disposal, contract engine or overhaul.
Maintenance
An important factor in operation is the maintenance of the engine. Many motorists do not understand this concept and rely on the experience of car services. What should be understood as maintenance of a car engine:
- Change engine oil in accordance with the technical charts and manufacturer's recommendations. Of course, each automaker sets its own framework for replacing the lubricant, but experts recommend changing the lubricant once every 10,000 km for gasoline internal combustion engines, 12-15 thousand km for a diesel engine and 7000-9000 km for a vehicle running on gas.
- Replacement of oil filters. Carried out at every oil change.
- Replacement of fuel and air filters - once per 20,000 km of run.
- Injector cleaning - every 30,000 km.
- Replacing the gas distribution mechanism - once every 40-50 thousand kilometers or as needed.
- Checking of all other systems is carried out at each maintenance, regardless of the prescription of replacement of elements.

With timely and complete maintenance, the resource of using the vehicle engine increases.
Refinement of motors
Tuning - refinement of an internal combustion engine to increase some indicators, such as power, dynamism, consumption, or more. This movement gained worldwide popularity in the early 2000s. Many motorists began to independently experiment with their power units and upload photo instructions to the global network.
Now you can find a lot of information on the improvements carried out. Of course, not all of this tuning has an equally good effect on the state of the power unit. So, it should be understood that power acceleration without full analysis and tuning can “ditch” the internal combustion engine, and the wear factor increases several times.
Based on this, before tuning the engine, everything should be carefully analyzed so as not to “get” on a new power unit” or, even worse, not get into an accident, which can be the first and last for many.
Conclusion
The design and features of modern motors are constantly being improved. So, the whole world is already impossible to imagine without exhaust gases, cars and car services. A working internal combustion engine is easy to recognize by characteristic sound. The principle of operation and the device of the internal combustion engine is quite simple, if you figure it out once.
But what is swinging maintenance, it will help to look here technical documentation. But, if a person is not sure that he can carry out maintenance or repair of a car with his own hands, then you should contact a car service.
What is an internal combustion engine (ICE)
Currently internal combustion engine is the main type of automobile engine. Internal combustion engine (abbreviated name - ICE) is called a heat engine that converts the chemical energy of the fuel into mechanical work.
There are the following main types of internal combustion engines:
- piston internal combustion engine;
- rotary piston internal combustion engine;
- gas turbine internal combustion engine.
Of the types of engines presented, the most common is piston ICE, therefore, the device and the principle of operation are considered on its example.
Virtues piston internal combustion engine, which ensured its widespread use, are:
- autonomy;
- versatility (combination with different consumers);
- low cost;
- compactness;
- small mass;
- the ability to quickly start;
- multi-fuel.
However, internal combustion engines have a number of significant shortcomings, which include:
- high noise level;
- high frequency of rotation of the crankshaft;
- toxicity of exhaust gases;
- low resource;
- low efficiency.
Depending on the type of fuel used, the following piston internal combustion engines are distinguished:
- petrol engines;
- diesel engines.
alternative views fuels used in internal combustion engines are natural gas, alcohol fuels - methanol and ethanol, hydrogen.
How does an ICE work?
Engine housing combines the cylinder block and the cylinder head. crank mechanism converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion of the crankshaft. Gas distribution mechanism ensures timely supply of air or a fuel-air mixture to the cylinders and the release of exhaust gases.
The engine management system provides electronic control operation of internal combustion engine systems.
The principle of operation of the internal combustion engine based on the effect thermal expansion gases that occur during the combustion of the fuel-air mixture and ensure the movement of the piston in the cylinder.
The operation of a piston internal combustion engine is carried out cyclically. Each work cycle occurs in two revolutions of the crankshaft and includes four cycles (four-stroke engine):
- inlet;
- compression;
- work stroke;
- release.
During the intake and power strokes, the piston moves down, while the compression and exhaust strokes move up. The operating cycles in each of the engine cylinders do not coincide in phase, which ensures uniform operation of the internal combustion engine. In some designs of internal combustion engines, the operating cycle is implemented in two cycles - compression and power stroke (two-stroke engine).
On the intake stroke the intake and fuel systems provide the formation of a fuel-air mixture. Depending on the design, the mixture is formed in the intake manifold (central and multipoint injection of gasoline engines) or directly in the combustion chamber (direct injection of gasoline engines, injection of diesel engines). When the intake valves of the gas distribution mechanism are opened, air or a fuel-air mixture is supplied into the combustion chamber due to the vacuum that occurs when the piston moves down.
On the compression stroke The intake valves close and the air-fuel mixture is compressed in the engine cylinders.
Stroke stroke accompanied by ignition of the fuel-air mixture (forced or self-ignition). As a result of combustion, a large number of gases that press on the piston and cause it to move down. The movement of the piston through the crank mechanism is converted into rotational movement of the crankshaft, which is then used to propel the car.
On tact release the exhaust valves of the gas distribution mechanism open, and the exhaust gases are removed from the cylinders to the exhaust system, where they are cleaned, cooled and noise is reduced. The gases are then released into the atmosphere.
The considered principle of operation of the internal combustion engine makes it possible to understand why the internal combustion engine has a low efficiency - about 40%. At a particular moment in time, as a rule, only one cylinder takes place useful work, in the rest - providing cycles: intake, compression, exhaust.
The engine is the heart of every car. Nevertheless, before turning into an ultra-modern device operating on the principle of internal combustion, he had to undergo many changes.
The history of the creation of the internal combustion engine
We need to start from the 18th century. It was then that the first attempts were made to create an engine that works due to internal combustion. It is worth saying that at that time many scientists worked on the process of converting fuel energy into mechanical energy.
Despite the apparent excitement, the palm was taken from France with the sonorous surname Niepce. It was they who came up with pyraeolofor. Conventional coal dust was used as fuel. The device had an extremely low efficiency. Moreover, it is more likely to be considered an ambitious project than a really working prototype.
Nevertheless, the first working concept of an engine based on the internal combustion process belongs to the aforementioned brothers. Commercial success belongs to a completely different person. Belgian Etienne Lenoir. It was he who in 1858 invented and created the internal combustion engine.
In an internal combustion engine, coal gas was used as fuel. It seemed new era, which gave an unprecedented impetus to the automotive industry, began, but it was not there. The scientist forgot to take into account the need for lubrication of parts. As a result, the device worked for a very short time. There was also no proper cooling system.
Fortunately, the scientist did not stop there. It took 15 years to refine and improve the engine powered by internal combustion. But the work paid off. In 1863, Lenoir presented an internal combustion engine with previously missing systems. Kerosene is already used as fuel.
The device was not extremely perfect. But the history of the creation of an engine powered by internal combustion did not end there. The main problem lay in overheating too quickly. In addition, lubricants and fuels were used extremely inefficiently. Nevertheless, even then, internal combustion engines were used on three-wheeled cars.
It took world scientists one year for Siegfried Markus to create his own version of an engine powered by the internal combustion of certain substances. The ICE of 1864 was the first to use oil.
A vehicle with a Marcus engine powered by internal combustion of petroleum products could reach speeds of up to 10 miles per hour. At the time, it was a real breakthrough.

Then there were many more scientists trying to create a really efficient engine that works thanks to internal combustion. But the first is technically correct and efficient device was created. Nicholas Otto. It effectively converted the energy of the fuel and had a very good efficiency for its parameters,
After Otto's discovery, the evolution of the ICE began to snowball. At 83, Delamare creates a blueprint for an internal combustion engine that runs on gas. However, the project could not be brought to life then.
Three years later, the big name Gottlieb Daimler thunders all over the world. It is he who owns the authorship of the first working engine due to the internal combustion of gas. The cylinders and carburetor were located vertically in the design, which gave a good performance boost. Moreover, machines equipped with these devices were able to develop a decent speed for those times.
Another big name of that time was Karl Benz. He was the first to create an enterprise that makes cars. In 1903, the enterprises of Benz and Daimler are merged. A new era in the automotive industry is about to begin.
In the same year, Henry Ford founded his legendary enterprise in order to release the first mass-produced car 5 years later and turn the world upside down. The factories of this great entrepreneur spread all over the world instantly. Even in the Soviet Union they were.
ICE - device, principle of operation, characteristics
Device

The key element of an engine powered by internal combustion of petroleum products is the piston. By appearance it resembles a hollow glass of medium size.
The piston head looks up. The skirt or guide part has shallow grooves. Piston rings are fixed in these holes. These elements ensure the tightness of the entire system. It is in it that the gasoline-air mixture instantly burns out during operation.
Important! The piston rings of an engine operating by internal combustion of the fuel-air mixture prevent oil from entering the space under the piston.
Rings play the role of seals. The lower ring is oil scraper, and the upper one is compression. It is the latter that is responsible for ensuring that the mixture has a high degree of compression.
Principle of operation
The fuel mixture enters the system from the carburetor (in some engines from the injector). Compression occurs when the piston moves up. A candle is responsible for lighting.
Important! An exception to this rule is the operation of a diesel. In this system, ignition occurs due to sharp compression.
When gas is produced, the piston moves sharply upwards. As a result, thermal energy is converted into electrical energy. The movement of the piston is transmitted to the shaft. This process made possible by the unique design of the piston skirt. It contains a finger top in the form of a rod.
The hinge is fixed on the crank, the latter is part of the crankshaft. The crankshaft rotates due to the thrust bearings. They are based in the crankcase of an engine operating on the principle of internal combustion.
The piston acts on the connecting rod, due to this, the crankshaft begins to move. The energy of movement goes towards the transmission. Only after passing this transit point, she through complex system gears drive the wheels.
The piston has two dead spots. This is the name of the two extreme positions in which the element is delayed for a fraction of a second. The distance between two points is called a stroke.
Attention! The volume at the top of the cylinder is called the combustion chamber.
Characteristics

The total volume of the cylinders of an engine powered by internal combustion of fuel is measured in liters. An important indicator is the compression ratio. For devices that operate at the expense of a carburetor, this indicator is in the range from 6 to 14 CC, for a diesel engine this indicator is about 16-30.
The volume and compression force determine the power of the engine, which operates due to the internal combustion system of the fuel liquid. The combination of these parameters also determines the efficiency of the device.
Important! The power of an internal combustion engine is measured in both horsepower and kilowatts.
Single cylinder engines run unevenly. The stroke of the piston accelerates sharply during explosive combustion. As soon as it approaches the BDC, it slows down. The flywheel disk allows you to partially extinguish this unevenness. As a result, the torque is stabilized.
Four bars

The operation of the engine can be divided into four cycles if it functions due to the internal combustion of the fuel-liquid mixture. Motors are either two-stroke or four-stroke. The latter are used much more often, at least in passenger cars.
The piston passes through the cylinder four times. The beginning of the beat takes place at the top point, and the end of the movement occurs at the bottom. In terms of time, each cycle occupies an equal interval. When the piston moves down on the first stroke, it sucks the mixture into the cylinder.
On the first stroke, the intake valve is open. Most engines have more than one of these valves. Moreover, their number and size affect the power of the car. In some engines, when the driver presses on the gas, the opening time of the exhaust valves is extended.
The amount of fuel entering the system increases. The power of an internal combustion engine increases as a result. As a result, the speed at which the car moves becomes faster.
On the second stroke of the engine with an internal combustion system, compression occurs. The piston reaches its lowest point and begins to rise. In this case, the mixture in the chamber is compressed. During the process, the valves are fully closed.
Important! In order for the fourth cycle to pass with due efficiency, there should not be large gaps in the structure. Otherwise, proper compression simply will not happen.
The compression inside the chamber is checked by means of special devices. By the way, this indicator makes it possible to conclude how much engine wear is great. If necessary, based on the data obtained, more detailed diagnostics can be carried out.

On the third stroke, the piston starts moving from top point. This cycle is called working. Which is not surprising. After all, it is thanks to this stage that the movement of the vehicle begins. It is here that the ignition system is connected, and the mixture inside is ignited.
Interestingly, when ignited, a microexplosion occurs. Because of it, the fuel increases sharply in volume, and the piston with high speed goes down. The valves are kept closed all the time.
The fourth measure is the last. It completes the work done by the engine, which operates according to the internal combustion scheme. When the cylinder reaches its lowest point, the valve opens and exhaust occurs.
Important! On the fourth stroke, all exhaust gases are removed from the system.
After the fourth measure comes to an end, everything returns to normal. As a result, four stages again, and so on until the internal combustion engine is running.
Not all the energy generated in 4 cycles is used to move vehicle from place. The fact is that it is also needed in order to spin the flywheel. By the way, it is he who, due to his inertia, rotates the shaft.
Types of engines

As mentioned above, the automotive industry is constantly evolving. It is not surprising that more and more new technologies are emerging that allow turn more efficiently thermal energy into mechanical. On the this moment There are five types of engines operating on the basis of an internal combustion system:
- diesel,
- rotary piston,
- gas,
- gas-diesel,
- petrol.
Each of the above types is a vivid illustration of the development of the automotive industry. Take, for example, diesel and gasoline engines, which are built on the basis of an internal combustion system.
In the petrol version, the fuel passes through special system to get into the carburetor through the distribution nozzles. In some schemes, injection is carried out directly into the exhaust manifold.
At the moment, the carburetor scheme is considered slightly outdated. The injection design, which is responsible for supplying fuel in an internal combustion engine, is gaining more and more popularity.
Gas engines with internal combustion systems have become a kind of response to society's ever-growing demands for economy. Besides this technology allows you to protect environment from various emissions.
Results
Engines with a design that works by internal combustion of fuel are still the most popular. This trend is easily explained by almost 150 years of evolution. Of course, modern electrical analogues practically do not differ from their competitors, but who knows, perhaps another technical breakthrough will change everything again.
With the advent of cars, mankind has stepped far forward, because now it is not necessary to overcome long distances on foot or on horseback, it is enough to comfortably sit in your car and go anywhere. This is the merit of the internal combustion engine, which converts thermal energy into mechanical energy. It's time to figure out what an internal combustion engine is, how it works, and what types of internal combustion engines exist.
The very first engine appeared on gasoline, so it will be considered the most. It consists of several mechanisms that make it work continuously.
- Cylinder block. It is a cast-iron (sometimes aluminum) structure, inside of which there are cylindrical holes. A crankshaft is installed at the bottom of the block, and connecting rods with pistons in the cylinders. The cylinder block provides support for many parts, and is also integral part combustion chambers.
- crank mechanism. Consists of connecting rods and crankshaft. The connecting rods are driven by pistons, and accordingly, they swing the crankshaft, which subsequently transmits torque to the flywheel and other parts of the drive mechanisms.
- Cylinder head and timing. It is a mechanism that is responsible for the entire gas distribution process. It has a camshaft, cams, and valves. The shaft is driven by the crankshaft and causes the valves to open and close at the right intervals. The work of the timing is clearly synchronized with the work of the crankshaft.
- In addition to the main parts, any engine has a cooling system, lubrication, as well as power supply, which can be carburetor, diesel or injection, in addition, an ignition system is required for the operation of a gasoline engine, which is a distributor or module, as well as high-voltage cables and candles.
The principle of operation of the internal combustion engine
To understand how such an engine works, consider the example of the simplest single-cylinder engine that has four cycles.
- Gasoline mixed with air is fed into the cylinder, the intake valve is open, the piston moves to the bottom point. In this case, the crankshaft rotates approximately 90 degrees.
- After filling the cylinder and reaching the BDC piston, it moves up, while both valves are closed, the mixture supplied is compressed. The position of the crankshaft changes another 90 degrees.
- As soon as the piston reaches the top point, at that moment a spark appears on the spark plug electrodes, which ignites the compressed mixture and the latter creates a lot of pressure, under the influence of which the piston moves down and causes the crankshaft to make another 90 degrees.
- As soon as the piston reaches the bottom point, it will go up again. At the same time, the exhaust valve will open and under pressure, the exhaust gases will exit into the exhaust manifold.
Of course, this whole process is much faster, and the work of all systems is very clearly synchronized. Throughout the work, the oil pump works, which creates the right pressure oils for lubricating parts and machinery. In addition, a water pump is driven by a belt drive from the crankshaft, which circulates water or antifreeze through the system.
Having dealt with the principle of operation, it's time to find out what ICEs are.
Types of internal combustion engines
There are a lot of such classifications, but we will start with the largest - diesel and gasoline.. The difference between these two engines is in the form of fuel that is burned in the cylinders. Unlike a gasoline engine, a diesel engine does not have an ignition system, since the mixture is ignited only by compression. In addition, the power is supplied by a pump high pressure and injectors. All other nodes and parts have a similar structure, as well as purpose. A diesel engine is much more powerful and economical due to more efficient use of the mixture.
By number of cylinders and location
This is where the most interesting thing is, because the more cylinders, the higher the volume, which means that the engine works much more productively. Initially, all engines were equipped with an in-line arrangement of cylinders, and their number was often limited to six. To increase the volume of the motor and save space, the developers created a V-shaped engine, in which two rows were located at an angle to each other. This type of engine is popular with American classic cars, as well as many trucks.
At the moment, there are engines in which the piston is completely absent. Bright to that an example is a rotary piston engine, which uses a circular cavity instead of a combustion chamber, and a rotor rotates inside, which divides this cavity into three unequal parts. The mixture is fed into the first, then, during rotation, the rotor compresses it against the walls and ignites it.
By a similar principle, a micro-explosion occurs, which causes the rotor to rotate faster, and the release is performed in the first cavity. This motor has big power and almost completely eliminates vibrations, making work more efficient, however, it has great difficulties with lubrication, which is very difficult to apply inside the RPD.
The last representative of the internal combustion engine is a gas turbine, but since it is not used on cars, we will not consider its device.
The main problem modern piston engine is that it has maximum performance only for a certain number of turns. For example, if we take an average car as a basis, then its maximum power will only be achieved at 3000 rpm. If their number is greater, then the efficiency of the motor drops sharply. Of course, modern engines have more power, but a common problem for them still remains.
