Loose ceiling insulation - Ceiling insulation for a cold attic: which is better inside the house, what should be the thickness? Bulk insulation: overview, types, tips and reviews Heat-insulating granules.
The popularity of heaters in the form of mats or plates is understandable - they are easy to transport, it is convenient to work with them, while saving time. But often builders use another type of thermal insulation - backfill. It differs from foam or mineral wool boards in its structure. Perhaps, for some works, backfill thermal insulation will be more preferable.
Insulation is a low-density porous material, the granules of which are produced by firing foam raw materials at high temperature. Ease of manufacture is reflected in the low cost of thermal insulation, and the structure also saves on labor costs.
The disadvantages of filling heaters are:
- their shrinkage by 10-15% of the initial volume;
- loss of thermal insulation properties when wet.
Backfill insulation is used, usually for horizontal surfaces. The job seems simple, but requires careful preparation. For example, when insulating the floor in buildings without basements, the soil is pre-compacted and covered with a screed. Next, a waterproofing material is laid on the latter, and a heater is poured on it. It looks like the situation is with the insulation of the roof, only the screed is not required. Instead, a layer of vapor barrier is laid on top of the backfill material.
When sheathing walls, a frame is constructed in advance, consisting of durable sheet elements. After that, a heater is poured inside the resulting structure.
Types of backfill thermal insulation
Hundreds of years ago, when building wooden houses from timber or logs, the very first bulk insulation was used - sawdust. Like modern counterparts, they were quite good in terms of thermal conductivity, but they shrank or lost their properties when wet. Today's materials are more perfect in many respects. The most popular of them are discussed in detail below.
Insulation, the basis of which is clay. It is used as an independent heat insulator for premises of residential or industrial buildings, and in combination with concrete (expanded concrete is obtained). Today it is obtained by firing shale.
The production technology varies depending on the required dimensions of the final granules.
Having studied the marking of the filling insulation, you can understand what size granules of the material are and for which parts of the house it is suitable. For example, expanded clay sand is used as a heat insulator for the floor or acts as an integral element of the concrete cladding. Granules with a diameter of 5-10 mm are suitable for pitched and flat roofs, floors, attics; larger than 15 mm - for warming the basement or foundation.

Expanded clay inevitably settles during operation, therefore, during the initial installation, it must be strongly tamped to minimize shrinkage. The material is recommended to insulate walls only in regions where the temperature in winter does not fall below -20 degrees.
The insulation is made from silicate volcanic rocks using the same technology as expanded clay. When heated to 1000-1200 degrees, moisture evaporates from the surface of the stones, leaving air inside them. The result is white or gray granules with a diameter of 1 to 10 mm. The density of perlite ranges from 75 to 150 kg / m3, and for its color it is also called "glass insulation".
The smallest granules (1-2 mm) form perlite sand used in such areas:
- insulation of residential buildings;
- production of acoustic materials;
- production of insulating plaster;
- creation of fire-resistant concrete.
Granules filled with air weigh less than expanded clay, therefore they are suitable for thermal insulation of walls. In addition, the material will resemble mineral wool, since, in addition to preserving heat, it will prevent the penetration of extraneous noise into the room.

Expanded material made of hydrated mica, increased in volume by 15-20 times by heat treatment. It has increased fire-resistant properties, due to which it is used in the installation of chimneys. Ideal for floors and walls.
A thin layer of vermiculite 5 cm thick will retain up to 70% of the heat of the room. This is enough to insulate the roof. For walls, floors and foundations, it is recommended to make a double layer of material.
The density of vermiculite is lower than that of expanded clay or perlite - the largest bulk density is 100 kg/m3. This filling insulation is supplied in bags of a certain volume, and is used in almost all areas of a residential building.

The benefits of vermiculite include:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity (0.04-0.06), comparable to polystyrene foam and mineral wool;
- no likelihood of voids and seams;
- high melting point (1400 degrees);
- absence of toxic materials;
- biological resistance (prevents mold, fungus, is of no interest to rodents);
- good sound insulation;
- the lightness of the material, allowing it to be used in frame houses, on load-bearing systems or foundations;
- ease of insulation work and time saving.
Relatively new material, only 10 years ago appeared on the market. It is produced from recycled paper raw materials, flame retardants (substances that prevent ignition), antiseptics. Safe for humans, resistant to decay, is not a fire spreader. It is often used for thermal insulation of walls, attics or roofs of complex construction.

Scope of filling insulation
Since the material in question is light and almost does not weigh down the structure, it is usually used when sheathing a sloping roof. It also finds application in the insulation of such sections of houses:
- attic floors;
- attic;
- frame structures (walls);
- floor, foundation;
- horizontal partitions between floors;
- brick walls.
The optimal combination of prices, qualities, as well as the combination of lightness with reliable thermal insulation contributed to the growth in demand for the considered bulk insulation. If the house needs good protection from the cold, and there is little time to work, expanded clay, perlite, vermiculite and ecowool will be excellent helpers in implementing the plans.
Various types of insulation are used to insulate houses. This is the famous mineral wool, polystyrene foam, expanded clay and many others. The line of heaters is numerous and varied.
A worthy place in it is occupied by loose heaters. Being a natural material, they have earned themselves worthy respect due to their qualities.
For floor
 In any construction, thermal insulation is given the closest attention. Not ignored and. Bulk insulation is best suited for this.
In any construction, thermal insulation is given the closest attention. Not ignored and. Bulk insulation is best suited for this.
The most common among them are:
- perlite;
- vermiculite.
Expanded clay in floor insulation is the most popular insulating material. Low price, mass production and high thermal insulation properties played an important role in this. And, although it is made of clay, the output is a rather light product. The weight of 1 m³ is on average 350 kg.
It is appropriate to mention that expanded clay is the most environmentally friendly material. It is not susceptible to moisture and at the same time it is frost-resistant. Sold in bags or in bulk. Expanded clay can be used as an independent heater, and in combination with concrete. Expanded clay concrete not only retains heat, but in addition it is also a very durable substrate, base.

 The next representative of bulk insulation will be perlite. Its origin is volcanic rocks.
The next representative of bulk insulation will be perlite. Its origin is volcanic rocks.
A distinctive, only inherent feature is a high percentage of moisture absorption. In studies, it has been found that it is able to absorb moisture four times its own weight. It is because of this that it is recommended for warming rooms with high humidity.
Environmentally friendly natural material that does not enter into any chemical reactions. It has high fire resistance.
You can learn about other fire-resistant thermal insulation from this material:
Withstands temperatures up to 900ᵒ C. Possessing a porosity of up to 40%, it is an excellent insulator. For insulation, it is used in the form of perlite sand. You can buy it in the same way as expanded clay, in bags or in bulk.
This is interesting: perlite is not only used in construction, it is also used to filter vegetable oil, fruit juices and beer.

 Vermiculite is also an excellent heater of natural origin. Distinguished by its hardness. Along with high fire resistance (up to 1200ᵒ C), it has an impressive moisture absorption coefficient - more than 530%. It has amazing thermal insulation properties.
Vermiculite is also an excellent heater of natural origin. Distinguished by its hardness. Along with high fire resistance (up to 1200ᵒ C), it has an impressive moisture absorption coefficient - more than 530%. It has amazing thermal insulation properties.
With a layer thickness of only 5 cm, heat loss is reduced by 75%. It is an environmentally friendly material. It has high chemical and biological resistance. Prevents the appearance of mold and mildew. Having a small volumetric weight, it does not create a load on the foundation. It is sold, like all bulk insulation - in bags and in bulk.
For floor insulation, not only bulk heaters are used. Styrofoam, mineral wool, liquid insulation, cork and a number of others are also often used. Each of them has both positive and negative sides. Some are very good, but expensive. For example, cork insulation. Others, like Styrofoam, are not flame retardant.
A good floor insulation is obtained from ordinary sawdust, but it requires special antiseptic treatment. In addition, it shrinks very quickly, caking. Loose heaters have the most optimal parameters for floor insulation.
Note: bulk insulation tend to shrink. Tight compaction reduces its size.
for walls

 To keep the heat in the house, it is necessary to insulate not only the floor, but also the walls. And not only from the inside, but also from the outside. The choice of heaters is large, but I want to choose the best one from them. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of heaters and choose the one that suits you the most.
To keep the heat in the house, it is necessary to insulate not only the floor, but also the walls. And not only from the inside, but also from the outside. The choice of heaters is large, but I want to choose the best one from them. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of heaters and choose the one that suits you the most.
Materials such as:
- foam glass;
- Styrofoam;
- penoplex;
- polyurethane foam.
The list of heaters is represented by a very wide range. Loose heaters are still very popular. The same old proven heaters that are used for the floor have proven themselves excellently. There are also more modern ones. For example, foam glass is very popular among builders.

 This environmentally friendly material is chemically stable and does not lend itself to biological destruction. Granular foam glass is used not only as an independent backfill, but also as the basis of heat-insulating plaster. It is obtained from foamed raw granules. It is produced in the form of slabs, crushed stone and in granulated form of various fractions.
This environmentally friendly material is chemically stable and does not lend itself to biological destruction. Granular foam glass is used not only as an independent backfill, but also as the basis of heat-insulating plaster. It is obtained from foamed raw granules. It is produced in the form of slabs, crushed stone and in granulated form of various fractions.
It is worth noting: granulated foam glass is absolutely not afraid of groundwater. Therefore, in addition to walls, it can be safely used for warming foundations and basements.
Penoplex - granules made of foamed polymers. It is sold in the form of slabs or crumbs. Doesn't absorb moisture at all. Very light weight material. Requires protection from sunlight and chemicals.
Consider: penoplex can only be used in the operating temperature range (from -50ᵒ С to + 75ᵒ С).
For work on wall insulation, loose foam is very convenient. Especially when making walls of a frame structure. Having in its composition very small granules (from 0.1 mm), it is able to penetrate into the smallest voids.
Mineral wool has found wide distribution in the insulation of not only walls. The size of the granules is from 10 mm. It has good vapor permeability. Fire resistant. Does not change its properties up to 1000ᵒ C. Good sound insulator. Recommended for internal insulation. Sold in bags, in bulk, in rolls. When working with mineral wool, it is necessary to take measures to protect the respiratory tract and skin.
Note: wet mineral wool significantly reduces its thermal insulation parameters. Very difficult to dry.
Summing up, it can be noted with confidence that as a heater for walls, the leading place is occupied bybulk insulation.
For ceilings

 Just like floors and walls, ceilings require insulation. The insulation materials discussed above can be used in this case as well.
Just like floors and walls, ceilings require insulation. The insulation materials discussed above can be used in this case as well.
A more specific insulation is penoizol. In appearance, it somewhat resembles a crumb of foam. This is where the similarity ends, if we do not take into account the characteristics of thermal conductivity.

 Penoizol is absolutely non-flammable. It has high chemical and biological resistance. Rodents avoid him. For insulation of ceilings, it is good because it has a very small weight. Its density is from 5 to 75 kg/m³. Due to the low thermal conductivity, a thickness of a layer of insulation from 5 cm is sufficient. When working, bulk material, sheets and in liquid form are used.
Penoizol is absolutely non-flammable. It has high chemical and biological resistance. Rodents avoid him. For insulation of ceilings, it is good because it has a very small weight. Its density is from 5 to 75 kg/m³. Due to the low thermal conductivity, a thickness of a layer of insulation from 5 cm is sufficient. When working, bulk material, sheets and in liquid form are used.
Note: penoizol shrinks slightly (0.1 - 5%). It is compensated when the work is performed by professional craftsmen using modern equipment. Otherwise, cracking of the insulation is inevitable. (this applies to the use of the liquid fraction).
Considering bulk insulation for the ceiling, one cannot ignore such a widely used material as sawdust. as the cheapest material. As an independent heater, their use is highly undesirable. The fact is that they are prone to decay due to moisture absorption.
In addition, they are an excellent breeding ground for mice. Even if we do not take into account the fact that they are a fire hazardous material, it is not difficult to conclude that they are unsuitable. "Craftsmen" go to all sorts of tricks to somehow reduce these negative factors. To do this, sawdust is mixed with expanded clay, lime, even broken glass and other building materials. Such events somewhat improve the properties of the insulation, but not by much.
As a conclusion, it should be noted that when insulating ceilings, the advantage is on the sidebackfillheat-insulating materials.
Advantages of bulk insulation
 Everyone is interested in warming their home. It remains to choose the right insulating material. Bulk insulation is best suited for this.
Everyone is interested in warming their home. It remains to choose the right insulating material. Bulk insulation is best suited for this.
Their advantages are obvious:
- environmentally friendly material;
- have a low weight;
- perfectly retain heat;
- fireproof;
- easy to handle when working with them;
- durable.
zasypnyeheaters easily penetrate into any space, do not leave gaps. The main thing is to choose the right faction, and success will be guaranteed.
Watch the video in which the specialist tells how to insulate the ceiling with a mixture of vermiculite and sawdust:
High-quality insulation of upper floors in buildings for various purposes significantly reduces heating costs. Among the available, convenient and cheap ways to prevent heat transfer is the use of organic and artificial insulators. To decide how to fill the ceiling in a bathhouse or a wooden house, you should be aware of the features of the materials, understand their advantages and disadvantages, and take into account the nuances of using TIMs.
The main criteria for choosing thermal insulation
Bulk insulation for the ceiling must comply with a number of parameters. Among the most important are environmental friendliness, ease of installation, hygroscopicity and resistance to high temperatures.
In addition, the choice of TIM is made taking into account:
- climatic zone;
- floor material;
- distances between roof beams;
- the weight of the insulator, the size of its fraction;
- proximity to the chimney pipe.
Most bulk heaters are durable, safe and low cost. A separate group of products is characterized by a lack of resistance to the influence of biological factors - such TIMs require the additional use of various impregnations that improve the properties of insulators.
List of the most requested materials
A thorough review of the materials posted on construction forums and portals allows us to identify the 9 most common types of insulation. Among them are sand, sawdust, small chips, vermiculite, expanded clay, boiler waste, penoizol, expanded polystyrene granules, ecowool.
Characteristics of traditional types of products
The group of classic materials includes slag, shavings, sawdust.
The last two of the listed insulators are characterized by high flammability. This disadvantage is minimized by the use of flame retardants. Antifungal treatment reduces the susceptibility of the considered TIMs to bacterial agents.

Among the significant disadvantages of traditional wood insulation is frequent damage by mice and rats. How to get rid of rodents arranging nests in sawdust will be prompted by the advice of “craftsmen”: builders who have several decades of work behind them recommend mixing insulators with lime at a rate of 10:1.
You can reduce the heat transfer of the ceiling in the bath with the help of slag. It is preferable to use waste from boiler houses in regions where negative temperatures do not exceed -20°C. Slag fillers are easy to install, high fire resistance. Their disadvantages include a lot of weight: only strong upper floors should be insulated with boiler waste.
Sand, vermiculite or expanded clay?
The modern bulk heaters of the ceiling of residential premises and saunas offered by the construction market are distinguished by a significant assortment. Each product has special properties.
A demanded insulator is a perlite shelter. A layer of compacted expanded sand of 3 centimeters is equal in thermal conductivity to brickwork 15 cm thick. If necessary, the covered perlite is additionally strengthened with cement mortar - this design allows you to arrange a warm room in the attic.

Ceiling insulation with vermiculite
Fire-resistant, frost-resistant expanded clay granules ranging in size from 5 to 40 mm are used for thermal insulation of various types of floors. The weight of the material depends on the size of the fraction. For wooden flat, pitched roofs, it is preferable to use TIM with markings up to 10 mm, for saunas and baths - up to 20 mm; the insulation layer must be protected by vapor and waterproofing.
The best filling is provided by a mixture of several types of granules. An additional advantage of expanded clay is good sound insulation.
Among the advantages of vermiculite are fire resistance, long service life (from 50 years). Among the advantages of the material, experts also note:
- environmental friendliness;
- high breathability;
- inertness to the effects of biological agents;
- ease of installation (TIM is enough to fall asleep and compact).
To prevent heat loss, vermiculite should be used with a layer of 5 cm.

Expanded clay - effective thermal insulation for the ceiling
Features of foam chips, penoizol
It is also possible to cover the ceiling in a wooden house with polymer granules, which are characterized by moisture resistance, low weight, fire resistance (when flame retardants are used) and economy.
A special method of manufacturing polystyrene chips gives the type of TIM under consideration elasticity and density; the balls do not change their structure when squeezed, they take their original shape in a short time. The diameter of the polymer spheres varies from 1 to 8 millimeters. The material is easy to fill and transport.
Styrofoam crumb loses these properties when acetone, dichloroethane, a number of other substances contained in paints and varnishes get on it.
Loose penoizol differs from polymer crumbs in shape - its granules are not round (visually they look like snow flakes). The thermal conductivity characteristics of TIMs are almost the same.

Advantages and disadvantages of ecowool
The material made on the basis of waste paper fills small voids well; It is used as a heat insulator for complex structural solutions.
Cons of ecowool - susceptibility to combustion and the effects of biological factors - is minimized by including boric acid, borax in the composition of TIM.
Thermal conductivity of products does not exceed 0.042 W/m*S. When wet, the material shrinks.

The duration of operation of ecowool varies depending on the climatic features of the territory. With small temperature differences, the service life can reach 50 years, in harsh winters - from 15 to 20 liters.
A wide range of bulk thermal insulators allows you to choose the most economical TIM, taking into account the characteristics of the building in need of insulation. Particular attention should be paid to modern materials that do not require significant time costs for laying, ensuring the maximum suppression of heat transfer.
14926 0 4
Which ceiling insulation to choose or 3 available ways to self-insulate the ceiling
When the question arises about maintaining heat in the house, the first thing that an ordinary person immediately remembers is the insulation of walls and floors. But such a one-sided approach is fundamentally wrong, because everyone knows from the school physics course that warm air rises and if you do not take into account the ceiling, then all other efforts and investments will be in vain. In this article, I will talk about which ceiling insulation is best to use and how to insulate the ceiling in the house in three different ways.
What to consider when choosing a material
When choosing a heater, there are several main evaluation criteria - this is the level of vapor permeability, flammability, weight and strength of the material itself, there is also a price, but this is more of a personal matter.
Ceilings only at first glance to an uninitiated person may seem different, in reality there are only 2 types of ceilings - concrete and wooden:
- With concrete floor slabs, everything is simple, they do not burn and have an enviable load-bearing capacity. By itself, concrete is considered to be partially vapor-permeable. But for floor slabs, this indicator is so low that when choosing which insulation it is better to equip the ceiling, it can simply be ignored;
- Attic floors in private houses are often mounted on a wooden base, and wood, as you know, is a living material that burns well and passes steam quite well. So if you block the access of air, then the rafters will sooner or later begin to rot. At the same time, combustible insulation under the arch of a wooden house is dangerous.

Now we have reached one of the main parameters, which directly affects how to choose a heater. This is the location of the insulating layer. After all, the ceiling can be insulated both from the inside of the room and from above, that is, from the unheated side.
For an amateur, the simplest, most affordable and inexpensive option is the arrangement of an attic floor. After all, you must admit that here a person does not need to “fence” improvised scaffolding and balance on them, hemming the ceiling from below.
In addition, the question of how thick the insulation should be, for outdoor installation, actually disappears, the more the better, there is enough space. Moreover, both slab and bulk material can be used.

Installation from the inside is a completely different matter. Really high ceilings are not so common in our houses, which means that every centimeter will have to be borrowed from the living space. In my experience, owners rarely agree to "lower" the ceiling by more than 150 mm. Accordingly, the insulation must be selected light, durable and with the lowest possible thermal conductivity.
Now let's look at the materials that are most often used in construction, and at the same time analyze which of them are suitable for insulation in certain situations.
Foam insulation
Styrofoam is currently breaking all records of popularity in the domestic sector. The material is really light, affordable, and most importantly inexpensive. In our case, the strength of the foam is more than enough. Thermal insulation of the ceiling with polystyrene foam does not require sky-high knowledge and high qualifications of the builder.

But there are a couple of unpleasant moments in this big barrel of honey. The vapor permeability of foam plastic is not much higher than that of the same concrete, plus the material burns pretty well.
Whether it is possible to sew up a wooden ceiling with foam plastic from the inside or outside is a moot point. Theoretically, the installation of foam from the inside on wood is possible, because in this case there will be free air access to the ceiling from above. But why build an environmentally friendly, breathing house, then to clog the ceilings with waterproofing?
Laying foam in a continuous layer on top is also undesirable. Then the warm and humid air will have nowhere to go, and it will begin to accumulate in the tree, hence mold, fungus, etc.

Some craftsmen mount foam between the floor beams, but I am against this approach. The minimum thickness of the beam starts from 150 mm, and if it is tightly clamped on both sides with a waterproofing material, then it simply cannot cope with the onslaught of moisture from below and begins to dampen.
Therefore, we conclude that polystyrene foam is perfect for insulating reinforced concrete floor slabs, both from the outside and from the inside. When it comes to wood flooring, the use of foam is undesirable.
Here I want to mention such a popular material today as extruded polystyrene foam. In order not to go into the intricacies of technology, I can only say that this is, figuratively speaking, the elder brother of polystyrene.

It absolutely does not allow moisture to pass through and holds heat by a third better. Therefore, it can only be considered as a more effective alternative to foam when insulating from the inside of a concrete floor. There is an opportunity to get by with a smaller sheet thickness.
If you insulate the concrete floor with foam from the inside, then you can get by with a thickness of 50 - 75 mm plates. In the case when the ceiling is insulated from the outside, the minimum thickness will be 100 mm.
Mineral wool as a heater
Mineral wool in terms of floor insulation is considered a more effective alternative to foam. The range here is much wider. Both soft elastic mats and cotton slabs with a sufficiently high density are produced.

In the past, there was only one type of such insulation - glass wool. Although the characteristics of glass wool are very mediocre, due to its low cost, it is still used today. But I don’t recommend it to you, if you don’t pack yourself in tight overalls, after “communication” with glass wool you will itch for another 3 days.
In the cheap segment, soft mineral wool mats can be used, they are no longer so dangerous. Although I prefer to work with dense stone wool slabs, they are versatile and can be laid on any surface.
Mounting cotton wool with your own hands is no more difficult than working with polystyrene foam, it is also not much heavier than a competitor in weight, and most importantly, cotton wool is an absolutely non-combustible material, plus it has a high level of vapor permeability.

But mineral wool has one very significant drawback. Along with high vapor permeability, it is able to strongly accumulate moisture. Moreover, if dense plates can still be dried somehow, then soft cotton mats after drying almost completely lose their previous volume, and hence their thermal insulation characteristics.
It is believed that the coefficient of thermal conductivity of wool varies between 0.3 - 0.4 W / mºK, that is, approximately at the same level as that of polystyrene. But these are tabular, laboratory data, due to the ability to collect moisture in the real conditions of a residential building, this same thermal conductivity coefficient for cotton wool is several times higher.
The thickness of the mineral wool when mounted on the ceiling, compared with the same foam, should be at least a third larger, and if we are talking about the insulation of a cold attic floor, then the thickness of the plates is taken on the order of 150 mm and more.

Do not think that I dissuade you from using cotton wool. It is very convenient to insulate ceilings with mineral wool, and most importantly, it is effective. It can be mounted with equal success on any type of ceiling, both from the inside and outside.
It's just that this material, figuratively speaking, requires respect. The instruction must be followed strictly and then a positive result will not keep you waiting.
Loose insulation
As you probably understand yourself, only attic floors from above can be insulated with bulk materials. At the moment, expanded clay is the leader in this direction.
Expanded clay granules are produced in three types of fractions. The smallest fraction is called sand and does not exceed 5 mm in diameter. Larger and running granules have a diameter of up to 20 mm, they are called gravel. The so-called expanded clay crushed stone is granules with a diameter of 20 - 40 mm.
According to their characteristics, they are absolutely identical, the difference is only in size.

Expanded clay is relatively inexpensive. Compared to other bulk materials, there is not much dust from it. A big plus is that rodents are often indifferent to expanded clay.
Any loose insulation, including expanded clay, is afraid of high humidity, since all of them are able to absorb moisture.
Another inexpensive, but quite effective insulation is sawdust. Everyone knows that the price for them is cheap, I think. But there is one nuance here, sawdust cannot be used fresh or in its pure form.
In order to prevent rodents from starting in such a dump, it is necessary that the sawdust ages in a dry room for about a year. After that, they are mixed with the so-called "fluff" (slaked lime powder) in a ratio of 8: 2 (sawdust-lime).

Insulating boards can also be made from the same deposited sawdust. This is of course not basalt wool, but the efficiency of such plates is quite high. The manufacturing technology is extremely simple:
- Sawdust, lime and cement are mixed in a ratio of 9: 1: 1;
- All this mass is well moistened, after which it is poured into pre-prepared forms and lightly compacted;
- At room temperature, after a week the plates will dry and be ready for use.
New technologies to help you
Of the most common now-fangled heaters, 3 main contenders can be distinguished:
- Polyurethane foam is a new and rather expensive material. According to its characteristics, it partly resembles extruded polystyrene foam. This material is not afraid of moisture and is considered quite durable. Manufacturers give a guarantee for 50 years.
But polyurethane foam, like extruded polystyrene foam, is a waterproofing agent and, given that it is applied in a continuous layer, it is not suitable for a wooden ceiling;

- The now widely advertised penoizol is also a new development, but behind the tricky name lies an ordinary foam plastic, only in a liquid state. In addition to the advantages of polystyrene already listed above, penoizol is applied in a continuous layer without gaps, which means that it is also desirable to use this material only for warming concrete floors;

- In our case, the most suitable option is ecowool. It is made on the basis of natural cellulose with the addition of a binder, flame retardants and antiseptics. Ecowool is of course afraid of water, but its water absorption level is much lower than that of mineral wool. While vapor permeability and thermal conductivity are approximately at the same level.

All of the above foam insulation can only be applied using expensive compressor equipment prepared by people. To some extent, the only exception is ecowool, you can fill it with your own hands in a dry state in an uninsulated attic. When it comes to spraying from the inside, ecowool also needs a compressor.
The main stages of installation of ceiling insulation
As I mentioned above, the ceiling can be insulated from the inside or outside. Accordingly, the technologies will be different.
I don’t see the point in talking about how to spray insulating foam, because you won’t buy a compressor anyway. This is professional equipment and it costs sky-high money. Therefore, we will focus on three main methods that are available for self-arrangement.
Method number 1. Styrofoam insulation
- Insulating the ceiling from the inside with foam plastic is not a difficult task. Concrete floor slabs, for which it is most often used, are mostly even, so there are often no problems with leveling the plane, except that the seams between these slabs will need to be puttied or it is better to foam with mounting foam, so faster;

- The next stage of our work will be a double coating of the ceiling with a deep penetration primer. Even a child can cope with such work, but I do not advise skipping this stage, the adhesion of smooth concrete is low and without soil in any way;
- Now we take pre-prepared sheets, spread them with glue and glue them to the ceiling. Some advise applying sheets to each other as tightly as possible, without gaps.
But I act differently. No matter how hard you try, gaps will remain in any case, so it’s better to immediately glue sheets with a gap of 5-7 mm. After the glue sets, I fill these gaps with foam. Thus, I get a really solid coverage;

Separately, I want to say about glues. There is enough of this product in the markets. But masters for the most part use three options:
- Glue "Liquid Nails" is good, but after application it must be applied to the surface, then immediately torn off and wait until it is ventilated for 5-7 minutes. And only then will he reliably take it;
- Ordinary polyurethane foam has proven itself well in this regard. Spread the “pattern” of foam on the sheet and apply the foam to the ceiling. Only here you will have to press the sheet several times within an hour, because as the foam expands and until this process is over, the sheet will gradually move away;
- For myself, I chose Ceresit CT83 dry mortar. She was simply spread according to the instructions, applied to the sheet with a notched trowel and glued. There is no notched trowel at hand, the same does not matter, you need to put a few “buns” at several points and glue it.

- But you can’t leave foam like that, firstly, it is combustible, and secondly, it’s just ugly. The ceiling will need to be plastered. To do this, I put a spatula on the ceiling with a layer of 3 - 4 mm Ceresit CT83 and immediately sink a sickle (reinforcing fiberglass mesh) into it;

- Next, we need to be safe. High-quality glue is good, but the foam must be additionally fixed to the ceiling with umbrella dowels.
You can't do without a perforator here. You drill a hole through the foam plastic through the concrete, insert a plastic dowel into it and hammer in the central rod. Consumption - about 5 dowels per 1 m²; - When all this is dry, you can apply a layer of decorative finishing plaster. If you do not want to buy Ceresit CT83, take any starting plaster, only in this case the foam will need to be primed first.

If you decide to insulate the ceiling with foam plastic in a wooden house, then there the material should be laid between the supporting beams, to their entire depth, and the gaps should be foamed. From below you will have a hemmed ceiling, and from above it is desirable to fill the subfloor, because you need to somehow move around the attic. In this case, no vapor barrier is needed, the foam is not afraid of moisture anyway.
Method number 2. Installation of mineral wool from the inside
Now let's talk about how to insulate the ceiling with mineral wool. From the inside, the mineral wool ceiling can be insulated in two ways.
I have already told you about the first one. The fact is that dense mineral wool slabs are glued and plastered on the ceiling in the same way as foam plastic. There is nothing to add here, except that you cannot do without a notched trowel.

The second no less common method is internal installation under a hinged crate. Such a crate can be equipped both on wooden ceilings and on concrete.
The frame of such a crate can be assembled from wooden bars or from UD and CD profiles. My advice to you, learn right away on metal profiles, they do not lead to temperature changes, and most importantly, such a skill may come in handy more than once.

- First you will need to beat off a horizontal line around the perimeter of the room, at the level of the future ceiling. The easiest way to do this is with a laser level, but if it is not nearby, use a hydraulic level (a long soft tube with graduated tips, working on the principle of communicating vessels);
- Further, according to this markup, on two longer walls, two UD profiles are mounted;
- Now, perpendicular to these profiles on the ceiling, you need to mark out how the CD profiles will pass. Usually a step is taken about half a meter;

- According to this marking, with an interval of a meter, we fasten perforated suspensions with dowels and immediately bend down the wings of these suspensions;
- After that, cotton slabs can be glued to the ceiling. Under the wings of the hangers, the plates are simply cut with a knife;
- Further, we insert CD profiles into the UD profiles and fix them with self-tapping screws between each other and to the suspensions. In principle, that's all, now you can hem or whatever you like.
Method number 3. Insulation of the ceiling from above
This is the easiest option. If you are dealing with a concrete floor slab or the load-bearing beams of a wooden ceiling are already sewn up and you do not want to touch them, then you will need to lay a crate in the attic.

As a crate, a wooden beam with a thickness of 50 mm or more is usually used. The tire of the beam, which will simultaneously be the depth of the crate, is calculated according to the principle: thickness of the future insulation, plus 30 mm for the ventilation gap.
Now the entire space of the attic over the crate is covered with a vapor barrier. Do not forget that the vapor barrier membrane allows steam to pass only in one direction and the steam must move upwards. Such membranes always have marks indicating which side is vapor permeable. The membrane is fixed on the crate with a furniture stapler.

Now you can lay or fill the insulation itself. With bulk materials, everything seems to be clear, poured out, leveled and ready. Here it is worth saying how to lay slab insulation, for example, the same mineral wool.
In order for the cotton mats or slabs to fit tightly between the wooden guides, they must be 20 - 30 mm wider than the gap. And so as not to get cold bridges at the junctions of these plates. The material is usually laid in 2 layers.

In the case of wool, 100 mm thick slabs are usually taken and first laid in one layer. Then the same layer is laid on it, but the joints of the lower and upper layers should not coincide with each other. So you get a monolithic insulation. The final touch in this design will be a rough flooring over the crate.

Output
What kind of insulation is better to work with, of course, you decide. For my part, I tried to talk about the simplest ways, in my opinion, available even for an amateur.

If you want to express gratitude, add a clarification or objection, ask the author something - add a comment or say thanks!
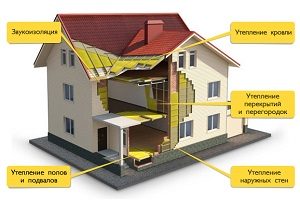
It is possible to insulate the walls, roof, floor in the house not only with heat-insulating mats and plates, but also with a loose heat insulator. For some, it will be much more convenient and cheaper.
If you fill the insulation between the walls, then the walls themselves do not need to be made thick, which means you will save on building materials. For a long time, sawdust has been the most popular bulk insulation. They warmed everything. Sawdust was poured onto the floor screed, between the walls, insulated the attic and roofing. Currently, other types of bulk insulation are also used.


Very often you can find such material in construction as hollow brick. Properties and application of hollow bricks.
No one will argue that the urinal is a very rare guest in our homes. Most often we see him in public restrooms, where there is a large flow of people.
The harvest of many owners of suburban areas directly depends on the chemical composition of the soil. Sometimes, in order to increase the fertility of the land, it must be deoxidized.
The paths in the summer cottage play an important role in life outside the city, thanks to well-made paths, water does not accumulate on them in the rain, and in winter they are easy to clear of snow.
Today it is impossible to imagine existence in everyday life without the presence of a minimum of power tools - devices for mechanical processing of various materials using an electric drive.
Transformer device. Deterioration of the converter windings. How and with what to monitor the transformer in order to avoid emergency situations.
Most experts believe that metal gutters are more durable and much better in quality than plastic gutters.
The yield of vegetable crops depends on the condition of the seed. It can be increased in two ways - to reduce the time of germination and increase the resistance of seedlings to diseases and pests. Review of seed preparation methods.
There are few things that are more inviting than a room filled with simple décor, and the wine interior theme is easy to do so you can add it to your own home.
It is difficult to take your eyes off the enchanting fiery dance that takes place behind the glass in the fireplace, and the blackened glass of the fireplace makes this visual enjoyment impossible. What is the reason for the frequent sooting of fireplace glass, and how to properly clean the glass of your fireplace.
Backfill thermal insulation – StroyMasterskaya
It is possible to insulate the walls, roof, floor in the house not only with heat-insulating mats and plates, but also with a loose heat insulator. For some, it will be much more convenient and cheaper ...
Once again about filling heaters
Variety of backfill heaters
Differences of bulk heat insulators from rolled, tiled and other heaters in a moderate, affordable price, in a simple laying technology. It is only required to distribute it evenly, taking into account correct vapor barrier. As a rule, only backfill insulation leaves no gaps, penetrates into hard-to-reach areas. However, the variety of material dictates its own rules - how not to make a mistake, take into account all the advantages and disadvantages and choose the one that is ideal for your home? Comparison after the review below will surely make this task easier.
Vermiculite (bulk)
 Thermal insulating filling Vermiculite belongs to natural materials, since it is a mineral of the hydromica group that has been fired. The thermal conductivity depends on the size of the fractions. For backfill thermal insulation in civil engineering, expanded vermiculite of a large fraction up to 1 cm with a gloss characteristic of mica and a scaly structure is used. Roasting allows you to increase the volume of raw materials by 7-10 times, its volumetric weight is about 90 kg per cubic meter. The heat insulator layer does not cake, easily gives off the absorbed moisture. It is used for insulation of ceilings, roofs, interstitial space, backfilling of foam blocks.
Thermal insulating filling Vermiculite belongs to natural materials, since it is a mineral of the hydromica group that has been fired. The thermal conductivity depends on the size of the fractions. For backfill thermal insulation in civil engineering, expanded vermiculite of a large fraction up to 1 cm with a gloss characteristic of mica and a scaly structure is used. Roasting allows you to increase the volume of raw materials by 7-10 times, its volumetric weight is about 90 kg per cubic meter. The heat insulator layer does not cake, easily gives off the absorbed moisture. It is used for insulation of ceilings, roofs, interstitial space, backfilling of foam blocks.
The most positive thing about its environmental friendliness is that when heated, Vermiculite does not emit toxins, it has no smell. It is bioresistant, fireproof, air permeability favorably affects the formation of the microclimate of rooms insulated with bulk expanded vermiculite. Vermiculite does not interfere with natural air circulation (not to be confused with drafts and convection). It is used as an additive in cement mortars, in finishing materials. High cost is not always a positive point when choosing.
Aerated concrete crumb (backfill)
 Aerated concrete chips, this is a mixture of porous gravel and sand ,
obtained after crushing aerated concrete. Irregularity of fractions up to 30 mm, irregular shapes of particles form a layer that does not lose its shape. It is used as a bulk insulation, additional bedding for sound insulation in building structures (walls, ceilings). It is in demand as a heater for a shed roof with a small angle of inclination. Does not interfere with natural circulation, providing optimal humidity and gas exchange. Backfill aerated concrete chips are used instead of expanded clay in lightweight concrete, when pouring the foundation. In this case, aerated concrete crushed stone insulates the foundation, due to its low thermal conductivity, and also contributes to its anti-swelling. Inexpensive drainage and insulation for road surfaces. The disadvantage is the dusting of fine fractions during backfilling.
Aerated concrete chips, this is a mixture of porous gravel and sand ,
obtained after crushing aerated concrete. Irregularity of fractions up to 30 mm, irregular shapes of particles form a layer that does not lose its shape. It is used as a bulk insulation, additional bedding for sound insulation in building structures (walls, ceilings). It is in demand as a heater for a shed roof with a small angle of inclination. Does not interfere with natural circulation, providing optimal humidity and gas exchange. Backfill aerated concrete chips are used instead of expanded clay in lightweight concrete, when pouring the foundation. In this case, aerated concrete crushed stone insulates the foundation, due to its low thermal conductivity, and also contributes to its anti-swelling. Inexpensive drainage and insulation for road surfaces. The disadvantage is the dusting of fine fractions during backfilling.
Expanded clay (backfill)
 Expanded clay, a traditional backfill heat insulator. Firing of light-melting clay makes it possible to obtain oval granules of various fractions. The porous structure, the low weight of hardened foamed clay, the natural base will keep this material on the bulk insulation market for a long time to come. Although, it is widely used in filling lightweight concrete, as a drainage. Fireproof, resistant to decay. Its cost is equal to the cost of rough building materials. It is widely used for ceiling insulation, but here it is necessary to take into account the disadvantages of expanded clay. It is fragile, easily absorbing moisture, hard to give it away. It is necessary to provide reliable waterproofing, it is undesirable to fall asleep on the floor itself. A vapor barrier substrate and mandatory waterproofing will slightly increase the cost of such insulation. Possible shrinkage. Expanded clay gravel of large fractions up to 20 mm is also suitable for insulating saunas and baths. For foundations and basements, a coarser fractional material is recommended, which can be attributed to crushed stone.
Expanded clay, a traditional backfill heat insulator. Firing of light-melting clay makes it possible to obtain oval granules of various fractions. The porous structure, the low weight of hardened foamed clay, the natural base will keep this material on the bulk insulation market for a long time to come. Although, it is widely used in filling lightweight concrete, as a drainage. Fireproof, resistant to decay. Its cost is equal to the cost of rough building materials. It is widely used for ceiling insulation, but here it is necessary to take into account the disadvantages of expanded clay. It is fragile, easily absorbing moisture, hard to give it away. It is necessary to provide reliable waterproofing, it is undesirable to fall asleep on the floor itself. A vapor barrier substrate and mandatory waterproofing will slightly increase the cost of such insulation. Possible shrinkage. Expanded clay gravel of large fractions up to 20 mm is also suitable for insulating saunas and baths. For foundations and basements, a coarser fractional material is recommended, which can be attributed to crushed stone.
Foam glass (backfill insulation)
 Foam glass. As a filling insulation, it can be of several types and this is due to the different technology of its manufacture. This:
Foam glass. As a filling insulation, it can be of several types and this is due to the different technology of its manufacture. This:
- filing of a plate from foam glass;
- foam glass crushed stone obtained by foaming the array and rapid cooling. This leads to destruction, additional mechanical crushing gives crushed stone without an outer melted layer at the exit;
- granulated foam glass, which has found wide application in the construction market, both as an independent backfill and as the basis for heat-insulating plasters.
Granulated foam glass is obtained from foamed raw granules. In fact, it is glass foam with a melted outer surface. The porous structure with a melted surface gives unique properties to the inorganic insulation. It is rigid, with high compressive strength, water-resistant, not subject to chemical and bacteriological destruction. Eco-friendly. It has practically no temperature restrictions during operation (from -200 to +500 ° С.). Great for arranging and insulating inverted roofs, insulating basements, foundations, because it is not afraid of external and groundwater. Can be reused and reused, the thermal conductivity remains unchanged (0.05-0.07 W/(m·°C)). It can be used as filling insulation in ceilings and walls. But this is not a budget option.
Penoplex or Polyfoam (Zasypny)
 Light air (from foamed polymers) spherical granules are often pressed into plates, which simplifies the installation of a heat-shielding layer. Penoplex, Polyfoam, Expanded polystyrene. But unpressed granules or expanded polystyrene chips, after the disposal of substandard sheets, are used as an independent heat insulator and as an additive in concrete (polystyrene concrete). Such a heater does not have absorbent properties - it does not absorb moisture, the shock-absorbing capabilities of a layer of polystyrene granules are high (recall the "live" Bubble chairs, a bag filled with a similar backfill). Crumb is always cheaper than granules, but its properties are not strictly regulated either. A very light material that needs protection from sunlight, chemical and temperature influences. Easily lifted by airflow. The material is relatively new, its properties have not been tested by time and often cause controversy, both among builders and consumers. The trend towards environmentally friendly housing is clearly against it. Although the heat and sound insulation properties declared by the manufacturers are high and the price is affordable for budget construction.
Light air (from foamed polymers) spherical granules are often pressed into plates, which simplifies the installation of a heat-shielding layer. Penoplex, Polyfoam, Expanded polystyrene. But unpressed granules or expanded polystyrene chips, after the disposal of substandard sheets, are used as an independent heat insulator and as an additive in concrete (polystyrene concrete). Such a heater does not have absorbent properties - it does not absorb moisture, the shock-absorbing capabilities of a layer of polystyrene granules are high (recall the "live" Bubble chairs, a bag filled with a similar backfill). Crumb is always cheaper than granules, but its properties are not strictly regulated either. A very light material that needs protection from sunlight, chemical and temperature influences. Easily lifted by airflow. The material is relatively new, its properties have not been tested by time and often cause controversy, both among builders and consumers. The trend towards environmentally friendly housing is clearly against it. Although the heat and sound insulation properties declared by the manufacturers are high and the price is affordable for budget construction.
Mineral wool (bulk)
 Raw materials for mineral wool are a number of rocks, metallurgy slags, quartz (fiberglass). Slag mineral wool is inferior in quality and characteristics to a heat insulator made from molten rocks. Since mineral wool fibers affect the mucous membranes and respiratory tract, the production process does not always stop at obtaining fibers and depositing them. Cotton wool is either glued with glue based on polymer resins (plates, rolled insulation) or mechanically granulated. Bulk mineral wool includes both fibers and granules. Loose mineral wool is not always suitable for insulation, since tamping breaks the fiber structure and there is a risk of shrinkage. And it is difficult to work with it, protective measures for the skin and respiratory tract are necessary. Granular mineral wool is recommended as an effective insulation of technological equipment, chimneys, it is resistant to high temperatures (resistance threshold 1090 ° C), non-flammable and has a lower weight in volume (250 kg / 1 m3) than loose. The size of the granules is usually 10-15mm. Minerals are not biodegradable, so mineral wool does not rot, it has good vapor permeability, but when wet, the thermal insulation properties decrease. Mineral wool dries hard.
Raw materials for mineral wool are a number of rocks, metallurgy slags, quartz (fiberglass). Slag mineral wool is inferior in quality and characteristics to a heat insulator made from molten rocks. Since mineral wool fibers affect the mucous membranes and respiratory tract, the production process does not always stop at obtaining fibers and depositing them. Cotton wool is either glued with glue based on polymer resins (plates, rolled insulation) or mechanically granulated. Bulk mineral wool includes both fibers and granules. Loose mineral wool is not always suitable for insulation, since tamping breaks the fiber structure and there is a risk of shrinkage. And it is difficult to work with it, protective measures for the skin and respiratory tract are necessary. Granular mineral wool is recommended as an effective insulation of technological equipment, chimneys, it is resistant to high temperatures (resistance threshold 1090 ° C), non-flammable and has a lower weight in volume (250 kg / 1 m3) than loose. The size of the granules is usually 10-15mm. Minerals are not biodegradable, so mineral wool does not rot, it has good vapor permeability, but when wet, the thermal insulation properties decrease. Mineral wool dries hard.
Cellulose insulation (ecowool)
 Backfill ecowool is recommended as an excellent insulation and soundproofing material for any structures. But having a wood base - recycled cellulose treated with borates, is ideal for wooden structures, since it has 100% compatibility of characteristics with wood. This avoids many of the incompatibility problems of contacting materials. It is widely used in low-rise frame construction as a filling heat insulator for walls, roofs and ceilings. Environmentally friendly material, does not rot, resists fire. Ecowool is the right insulation for houses with natural ventilation without the risk of exposure to volatile toxins. Eliminates the issue of the appearance of rodent populations in the ceilings. Along with the advantages, backfill ecowool has disadvantages. Manual laying is a very laborious process, in which it is difficult to adhere to the recommended density. It "dusts", because it has a fibrous structure of wood fluff. In the cost of insulating a house with ecowool, it is advisable to include the service of installing the layer in a mechanized way (under measured pressure and using a blowing machine). But ecowool insulation produced once, it does not reduce its thermal insulation properties under the influence of time and external factors for the entire life of the house.
Backfill ecowool is recommended as an excellent insulation and soundproofing material for any structures. But having a wood base - recycled cellulose treated with borates, is ideal for wooden structures, since it has 100% compatibility of characteristics with wood. This avoids many of the incompatibility problems of contacting materials. It is widely used in low-rise frame construction as a filling heat insulator for walls, roofs and ceilings. Environmentally friendly material, does not rot, resists fire. Ecowool is the right insulation for houses with natural ventilation without the risk of exposure to volatile toxins. Eliminates the issue of the appearance of rodent populations in the ceilings. Along with the advantages, backfill ecowool has disadvantages. Manual laying is a very laborious process, in which it is difficult to adhere to the recommended density. It "dusts", because it has a fibrous structure of wood fluff. In the cost of insulating a house with ecowool, it is advisable to include the service of installing the layer in a mechanized way (under measured pressure and using a blowing machine). But ecowool insulation produced once, it does not reduce its thermal insulation properties under the influence of time and external factors for the entire life of the house.
How to choose the best bulk insulation for your home?
Varieties of bulk insulation, the scope of bulk heat insulators, properties
Bulk
Our ancestors insulated the caves with skins. The walls of medieval castles were covered with tapestries and ... skins. Russian boyars also lined the bedrooms with furs. And when there were almost no animals left in the forests, mankind thought - and invented polystyrene foam and foam glass, polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, mineral and glass wool, expanded clay and cork chips.

Modern heaters are of three types. The "hard" type includes foam plastics - expanded polystyrene, foam glass - that is, options that are produced in the form of layers with rigid geometry. To the "soft" - fiberglass and mineral wool, which are found in the form of separate plates or rolls. Well, the most common "loose" insulation is expanded clay.
Expanded clay- one of the most environmentally friendly materials, it is almost 100% natural. It is obtained by accelerated firing of light-alloy clays. With a sharp thermal shock, the prepared clay swells, becomes porous, and its surface, melting, creates an airtight shell.




Expanded clay is produced in the form of rounded granules various sizes (from 2 to 40 mm) and density. This material is so light that it practically does not sink in water (and does not absorb it!). It is this indicator - lightness (from 200 to 400 kg / m 3) - that makes it indispensable when it comes to warming rooms with ceilings, which are contraindicated in heavy loads. For example, when warming balconies. For comparison: 1 m 3 of ordinary water weighs a whole ton.
To the undoubted advantages of expanded clay it should also be attributed that it is refractory, frost-resistant, chemically inert, durable and, importantly, relatively cheap.
Advantages and disadvantages of modern heaters. Debunking marketing myths.

They shrink, they need to be poured (if you plan sawdust as a heater on the roof). They do not have refractory properties, so sawdust and ash used to interfere, and a sand or clay castle was made on top, which completely block the spread of fire.
Cellulose insulation: paper, including newsprint. Cardboard is added, but not more than 10%. Boron salts are added for flame retardancy.
If you remove the source of the flame, it will smolder for 5-6 hours. After a fire, you need to remove a piece of the wall, because. smolders well.
Manufacturers save raw materials, use more air.
It is better to lay only by hand, only a good seal. Shows how to avoid cold bridges. If blown out, the shrinkage will be even greater.
If cardboard is added instead of paper, then the color is more brownish. At the same time, the weight increases, and they are sold by the kilogram. The thermal properties are significantly reduced in this case.
Ecowool has environmental properties, unless, of course, we close our eyes to the boron content (somewhere around 15 percent or something), etc.
Appeared in Europe as a result of recycling. Therefore, it is not worth placing hopes on it for economic feasibility.
They serve only 10-15 years, after which they become damp, they need to be changed. Under ideal conditions, by factory standards, the service life is 25-35 years.
In 15 years, each owner of such a house will pay extra for heat loss in such a house. Imagine removing tiles and replacing insulation in a 17-story building. The rise in heating costs is enormous. In 15 years, heating costs will be enormous. It turns out that the developer is selling a house that obviously uses low-quality materials, because of which you will have to spend money in the future.
The manufacturer recommends the use of wind and steam protection. porous and fibrous material has the property of accumulating liquid in its structure, so it must be protected. It is humid in our house, plus the air moves from the high pressure area to the low pressure area. Thus, the air tries to break out of the house into the street, taking it with it into the water in a vaporous state. In this case, the air tries to break through the walls and ceiling. It is unlikely to pass through the floors, there may already be enough moisture there, especially if the underground space is poorly ventilated. Therefore, to protect against steam, everything is tightened with a film. At the same time, they do not talk about the service life of small holes in the film. And after 10 years, these holes can become clogged with small fibers of mineral wool, which will begin to crumble. The fibers are glued together with formaldehyde and other resins. The resin breaks down over time, the fibers delaminate. Outside, a windscreen is used to prevent the fibers from loosening and weathering. When cotton wool is moistened by 10-15%, the thermal properties are lost by 30%. When the small holes in the film get clogged, you get a regular stretched plastic film that prevents steam from escaping, steam accumulates, and additional ventilation is required. The windscreen is on the outside and therefore subject to freeze/thaw cycles. How long she will live is unknown.
The usual plastic film on greenhouses is destroyed due to temperature changes (closer to autumn, when sub-zero temperatures begin). Therefore, we can lose the windproof structure before the insulation loses its properties. Plus, the vapor barrier is installed incorrectly.
Has no damping properties. If you try to stuff 60 cm of cotton into 58 cm, then it will bend.
This type of insulation has too many disadvantages.
In Europe, they have adopted the standard that the fibers must completely decompose in 40 days.
At 17-20 kg/m3, convection starts in the wool layer.
The melting point of basalt is 1500 degrees. The technology for the production of small threads is not cheap.
The segment with larger and sharper fiber is now actively decreasing.
- thermal conductivity (heat transfers from hot to cold), The thermal insulation material should be with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Sausage-type materials sold in rolls packed in polyethylene film often have a density of no more than 15 kg/m3. When you spin the roll, it gains height. In less dense mineral wools, the vacuum between the fibers is greater, so the air, due to convection, moves more easily from cold to warm, transferring heat.
Available. Eco-friendly. Lives longer than a bar on which moss is laid. 7 magic antiseptics, different in structure (of which you can make dressings for wounds, dressings that draw out pus.) No bikarasiki start up in it. In dry material, no one starts. If you put wet moss, it will still dry quickly, even in a confined space. Moss is used as a material for storing vegetables. It has shock absorption properties. It's a pleasure to work with the material. Disadvantage: Does not have refractory properties. From the inside, ordinary plaster on shingles is required, and from the outside it can be sheathed with flat slate. You don't have to worry about asbestos. Russian chrysotile asbestos does not have such a needle structure as foreign amphibole asbestos.
Peatlands have self-ignition properties. Peat is mixed with cement and aluminum chips. It turns out a kind of porous sibit. Such a thermal screed in many villages was previously used on ceilings and, it seems, on the floor. The 100 year old building was demolished. The floor beams were not damaged at all. Since there is no oxygen in peat, it perfectly preserves various materials (in fact, it mummifies). If you mix it with some kind of composition or take vermiculite, which has good refractory properties and works well with a liquid, then you can conduct an experiment, how it all stays idle.
Good sandwich: A good thick-walled pipe is taken (for example, 150 mm), with a galvanized metal casing on the outside. The pipe is placed at the base of the boiler. A space of 5 mm is filled with a mixture of vermiculite with liquid glass, carefully compacted. Even if the pipe burns out, the vermiculite will work as guides.
Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS, EPS, XPS), if I'm not mistaken, is produced in the same way, only obtained by extrusion (the material is squeezed out through a nozzle), a high-density composite material is obtained. There are almost no voids between cells.
Konrad Fischer studied the materials well. He restores museums, the structure of buildings.
Fire-resistant properties at foam plastics are absent. Flame retardants are added to them so that the flame does not spread.
Raw materials began to be mined in the 60s
Different composition, different impurities
In Russia, it is often idle because the equipment is old
Raw materials from Uzbekistan have unique properties
In addition to floors, it can be poured into the floor or frame structures. If the plywood is in the frame, then the vermiculite is simply poured and compacted. When mixing with fine chips 1:1, it can be mixed directly on the building (hand mixer, drill, perforator) in the ceiling. Mixed until smooth.
Chips and sawdust can burn and absorb moisture. But vermiculite absorbs moisture, evens out the humidity regime, and in about a month the sawdust / shavings will become dry. There will be no debate. Fungi and mold may appear. Sawdust has good thermal insulation properties (0.08), vermiculite (0.05-0.06).
Vermiculite when moistened by 15% does not lose its thermal properties.
Polupanov promises to check the refractory properties with a blowtorch.
For other plants (flowers.) Make special primers. Almost all flower soils sold in stores use vermiculite. Previously used expanded clay.
In animal husbandry, vermiculite is added to feed. For example, cows that have a large mucus. Vermiculite, as an absorbent, cleans the intestinal tract of the cow, it is less susceptible to diseases.
Smell-soaked vermiculite bags can keep them for a long time.
If you instead sew up with drywall, you will get an air gap between the wall and drywall. This is a reason to get rodents there. The main mass of the wall does not warm up, since the interior of the house uses mainly convective heating, and not infrared. The air heats up the structure very slowly. Behind a layer of air gap and drywall, the wall will not warm up. Therefore, the wall will freeze more from the outside. Frost will accumulate, water will freeze. Water expands when freezing, the timber cracks even more. The structure of the house is moving. Therefore, the use of gypsum structures on external walls is not recommended.
The walls need to be heated not only in the places where window openings are installed, but also with the contour of warm pipes. Heating will be not only due to convection, but also infrared radiation.
Stretch ceiling is quickly done. But it is acceptable in apartments, but in private houses I would not recommend it. An air gap is formed. On floors, backfill from 20 cm plays the role of a heat-intensive base for heat stabilization, it accumulates heat. This pad cannot be cut off from the heat circuit.
Basically, all heaters work to protect convective flows.
Similar to warm plaster, warm floors with vermiculite are poured. Vermiculite is poured into the mixer, everything is mixed, then the screed is poured with a warm solution, aligned with the beacons. Canadians and Americans mainly use warm solutions in frame housing construction. It is not concrete that is poured, but a lighter solution.
Ceramic porous blocks are recommended for use only on a warm solution. This solution has less thermal conductivity. Outside and inside, you can also make plaster with vermiculite. To avoid heat breaks, it is leveled with a layer of plaster.
This is an environmentally friendly material. During operation, inert gases, resins are not emitted.
Foam balls are large (2-5 mm) form large pores, while rather heterogeneous. Vermiculite has a rather fine structure, these pores are tied up with an array of plaster or screed. The surface is more uniform. Such plasters are more refractory than classic ones.
Drywall 2cm layer has some refractory properties, but you need to put it in several layers (and not one layer), overlapping. Plaster with vermiculite behave better. At the same time, fire resistance is relevant in wooden houses.
Perlite is a fine expanded glass. Density - 50-55 kg / m3. There are varieties and 60-100 kg / m3. With equal density, the thermal conductivity of vermiculite is slightly better than that of perlite.
Expanded clay, unfortunately, is heavy. The thermal conductivity is three times higher, the granules are large. Air moves between the granules. Therefore, a much larger layer would have to be poured. Although, it would seem, a cube of expanded clay is cheaper than a cube of vermiculite.
Heat capacity modern materials are often ignored. Lightweight, including fibrous materials are used. Protection in this case occurs only from convective heat flows. The air is immobilized, so there is less heat loss. If you insulate with a light material like foam, then there will be no stabilizing properties in terms of temperature. The house will not have the properties to accumulate heat or cold. Temperature fluctuations will affect the house. If complex electronics ahead of schedule in a frame house does not work, then there will be spasmodic processes.
More heat-intensive heaters, for example, sawdust, have a mass (300-400 kg / m3), while small air pores do not allow air to quickly accelerate. If it is normal to lay ecowool, then it has approximately 85 kg / m3. Foam plastics and foam plastics do not have a significant mass, therefore they do not accumulate heat. Vermiculite from mountain mica, therefore retains heat. It is good as a drive both on ceilings and in wall cavities. It is also good when mixed 1:1 with sawdust. The properties of expanded clay are many times different from vermiculite (20 cm of vermiculite in the backfill - 1-1.5 m of expanded clay).
During the construction of brick buildings, foam plastic / extruded polystyrene foam is also laid in the monolith of the wall, although this is unacceptable. Often it is laid closer to the facing brick, often with gaps. The material is vapor-opaque, the wall begins to dampen.
Old buildings - 50-70 cm of monolithic brickwork.
If the masonry is well, you want to place a heater there between the bricks, then the mineral wool lasts 10-15 years, and the brick is much longer. Disassemble the facing masonry and change the insulation? Therefore, outside they make metal siding, false timber.
Vermiculite can be poured into the cavity of the well masonry. The thickness of the backfill should be at least 15-20 cm. The approximate life of vermiculite is 70 years. At the same time, do not forget to reinforce the outer facing brick with the bulk of the wall. This is the perfect solution.
Natural insulation: sawdust, moss and vermiculite.
Geokar (peat block), straw, foam glass are of low prevalence, since the place of production can be removed from the consumer. All three are environmentally friendly.
Geokar is made from peat. Peat is subdivided into upper and lower peat. Mostly used riding. Where the moss turns into a state of peat (1 mm per year) - riding.
Trillions of tons a year Russia receives peat for free. Natural wax is even obtained from peat, which is used in perfumery. There are less decomposed fractions in high-moor peat. They, in my opinion, are used in geocar. Horse peat is also used for fuel (briquetted peat). Peat is hard to come by. It is necessary to drain the swamps, to roll the peat, to dry it.
Geocar production: Peat is mixed with water, resulting in viscous properties. The fibers are small, like cement. At the same time, the solution is plastic, you can even glue something on it. The geokar also includes sawdust (usually 50% of a briquette). Pressing, drying. Sawdust acts as a stabilizer in terms of geometric parameters. Combustibility class - slightly combustible. Up to 5 floors were built from the geocar block.
Geocar has very good antiseptic properties, completely disinfecting the room. In the prison, they laid out a geocar inside and the incidence of tuberculosis decreased by 90%.
The heat-saving ability is good. The block is structural. Blocks 200 by 500, if I'm not mistaken, the height is approximately 5 cm. Thin blocks dry faster.
Inside, a brick house can be lined, or outside. The top must be plastered to protect from fire. Rodents generally do not perceive it, if I'm not mistaken. It can be used, in principle, in well masonry, but I have not seen this. According to the operational regime, in my opinion, it has 50 years of operation. The material is translucent. Poorly accumulates harmful impurities. The building is environmentally friendly with good side effects, such as air purification from germs and bacteria.
In terms of cost, it is quite competitive. But peat extraction is very costly. Plus, you need a lot of sawdust in production. All this can deter manufacturers from expanding their range. The equipment is offered for 20 million rubles. Technologically, everything seems to be simple, so this price seems too high. You need a good peat deposit. With state support, the material could be widely disseminated. I liked the material and love it. Safe, non-toxic, durable, completely fireproof, can be used for self-supporting structures.
In adobe housing construction, hay or any straw in a row is not used. Straw baled either after buckwheat, or millet or rye, I don’t remember. The peculiarity is that there should be tubules that have a vitreous hexagonal shape, which are preserved for a long time, do not rot, do not fade. It turns out a very good building material. You need to decide what adobe is made of and whether there are opportunities for its production in your area.
Straw harvesting is carried out using a baler directly on the fields during harvesting. It turns out ready-made building material. It is worth transporting it and you can insulate the under-roof space with it, you can make a self-supporting adobe out of it.
Cob blocks can be laid, penetrating with carbon fiber reinforcement. I don’t consider metal in construction at all in large volumes, especially looped, pin-shaped, sticking out in the wall.
I admire the desire for harmony with nature. But it is wrong to pierce an adobe house with metal fittings vertically or horizontally, to use a metal mesh for plastering.
The self-supporting structure tends to shrink. After installing the roof, shrinkage occurs, then finishing. The self-supporting frame distributes the load on the straw blocks (somewhere a bubble may come out, the height may decrease). The use of adobe in frame housing construction was optimal, in my opinion. Classic frame, double frame (for interior and exterior cladding).
There are straw knitters themselves. The price of straw is cheap, but delivery can be expensive if the distances are long.
Adobe construction has become widespread in the South of Russia, in Ukraine, in Belarus. In Siberia, I have not seen such constructive. Condensation occurs when there is a large temperature conflict. Such fluctuations are repeated during one winter from 20 to 50 times, which can lead to the dampening of the adobe. A large amount of snow also suggests a solid foundation. Our foundation is either stone and cobblestone or completely absent. We also need a high base so that the snow does not sweep.
From a commercial point of view, the market price will be ridiculous, as buyers will not appreciate. Although the cost of construction is comparable to a wooden house. Beam, frame, foam concrete in the client can cause a greater sense of reliability, durability, practicality.
The adobe has no refractory properties. It must be plastered inside and outside with clay mortars and plasters. Tests have shown that plastered straw holds fire for about two hours, if I'm not mistaken.
Many people say that such a house calms, creates good energy. Residents in such a house are very comfortable. It is an integral part of green building. The tree is some kind of violence. Previously, they cut it correctly, asked for forgiveness from the tree. Straw has a minimal death that will not upset anyone. Plus, straw continues life in your home. That's so smart.
The minimum wall thickness is 50 cm, if I'm not mistaken. Those. up to 10 sq.m. in the house we lose 10 by 10 meters. The market price is from 10 to 15 thousand rubles per square meter, so count.
A house 10 by 10 meters 3 meters high requires 24 cubic meters of vermiculite in the well masonry for the frame (the cost will be 103 thousand rubles, and about 100 thousand rubles will come out with insulation of the ceiling and floor of 20 cm with vermix (vermiwood).
Equipment and production, which I know, are located in Ukraine. Therefore, this insulation will be of interest to residents of Ukraine. He goes to Russia. But its cost, if I'm not mistaken, is 10-14 thousand rubles per cubic meter.
Production: Broken glass is heated to a fluid state, then the foaming process takes place. Inside are small bubble voids. Black material, porous. By properties, it is indistinguishable from ordinary glass: durable, vapor-tight, does not burn. It can be cut, adjusted, i.e. pretty good at handling. The compressive load is similar to a brick of 120th density or something, i.e. it can well hold the load on itself, it can be built from it, like from a brick.
Foam glass is used as insulation in nuclear reactors, in all important buildings like hotels.
It can be used in regions with high humidity and underwater. It does not absorb liquid. Two sizes: one is like a brick, the other is bigger.
The service life is more than 70-100 years.
Ideal for use in basements. As well as in penoplex (penoplex) there are no open pores.
It strongly resembles rock after a volcanic eruption. Such a heater was used in ancient times.
The vapor transparency of the building will be reduced to zero, with the exception of masonry joints. Many experts say that it can be used to insulate brick houses. But in my opinion the liquid will remain in the design.
It makes sense to build entirely of foam glass so that the liquid does not pass at all. But the market price is high.
Penoplex costs 4600 rubles per cubic meter.
Foam glass crumb (battle) is cheap. It can also be used in well masonry, since gaps form between the particles, in my opinion, steam can pass between them. In this form, no matter where else it went.
I may be mistaken as there are plenty of sources.
Thermal conductivity is worse than that of the same vermiculite. Foam glass needs twice as much.
In Ukraine (and not in Siberia) 15-20 cm for heat stabilization, I think, will be more than enough.
The product often has an industrial purpose.
Advantages and disadvantages of modern heaters
Huge marketing budgets for the promotion of heaters Rockwool (Rockwool), URSA (Ursa), Isover (Isover, Isover), Tehnonikol (TechnoNIKOL), Penoplex (Penopeks, Penoplex), Knauf (Knauf), Isoroc (Isorok, Izorok), Isolon (Isolon , Izolon), Energoflex (Energoflex) very often interfere with taking ...
