Analytical reporting in personnel management. Progress report: sample
If the assessment is positive, the probationary period ends at the moment that was written down in the employment contract, or can be completed earlier than scheduled at the discretion of the manager. So, the end has arrived probationary period, what are the employer's next steps? At the end of the probationary period, a certification is carried out to determine how well the new employee copes with the job and how he fits into the team. Certification at the end of the probationary period will allow you to make a decision:
- about further continuation of work;
- on termination of the contract at the initiative of the employer or employee. Moreover, the termination of the contract takes place within three days in accordance with Article 71 of the Labor Code.
Certification during the probationary period includes the preparation of a report. It is usually written by the curator according to the plan adopted at the beginning of the trial.
The procedure for passing the probationary period according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Attention
These may be reports of poor quality work, defective products and reports of violations by the employee job descriptions or an employment contract. If the employee was given additional tasks, these facts must also be recorded in memos and a written conclusion about the completion of the probationary period. The tasks must clearly state the result to be obtained, its assessment, criteria and deadlines.
Tasks are handed over to the employee against signature indicating the essence of the task and the date. Only in this way will it be possible to prove in court that the employee failed to cope with the assigned tasks. Failure of an employee to meet any criteria gives the employer the right to prepare evidence in in writing that the employee cannot cope with the work and does something untimely and poorly and, accordingly, dismiss the employee.
Report (conclusion) on completion of the probationary period
Important
For the final decision on hiring an employee to the main staff, he is assigned to work for a probationary period. It was at this time new employee can prove himself, and the employer appreciates him professional quality. In this article we will talk in detail about what happens if a person is on probation.
... Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right! It's fast and free! Table of contents:
- Regulations on the procedure for passing the probationary period
- Work plan for the probationary period
- Adaptation period
- Progress report
Regulations on the procedure for passing the probationary period Passing the probationary period is fixed in Article 70 of the Labor Code.
Procedure for checking a new employee. What does “probationary period passed” mean?
The basis for the order is indicated employment contract, which indicates the condition of passing the probationary period, and a conclusion on the test results or a report from the commission. What are the benefits of a probationary period? Despite the fact that the probationary period is the same part of the work process as regular working days, and the employee is subject to all the rights and obligations provided for by the labor code and internal documents enterprises, during the test there is one significant nuance that makes it attractive for both the employee and the employer. We are talking about dismissal during the probationary period. Under normal circumstances, dismissal at the initiative of the employer is almost impossible, especially if a permanent employment contract is signed.
Dismissal during probationary period
It is developed by an experienced employee who knows the intricacies of this profession together with the new employee’s supervisor. A plan is first drawn up for the first month of inspection. If the subject showed himself to be positive side, then after summing up the work of the new employee for the first month, a decision may be made to end the trial period early. If further testing is required, a plan is made for the remainder of the test period.
The plan includes the following items:
- Full name of the employee, department and position;
- test period;
- full name of the curator, department and position;
- list of assigned tasks, completion time, planned result, actual result, supervisor’s comments.
The employee must be familiar with the plan and objectives for the probationary period.
Report on the results of the probationary period
Download Downloaded: 25 Full name for work as Test period Results of checking the employee’s compliance with the work assigned to him (whether the subject has necessary knowledge and practical skills to perform job responsibilities, ability to learn): During the test, he showed himself as (business, personal qualities, compliance with requirements corporate culture companies): Conclusions (feasibility further work in the company, the reasons that served as the basis for recognizing the employee as having failed the test): Supervisor (full name) (Signature) (Date) Conclusions on the employee: Manager structural unit(Full name) (Signature) (Date) Deputy Director for HR (Full name) (Signature) (Date) Download Downloaded: 20 Full name Division Position Manager 1.
Please list the personal qualities and professional skills that a specialist at your workplace needs to perform his job duties most productively, and rate the degree of development of these skills in you on a 5-point scale. Knowledge, abilities, skills Assessment 2. Which of the above skills were you able to master during the probationary period? Which ones failed? What knowledge and skills do you currently lack to work productively in this position? 3. What are the requirements for your work? To what extent do you think your actions meet these requirements? 4.
What is the significance of your work to the success of the department as a whole? Please describe how you see your place in the company in the future? 5.
Report on an employee on probation
A probationary period is a working period during which the employer and employee have the opportunity to finally take a closer look at each other and decide whether it is worth continuing cooperation. Moreover, although it seems that the final word here remains with the employer, the employee can also change his mind during the probationary period, so it is probably worth drawing the conclusion that setting a probationary period is beneficial to both parties labor relations. Legal norms The norms and nuances of the probationary period are specified in the articles Labor Code Russian Federation:
- 70 “Test for employment”;
- 71 “Result of the test when applying for a job.”
Some features of the test setup for government civil servants are specified in Federal laws Russian Federation.
Info
Attention! If during the testing process the employee realizes that this place is not suitable for him, in order not to waste time, he must notify the employer 3 days in advance (in writing) and resign. Report The most important document is the completion report, which is prepared after the tests are completed. It precisely reflects the employee’s ability to perform his job duties.
- Who writes? The report is usually compiled by the curator assigned to the subject.
- How to compose it? It is not difficult to write a report; it must strictly correspond to the specific test plan developed earlier.
It should be described in detail, for each task set in the plan - how it was completed, what mistakes were made, how they were corrected. It is convenient to use a point scale in such a report; it will look more objective.
Example of a report on an employee on probation
A report on completion of the probationary period is generated several weeks before the end of the inspection period. The results of the probationary period are assessed according to the following criteria:
- quality of work performed;
- level of professional training;
- ability to work together;
- independence in completing tasks;
- the ability to bring work to the final result.
Based on this report and personal observations, the new employee’s boss draws up a testimonial for him during the probationary period. Together with the report and characteristics, a conclusion is written by the HR manager.
It should summarize the performance results during the review period. The employee must be familiarized with the conclusion after completing the probationary period. This must be done if the subject fails the test and will be dismissed.
Today, personnel is one of the main resources of the company, the management and development of which largely determines the state of the organization as a whole. Working with it requires an effective management policy, essentially unique for each enterprise.
One of the problems of working with personnel is staff turnover. It can lead to loss of profits, loss of skilled workers, decreased product quality, an increase in defective products and increased absenteeism. To control attrition and understand how to retain your best employees, you need to identify the reasons why people leave the company. To study motives for leaving great importance has the collection and analysis of information about them. First of all, this is information about total number those who quit, the proportion of employees of different age categories, low- and high-skilled workers, as well as their work experience and education.
To study personnel management problems, the following methods can be used:
- Assessment of the state of the personnel structure. Analysis of the personnel structure allows us to draw conclusions about the impact of a particular category on the total productivity and results of the company; identify expansion needs, determine the required number of employees and their professional and qualification composition.
- Qualification composition.
- Dynamics of hiring.
- Age composition.
- Assessment of the causes of temporary disability. Temporary disability is the inability for health reasons to perform work for a relatively short period of time. Analysis of this indicator allows us to determine the causes and timing of temporary disability, identify seasonal dependencies, and reduce the cost of compensation payments.
- Studying the movement of personnel:
- Assessing staff turnover. Excessive loss of personnel leads to additional costs associated with the cost of replenishing the number, training new employees and eliminating deficiencies due to incompetent actions. Often used to measure staff turnover staff turnover rate- this is the ratio of the number of dismissed employees of an enterprise who left over a certain period for reasons of turnover (for at will, for absenteeism, for violation of safety regulations, unauthorized departure, etc.), to the average number of employees for the same period of time. Fluidity can be natural or excessive. The first contributes to the renewal of the team (for office workers it usually ranges from 3 to 5%). This process occurs continuously and does not require any emergency measures on the part of personnel services and management. The second leads to economic losses; it destabilizes the business and affects the productivity of not only employees who intend to leave, but also those who continue to work.
- Study of layoff chart and survival curve. The main issue in analyzing dismissal data is the ability to estimate the duration of an employee’s work from the moment he took office. In addition, the manager is interested in at what point in time the employee should be expected to leave. For analysis, the following is used: the cumulative share of remaining employees - an estimate of the survival function, that is, the probability that an employee will work for more than t years in the organization, and the probability density - an estimate possible departure employee at this interval.
- Determining the economic damage caused by employee turnover. When employees leave, there are not only losses associated with the departure of highly qualified personnel, but also significant financial costs. Economic damage consists of the costs of paying dismissal benefits, recruiting new personnel, costs associated with defects in production when attracting workers with a low professional level, etc.
There is a solution
Most organizations accumulate a huge amount of information about employees during their work. Often, various methods are used to obtain and process it. software. In addition, the company may have remote branches. All this leads to difficulties when trying to connect data together. The optimal solution in this case is the use of specialized systems focused on solving data consolidation problems. Such complexes make it possible to collect information from various sources, unify the presentation, clear redundant and incorrect information. To maintain data consistency and high speed of data retrieval, it is advisable to implement a data warehouse. The Deductor analytical platform contains everything you need to implement such tasks and build complete solutions.
Consolidated data is most often used to obtain various reports, including in the initial analysis of personnel. Deductor supports many visualization methods in the form of a variety of tables, graphs, charts, maps...
Assessment of the state of the personnel structure and the causes of temporary disability
Reporting is a set of multidimensional tables, cross-charts and graphs; the report tree is shown in Fig. 2.

Personnel dynamics makes it possible to identify the age composition of employees, their level of qualifications, the main causes of disability, etc. Below are examples of reports built using Deductor Studio.
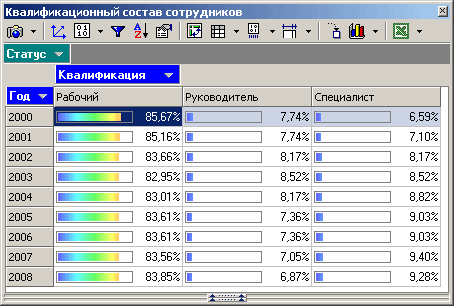

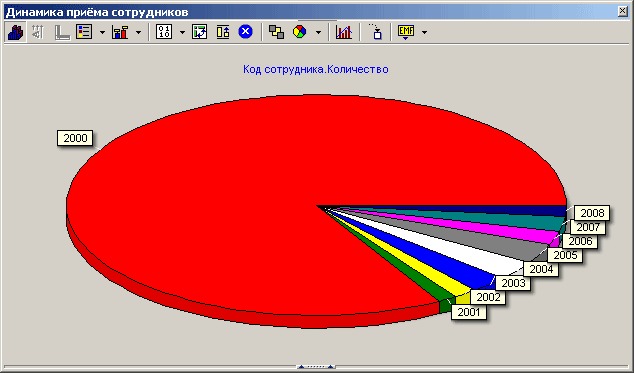

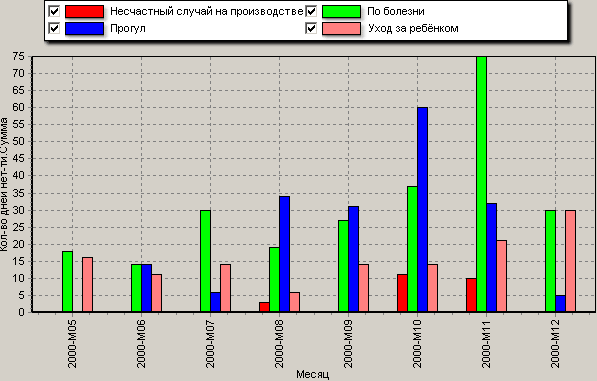
Studying the movement of personnel
There is a relationship between the length of time people work for a company and the reasons for their dismissal, which can be discovered by examining dismissal charts.
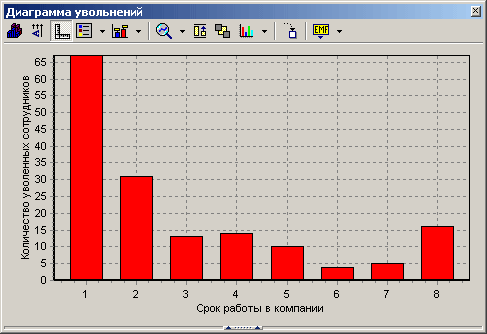
Confirmation stage. Based on statistical data, greatest number layoffs occur during First stage work (from one year to one and a half years). The main reasons for high staff turnover are incompetence of personnel (lack of knowledge, experience, skills), non-acceptance of the organizational or corporate structure, and inadequate introduction to the position. In most cases, at this stage, employees with weak motivation and low development potential leave.
Consolidation stage. During the second and third years of work, the reasons for dismissal are: dissatisfaction with technical resources, material and moral incentive systems, lack of prospects career growth. At this stage, employees with high development potential in this company leave.
Stage of a new impulse. Employees leave the organization whose long-term plans have not been realized, there is no promotion, no increase in earnings, and wages are lower than in other companies engaged in similar business. Personnel losses during this period are especially undesirable, since key employees leave the company, in whose development considerable effort and resources have already been invested.

Analysis of the turnover rate will allow you to form a personnel structure based on:
- industry specifics;
- personnel qualifications;
- seasonality of production;
- features of the organization's structure (management style, personnel policy, attitude towards hiring and firing personnel on the part of management).
The turnover rate provides only a generalized result for the entire organization. More detailed analysis allows you to determine whether the coefficient characterizes the entire company, covering positions and employees, or whether its formation is largely influenced by only a small category of employees.

Such an analysis will help the manager identify positions that experience the greatest turnover. Similarly, you can assess what age and qualifications employees are most likely to leave the company. All this will allow you to take timely measures to retain the most valuable employees.
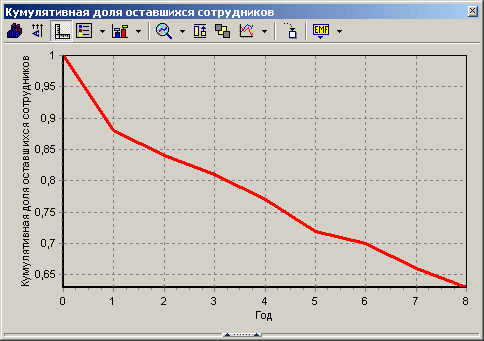
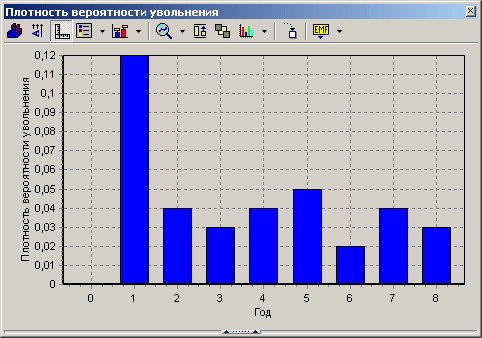
Thanks to the resulting graphs, it is possible to draw conclusions about when the probability of layoffs is maximum.
To predict employee behavior, the layoff intensity parameter or risk function is used, which shows the probability that the employee will quit in the next reporting period provided that he worked for the company at the beginning.
Determining the economic damage caused by staff turnover
To determine the amount of economic damage from staff turnover, the following calculations are used.
Losses caused by the dismissal procedure
Payments of severance pay to resigning employees (if any were made). Here you can also take into account the legislative features of calculating payments made according to for various reasons dismissals. In case of staff reduction and voluntary dismissal, the payment amounts will be different. The legal service (lawyer) of the enterprise can provide advice on these issues. Based on the information received, you can calculate the “overpaid” funds and include them in losses.
Losses from legal costs associated with illegal dismissal, subsequent reinstatement and payment for forced absence time
If the dismissal or transfer to another position is considered illegal, the employee must be reinstated in his previous job by the body considering the individual labor dispute. He can also decide to pay the employee the average salary for the entire period of forced absence or the difference in wages for the entire period of performing lower-paid work.
This loss item can be very significant, because... the chances of being reinstated in your previous job are very high.
Losses caused by the procedure for hiring workers for a vacant workplace
- costs of searching for candidates (ads in the media, on billboards, etc.);
- expenses for selecting candidates (working time spent on conducting the selection procedure - testing, interviews, reviewing questionnaires, etc. and on recruiting personnel, including posting recruitment advertisements and paying for the services of recruitment agencies, i.e. financial, do not reduce taxable profit , if as a result of these activities no employees are recruited);
- costs caused by the registration of hired employees (working hours of HR department employees and financial costs for this procedure);
- direct costs of searching, selecting and processing candidates in the form of payment for the services of consulting, personnel, recruiting agencies.
Business interruption losses
They are caused by downtime in the workplace between the dismissal of an employee and the hiring of a new one. They are defined as the product of three indicators: the average daily output per employee, the average duration of breaks in work caused by turnover, and the number of employees who left due to turnover:
N pr = W*T*H t,
where B is the average daily output per person;
T is the average duration of a break caused by turnover;
T - number of people leaving due to turnover.
Losses due to the need to train and retrain new employees
These losses show the costs of employee adaptation, on-the-job training, and off-the-job training costs. They are calculated as the product of the amount of funds spent on training, the share of turnover in the total number of leavers, divided by the coefficient of change in the number of employees in the reporting year compared to the base year:
P o = Z o *D and *K i,
where Z o - costs of training and retraining;
D and is the share of excess turnover;
K and is the coefficient of change in the number of employees in the reporting period.
Losses caused by a decrease in labor productivity among workers before dismissal
They determine the cost of lost products and are calculated as the product of the coefficient of reduction in labor productivity, its average daily level, and the number of days before the dismissal of employees who left due to turnover:
P spt = C rv * K sp * Ch u,
where C rv is the average output;
K sp - coefficient of reduction in labor productivity before dismissal;
Ch y - the number of days before dismissal, when there is a drop in labor productivity.
Losses caused by insufficient labor productivity of newly hired workers
They are defined as the product of the number of employees who left due to turnover, the sum of the products of the employee’s average daily output in each month of the adaptation period, monthly reduction rates in labor productivity and the number of days in the corresponding month:
N pr = From ditch *K m *H m,
where C ditch is the average daily output of a worker in each month of the adaptation period;
K m - monthly coefficient of reduction in labor productivity during the adaptation period;
H m - the number of days in the corresponding month.
Recruitment costs due to turnover
Z org = (Z n * D t) * K change,
where Z n - recruitment costs;
To change - the coefficient of change in the number of employees, equal to the ratio of the number at the end of the period to the number at the beginning of the period;
Dt is the fraction of fluidity.
Losses from defects among newly hired workers
They are calculated as the product of recruitment costs and the share of turnover in the total number of quitters, divided by the coefficient of change in the number of employees:
P bn = (O b * D br) / K meas.
where P bn - losses from marriage among newcomers;
About - total losses from marriage;
Dbr - the share of losses from marriage among persons who worked for less than one year;
The development of such systems is inseparable from studying the specifics of the work of a particular organization. In addition, the use of KPI will allow timely detection of deviations and identification of " weak spots"business processes. A dynamic model of indicators will help adjust the direction of the company's development.
conclusions
Such an analysis will help prevent the above-mentioned problem and create a more effective and holistic personnel strategy aimed at retaining specialists. Staff turnover can be predicted, which will allow timely measures to be taken to maintain valuable employees. This provides a case for the most effective personnel changes. Studying reporting makes it possible to determine what is common between employees who are late for work, or what are the reasons for temporary disability, what traits do good top managers have in common. A thorough analysis of previous experience will, for example, reveal what delays lead to wages. The knowledge gained from such research will help to better select candidates for vacant positions, invest money in training the most promising employees.
Renowned psychologist Dr. David Merrill discovered that you can predict a person's behavior by classifying all possible behavior types into four styles: Doer (wants to get things done), Analyst (wants to get things done right), Friend (wants to be together), Artist (wants to get things done). to be noticed). Nobody's style is better or worse than others, it's just different. But understanding these differences will help the manager get top scores from your employees.
Your employee is a Doer
Doers are focused on business, have high persistence and low responsiveness, prefer to rely on reasonable assumptions and intuition rather than facts. They want quick action, tangible results, are intolerant, speak in a persuasive tone, and prefer oral communication to written communication. Decisiveness is the most prominent trait of a Doer. He is capable of intimidating any less determined member of your team.Problem
Managing Doers is not easy, because they want to control you. A doer can accomplish a great deal of work in a short time. But if he feels that he is being forced or depersonalized, the whole process will be illusory. If he is uninspired or reluctant, your project will be sabotaged.
How to work with a Doer
Doers prefer change and innovation, so the best place for them these are new projects in which they can implement their ideas. Winning motivates them the most. When communicating with a Doer, stick strictly to the facts, focus on tasks, not feelings. You must demonstrate that your recommendations are exclusively workable; no fancy methods will work here. Respect the Doer's need for high self-esteem.
Your employee is an Analyst
The analyst has low both persistence and responsiveness. Relies only on facts and details. Well organized, neat, taciturn, prefers written communication, you can always find him at his workplace. Likes to work alone. Often sets high standards (primarily for himself) and is ready to do any work to meet them. I tend to speak in a structured, precise manner, weighing my words.Problem
The analyst is obsessed with collecting information, has difficulty making decisions, constantly worrying whether he is making the right choice. Tries to avoid conflicts. If the interlocutor gives in to emotions, the Analyst withdraws into his own thoughts and becomes emotionally insensitive, believing that a rational approach can cool the overheated situation. True, the effect is often the opposite.
How to work with an Analyst
Analysts value accuracy, punctuality, and organization. When communicating with them, express your thoughts clearly and systematically, study every detail. The analyst will appreciate that even for one-on-one conversations, you have a written agenda. It is better to give it to him in advance so that he has time to think through all the issues. Appeal to his need for precision and logic. Your approach must be clearly stated and documented.
Your employee is a friend
Friends have low persistence but high responsiveness. They reflect other people's feelings, have a lot of patience, and believe that it is important to take time to build relationships. They prefer direct personal communication to telephone or written communication. Clients are dealt with in a consistent and methodical manner. True, goal setting and planning are not their thing.Problem
Friends express themselves insecurely, prefer to stick to proven paths in everything, and often postpone making a decision. They tend to keep their opinions to themselves.
How to work with a Friend
Friends are great team players. To build a relationship with them, you need to show sensitivity to their feelings, be patient and take the time to communicate with them. Appeal to their need to strengthen the relationship. Friends are usually the most helpful people. They often drop everything they are doing to help a colleague. And they will really appreciate it when you give them a helping hand when difficult situation they will be.
Your employee is an Artist
The artists are both persistent and responsive. They do not hesitate to communicate their feelings and often appear to be very enthusiastic. They are sociable, flamboyant, have a penchant for drama, and enjoy being in the spotlight. They prefer to work with others, are excellent at networking, and always have a large number of contacts who can help them achieve their goals.Problem
The artist is very impulsive and often does something first and then thinks. He prefers to work according to the available opportunity rather than according to a plan, and very rarely knows how to manage his time. And although he is usually a good motivator when he is on an emotional high, he more often than others ends up in a trap. The Artist has a lot of ideas, but often he has no idea how to implement them.
How to work with an Artist
When communicating with the Artist, show that you are interested in him primarily as a person. Keep in mind that he often behaves in a dramatic and exaggerated manner. Artists are dreamers. Support their ideas and dreams while showing them how to turn conversation into action. A reference to the opinions of those people whom the Artist respects helps a lot.
This technique is described in David Meister's bestselling book, First Among Equals.
How to organize and conduct a morning five-minute meeting (operational meeting). Rules, tips, recommendations. (10+)
Tips for Conducting a Situation Meeting
The operational meeting can be a very effective management tool, or it can turn into a powerful time sink that greatly reduces work efficiency. How to make sure that the five-minute RAM brings benefit and not harm?
Planning meeting goals
How often should a planning meeting be held? It depends on why we are doing it. How quickly the situation changes, how often it is necessary to check whether the work plan is being implemented and adjust it.
Important! At an operational meeting, it is impossible to make any responsible decision that requires elaboration and discussion. Such decisions are made at more detailed meetings. Their implementation is described in the article linked above. A planning meeting is needed in order to:
- or make sure everything is going according to plan,
- or understand that there are minor deviations that can be resolved in current order, through advice or some assistance to those left behind,
- or establish that more serious adjustments or new design solutions are required, appoint those responsible for studying the issue, preparing and holding a full-scale meeting on this issue.
Plan, operational regulations
Based on the above, we can formulate the basic rules:
Work plan. There must be a detailed work plan. This plan should be as detailed as a five-minute meeting. For example, if we hold an operational meeting every day, then the plan should be in daily detail, at least a couple of weeks in advance. Otherwise, there will simply be nothing to discuss at the planning meeting. It is pointless to listen to an employee report on the work done during the day if it is not known what he should have done that day.
Regulations. A minimum amount of time should be allocated for each participant’s report. Usually about five minutes are allocated, but you can get by with less time. There may be special cases when, for example, an employee reports news. He needs to be given time based on the volume of news. The same amount of time is allocated for discussion as for the report. During the discussion, you can ask clarifying questions, give short advice, and agree on what the employee needs to do before the next planning meeting. If it is not possible to discuss the issue in the time allotted during the operational meeting, then you need to plan to work it out after it, with the participation of only those employees who are related to the issue. This will allow you not to distract or waste the time of others who have nothing to do with the issue.
Protocol. All decisions made must be recorded in the protocol. Then at the next planning meeting we simply take the minutes of the previous one and check whether all the participants did what was planned at the previous meeting. If an employee was unable to complete a task, you need to decide how to help this employee. It is stupid to expect that without completing the task in the first week, he will do it in the next. It is necessary to find out what difficulties the employee has stopped, and how these difficulties can be overcome through joint efforts.
Is an operational meeting useful?
Properly organized five-minute sessions allow you to:
- All employees should be kept informed of the progress of work.
- Each employee has a clear idea of what they need to do right now.
- Quickly diagnose when an employee encounters difficulties, promptly help, advise, and push.
Example of a meeting protocol
I keep the minutes in a spreadsheet. In the first vertical column I list all the participants in the planning meeting. The first line contains the dates. There are two columns for each date. The first is filled out at the planning meeting on this date, and the second - at the next planning meeting based on the results of the past week, simultaneously with filling out plans for the next week. The first column can be frozen, and the rest can be gradually shifted to the left so that you can see only the past and current dates. And if necessary, you can also look at previous dates.
| 15.07.13 | 22.07.13 | |||
| Exercise | Result | Exercise | Result | |
| Head of Support Department | Respond to customer inquiries about delivery times new version Prepare a list of unresolved implementation problems with the client 1 Sign an Act with the client 2 | Deadlines have been determined, information has been provided to clients. A list of problems has been prepared and submitted to the development department. The act has not been signed, there are comments | Monitor work on the preparation of a new version. Together with the development department, work through the client’s comments 2 | |
| Head of Development Department | Prepare a new module for display Make changes to the accounting mechanism Fix an error in the reporting form | New module not prepared, errors found Changes to the accounting mechanism have been made Reporting form has been changed | Together with the support department, work out a list of problems for the client 1 Together with the support department, work out the client’s comments 2 Together with the sales department, prepare the module for demonstration | |
| Head of Sales Department | Prepare and send proposals for the delivery of a new module to 10 clients Demonstrate the new module with clients 3 and 4 | Commercial proposals have been prepared and sent. The demonstration was not carried out due to the unavailability of the new module. | Send commercial offers 10 more clients. Monitor the preparation of a new module for demonstration | |
| Head of Methodological Department | Prepare an overview of changes in legislation | Review prepared | Process the request from client 1 to ensure it complies with the accepted methodology | |
There is no leader who does not demand from his subordinates at least once a year a report on what has been done. And the problem is that with routine work, developing such a document seems to be quite a difficult task. And for some reason we are embarrassed to ask our superiors for examples of reports on the work done. What if he decides that we are not suitable for the position we occupy?
Who needs it
This question is asked by the performer who has received the task of reporting. Most often, company employees feel almost insulted by such demands. But everything has a meaning.
Firstly, the contractor himself needs a report on the work done. Not a formal, but an interested attitude to this process will allow you to find bottlenecks and weaknesses in your qualifications. This means that the directions in which it is possible (and necessary) to develop have been identified. After all, we all learn from our mistakes.
Secondly, the leader needs it. A progress report allows you to objectively assess the quality and speed of solving assigned tasks. Thanks to this document, many questions will disappear - from the most primitive “what do you do all the time” to the complex “why should I change your computer to a more modern one?” Because the report will indicate that it takes a lot of time to save changes to the document. And this does not depend on the contractor - outdated office equipment cannot work faster. Actually, this is why it seems that the employee is drinking tea all the time - he is simply waiting for the operation to be completed.
And the question: “Why do you need to write a report on the work done for the month?” itself is incorrect. Because accumulating and filling databases makes sense for strategists, and not for them. It is simply easier to solve a problem than to talk about methods for solving it.
What to write
Examples of progress reports show that you need to write in great detail. Anything that seems like a small thing or an insignificant body movement can turn out to be a key element in the performance of specific functions. But understanding of this will come only after studying several written reports.
If the work is routine in nature, for example, reconciling documents and identifying inconsistencies, then it makes sense to develop a tabular form. In this case, again, at first the table should be very detailed and contain many columns; Over time, the need for some columns will no longer be necessary, and the report form will take on a normal (read: reasonable) form.
In some cases, when compiling a report on the work done (teachers, for example), it is impossible to formally approach the issue of self-analysis. Indeed, in addition to the planned educational and methodological load and study required material, the school is also engaged in educational activities. This requires a special approach to drafting the document: it is necessary to understand the reasons for the lag of a number of students, to find ways to interest children in their subject. And at the same time, we must not forget about high-achieving (or even gifted) schoolchildren.

Purposes of reports
For proper preparation and minimal time expenditure, it is necessary to decide from the very beginning for what purpose and why the report on the work done for the year is being written. Let's name the most popular:
Rationale real benefit from a specific position in the organization;
Confirmation of the qualifications of a particular employee;
Demonstration efficient work management;
Obtaining funding for the next reporting period;
Obtaining consent to develop a direction (idea);
Justification for spending allocated resources and finances, etc.
The well-known formulation is correct positioning problem provides 50% of the solution - works in this case too. The better we understand why a report is needed, the easier it is for us to write it. To the point that the document “for show” does not require us at all creative approach. And time consuming.

Document structure
If the company does not have one developed, then it has to be developed independently. Knowing the purpose of the document, it is necessary to think about its structure. Examples of progress reports suggest that a clear and simple outline is needed.
At the very beginning, the purpose and logic of presenting information should be explained. Explain the sequence of presentation and create a table of contents. For the table, it is necessary to give a brief explanation of why this particular form was chosen.
Within sections and subsections, unity of presentation should also be maintained. This will make the document more understandable and, as a result, easier to understand. In a report over a long period of time, illustrations and graphs are quite appropriate to make it easier to understand. But here you need to adhere to the rule of the “golden mean”: solid text, as well as exclusively visual materials, get boring very quickly.

Stylistics
For an ordinary employee, perhaps the most difficult thing to write is terminology and wording. A pretentious report will look unnatural and will cause a negative reaction from management. Too simple formulations (25 documents were xeroxed, for example) will also alienate the reader.
But you should avoid templates. The only exception is the document that no one will ever read. We sometimes encounter such problems, but in this article we are interested in real (not created for pro forma) reports.
In any case, you shouldn’t talk only about achievements. To highlight them, it is necessary to talk about the difficulties that had to be encountered during the work. Among other things, complexity analysis is about optimizing work for management employees. Examples of reports on the work done suggest that you should not use streamlined phrases like “unsatisfactory condition”, “difficulties encountered”, etc. It is better to call everything by its proper name: “broken photocopier”, “lack of access to the Internet”, “lack of or untimely receipt of information from the related department.” All this allows us to adequately and objectively assess the current situation in the company.
Evaluation of results
Each result obtained must be supported by numbers. Such specification provides an understanding of the dynamics of development.
In addition, it is necessary to set criteria for evaluating the results. Whether it is the previous one (if it is a quarterly report, for example) or, conversely, the percentage of fulfillment of the set goals, is up to the author of the document to decide.
In general, indirect indicators can tell a lot about the process of solving assigned tasks. There is also a lot of information here for further analysis. From determining labor costs to understanding the correctness of setting goals.

From problem to solution
Most reports are prepared on the principle of describing the progress of work. A document that clearly shows the problem-solution relationship looks more advantageous. The reader immediately understands what methods and techniques (if necessary) the performer used to complete the task in a timely and high-quality manner.
An even more detailed chain of “a specific problem - the reasons for its occurrence - setting tasks - solution” immediately suggests the need to present a daily report in tabular form. Moreover, the names of the graphs are already known. The information presented in this way is easy to read and analyze.

Presentation of quantitative indicators
In cases where the report consists mainly of digital data, the tabular form can be very difficult to understand. A continuous stream of numbers literally bores the reader after just a few minutes. Another thing is multi-colored charts and graphs. They are clear, understandable, and easy to read.
Each diagram must be commented on. In addition, it is necessary to indicate how the various graphs are interconnected; Clarification of cause-and-effect relationships will further facilitate the analysis of the report.
If material resources were expended during the work, you should not simply list them all. Instead, the goods acquired should be indicated. The dry phrase: “Office equipment was purchased” will sound completely different if you write: “2 jobs were created, which made it possible to increase the department’s output.”

How to draw up a document
Despite the fact that there is no single form of preparation, a report on the work done can be prepared in accordance with GOST, which defines the main criteria scientific work. It specifies the requirements for formatting, font type and size, etc.
As for the readability of the document, here are some tips:
Try to keep no more than 5 sentences in one paragraph;
Key indicators can be highlighted in font or color;
Break up the text so that the table or graph does not take up the entire page; be sure to leave space for comments on them;
Write a clear and concise summary of the report.
These tips will help make your report easier to perceive, and therefore will initially set the reader up for a loyal attitude towards the author of the document. Imagine that you are the boss. And make the report something that would be useful and interesting for you to read.
