Translation of various quantities. Online converter of measurement units of physical quantities
A program for converting units of measurement. Works with units of length, mass, volume, speed, area, temperature, angles, energy, pressure and power.
Any schoolboy, technical student or engineer is constantly faced with the need to deal with a variety of quantities, whether it be areas and angles in geometry or speed and mass in physics. And all these quantities can be expressed in completely different units of measurement.
And if almost everyone can say that 1 pood is equal to about 16 kg (although, to be precise, then 16.38 kg), then not everyone can say offhand how many grams in an ounce, karate, or even more so - a drachma.
To make calculations using such values, you will have to go to Google or Wikipedia (and the older generation, perhaps to your home library for a reference book). Then you will need a calculator to convert the required units.
But, there is always an easier way. In our case, this is the Metrix program, which can recalculate almost all basic physical quantities quickly and conveniently. You just need to enter the value that we have in the required field and immediately get its conversion to all other relevant values.
Let's take a closer look at this wonderful (though not perfect) program.
Launching and working with Metrix
Metrix does not require installation, just download the archive and unzip it to a folder convenient for you. Then, open this folder and run the Metrix.exe file. The main window of the program will appear in front of us:
![]()
Everything is simple here. For example, to convert 20 sazhens into meters (let's imagine that you are an archaeologist and you need to accurately measure the distance from an ancient oak tree to an ancient treasure :), then enter the number 20 in the "Sazhen" field and press the "Recalculation" button opposite this number:
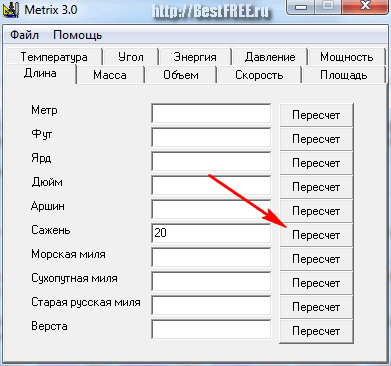
In all other fields, lengths in other units equal to 20 fathoms will appear:
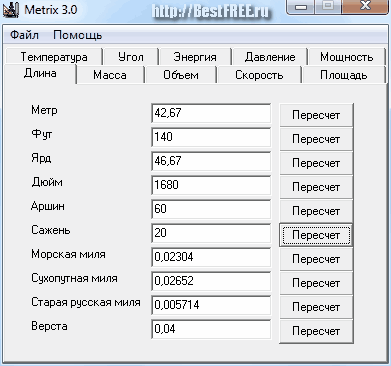
In the same way, the program works with all other quantities.
Program menu
The program has a couple more menu items. They don't offer any special opportunities. In the "File" menu, these are the items "Clear" (to clear all filled fields) and "Exit" (similar to the cross in the upper right corner of the window).
In the "Help" menu, you can try to "Update" the program (you will open the page of the program website, but there have not been new versions there for many years). Or you can see the data "About the program":
That's actually all that can be said about this program. Let's sum it up.
Advantages and disadvantages of Metrix
- extremely easy to use;
- a fairly large stock of various units of measurement;
- portability;
- works on all versions of Windows.
- nevertheless, some units are missing, for example: eV;
- boring interface;
- no new versions are expected.
conclusions
A simple and unpretentious converter of various units of measurement for schoolchildren, students and workers in technical specialties. There are not enough stars from the sky, but it copes with its tasks.
P.S. It is allowed to freely copy and quote this article, provided that an open active link to the source is indicated and the authorship of Ruslan Bogdanov is preserved.
In this lesson we will learn how to convert physical quantities from one unit of measure to another.
Lesson contentConverting length units
From past lessons, we know that the main units of length are:
- millimeters;
- centimeters;
- decimeters;
- meters;
- kilometers.
Any value that characterizes length can be converted from one unit of measure to another.
In addition, when solving problems in physics, it is imperative to comply with the requirements of the international SI system. That is, if the length is given not in meters, but in another unit of measurement, then it must be converted to meters, since the meter is a unit of length in the SI system.
To convert length from one unit of measure to another, you need to know what this or that unit of measure consists of. That is, you need to know that, for example, one centimeter consists of ten millimeters or one kilometer consists of a thousand meters.
Let's use a simple example to show how you can reason when converting length from one unit of measurement to another. Suppose that there are 2 meters and you need to convert them to centimeters.
First you need to find out how many centimeters are in one meter. One meter contains one hundred centimeters:
1 m = 100 cm
If there are 100 centimeters in 1 meter, how many centimeters are there in 2 meters? The answer suggests itself - 200 cm. And these 200 cm are obtained if 2 is multiplied by 100.
So, to convert 2 meters to centimeters, you need to multiply 2 by 100
2 × 100 = 200 cm
Now let's try to convert the same 2 meters into kilometers. First you need to find out how many meters are contained in one kilometer. One kilometer contains a thousand meters:
1 km = 1000 m
If one kilometer contains 1000 meters, then a kilometer that contains only 2 meters will be much smaller. To get it, you need to divide 2 by 1000
2: 1000 = 0.002 km
At first, it can be difficult to remember which action to use to convert units - multiplication or division. Therefore, at first it is convenient to use the following scheme:
The essence of this scheme lies in the fact that when moving from a higher unit of measurement to a lower one, multiplication is applied. Conversely, when moving from a lower unit of measure to a higher one, division is applied.
The arrows pointing up and down indicate that the transition is from a higher unit of measure to a lower one and a transition from a lower unit of measure to a higher one, respectively. At the end of the arrow it is indicated which operation to apply: multiplication or division.
For example, let's convert 3000 meters to kilometers using this scheme.
So we have to go from meters to kilometers. In other words, go from a lower unit of measure to a higher one (a kilometer is older than a meter). We look at the diagram and see that the arrow indicating the transition from lower units to higher ones is directed upwards and at the end of the arrow it is indicated that we must apply division:
Now you need to find out how many meters are contained in one kilometer. There are 1000 meters in one kilometer. And to find out how many kilometers are 3000 such meters, you need to divide 3000 by 1000
3000: 1000 = 3 km
So, when translating 3000 meters into kilometers, we get 3 kilometers.
Let's try to convert the same 3000 meters into decimeters. Here we must move from higher units to lower ones (a decimeter is less than a meter). We look at the diagram and see that the arrow indicating the transition from higher to lower units is directed downwards and at the end of the arrow it is indicated that we must apply multiplication:
Now you need to find out how many decimeters are in one meter. There are 10 decimeters in one meter.
1 m = 10 dm
And to find out how many such decimeters are in three thousand meters, you need to multiply 3000 by 10
3000 × 10 = 30,000 dm
So when converting 3000 meters to decimeters, we get 30,000 decimeters.
Mass conversion
From past lessons, we know that the basic units of mass are:
- milligrams;
- grams;
- kilograms;
- centners;
- tons.
Any value that characterizes mass can be converted from one unit of measurement to another.
In addition, when solving problems in physics, it is imperative to comply with the requirements of the international SI system. That is, if the mass is given not in kilograms, but in another unit of measurement, then it must be converted to kilograms, since the kilogram is the unit of mass in the SI system.
To convert mass from one unit of measurement to another, you need to know what this or that unit of measurement consists of. That is, you need to know that, for example, one kilogram consists of a thousand grams or one centner consists of a hundred kilograms.
Let's use a simple example to show how you can reason when converting mass from one unit of measure to another. Suppose there are 3 kilograms and you need to convert them to grams.
First you need to find out how many grams are contained in one kilogram. One kilogram contains one thousand grams:
1 kg = 1000 g
If there are 1000 grams in 1 kilogram, how many grams will be contained in 3 such kilograms? The answer suggests itself - 3000 grams. And these 3000 grams are obtained by multiplying 3 by 1000. So, to convert 3 kilograms to grams, you need to multiply 3 by 1000
3 × 1000 = 3000 g
Now let's try to convert the same 3 kilograms into tons. First you need to find out how many kilograms are contained in one ton. One ton contains a thousand kilograms:
1 t = 1000 kg
If one ton contains 1000 kilograms, then a ton that contains only 3 kilograms will be much smaller. To get it, you need to divide 3 by 1000
3: 1000 = 0.003 t
As in the case of converting length units, at first it is convenient to use the following scheme:

This scheme will allow you to quickly figure out what action to perform to convert units - multiplication or division.
For example, let's convert 5000 kilograms to tons using this scheme.
So we have to move from kilograms to tons. In other words, move from a lower unit of measure to an older one (a ton is older than a kilogram). We look at the diagram and see that the arrow indicating the transition from lower units to higher ones is directed upwards and at the end of the arrow it is indicated that we must apply division:

Now you need to find out how many kilograms are contained in one ton. One ton contains 1000 kilograms. And to find out how many tons is 5000 kilograms, you need to divide 5000 by 1000
5000: 1000 = 5 t
So, when converting 5000 kilograms into tons, it turns out 5 tons.
Let's try to convert 6 kilograms to grams. In this case, we are moving from a higher unit of measure to a lower one. Therefore, we will use multiplication.
First you need to find out how many grams are contained in one kilogram. One kilogram contains one thousand grams:
1 kg = 1000 g
If there are 1000 grams in 1 kilogram, then there will be six times as many grams in six such kilograms. So 6 must be multiplied by 1000
6 × 1000 = 6000 g
So, when translating 6 kilograms into grams, we get 6000 grams.
Time units conversion
From past lessons, we know that the basic units of time are:
- seconds;
- minutes;
- clock;
- day.
Any value that characterizes time can be converted from one unit of measurement to another.
In addition, when solving problems in physics, it is imperative to comply with the requirements of the international SI system. That is, if time is given not in seconds, but in another unit of measurement, then it must be converted to seconds, since the second is the unit of time in the SI system.
To convert time from one unit of measurement to another, you need to know what this or that unit of time measurement consists of. That is, you need to know that, for example, one hour consists of sixty minutes or one minute consists of sixty seconds, etc.
Let's use a simple example to show how you can reason when converting time from one unit of measurement to another. Suppose you want to convert 2 minutes to seconds.
First you need to find out how many seconds are in one minute. There are sixty seconds in one minute:
1 min = 60 s
If there are 60 seconds in 1 minute, how many seconds are there in 2 such minutes? The answer suggests itself - 120 seconds. And these 120 seconds are obtained by multiplying 2 by 60. So, to convert 2 minutes into seconds, you need to multiply 2 by 60
2 x 60 = 120 s
Now let's try to convert the same 2 minutes into hours. Since we are converting minutes to hours, we first need to find out how many minutes are contained in one hour. There are sixty minutes in one hour:
If one hour contains 60 minutes, then an hour that contains only 2 minutes will be much less. To get it you need 2 minutes divided by 60

Dividing 2 by 60 results in a periodic fraction of 0.0 (3). This fraction can be rounded to the hundredth place. Then we get the answer 0.03
When converting time units, a scheme is also applicable that tells you what to use - multiplication or division:

For example, let's convert 25 minutes to hours using this scheme.
So we have to move from minutes to hours. In other words, move from a lower unit of measurement to a higher one (hours are older than minutes). We look at the diagram and see that the arrow indicating the transition from lower units to higher ones is directed upwards and at the end of the arrow it is indicated that we must apply division:

Now we need to find out how many minutes are contained in one hour. One hour contains 60 minutes. And an hour that contains only 25 minutes will be much less. To find it, you need to divide 25 by 60

Dividing 25 by 60 results in a periodic fraction of 0.41 (6). This fraction can be rounded to the hundredth place. Then we get the answer 0.42
25:60 = 0.42 h
Did you like the lesson?
Join our new Vkontakte group and start receiving notifications of new lessons
- Length: kilometer, meter, decimeter, centimeter, millimeter, micrometer, mile, nautical mile, league, cable, fathom, furlong, rod, yard, foot, inch, verst, chain, pole, fathom, arshin, foot (old Russian .), vershok, line, point.
- Area: sq. kilometer, sq. meter, sq. decimetre, sq. centimeter, sq. millimeter, sq. micrometer sq. mile, acre, hectare, ar (weave), sq. genus, sq. yard, sq. ft. sq. inch.
- Volume: cube kilometer, cu. meter, cubic decimeter, cubic centimeter, cube millimeter, cube micrometer, cu. mile, liter, quart (UK), quart (US liquid), cu. genus, cub. yard, cube ft, cu. inch, pint (UK), pint (US liquid), gallon (UK), gallon (US liquid), barrel of oil, barrel (US liquid), beer barrel, fluid ounce, barrel, bucket , mug, pound of water, vodka bottle, wine bottle, cup, scale, tablespoon, teaspoon.
- Weight: metric ton, English ton (long ton), American ton (short ton), centner, kilogram, pound, ounce, gram, carat, Berkovets, pood, half pood, steelyard, ansyr, pound, large hryvnia (hryvnia), libra, small hryvnia (hryvnia), lot, spool, share, troy pound, troy ounce, troy gran.
- Temperature: Fagenheit temperature, Celsius temperature, Réaumur temperature, absolute temperature.
- Speed: kilometers per hour, kilometers per minute, kilometers per second, miles per hour, miles per minute, miles per second, knots (nautical miles per hour), meters per hour, meters per minute, meters per second, feet per hour, feet per minute, feet per second, speed of light in vacuum, speed of sound in pure water, speed of sound in air (at 20°C).
- Pressure: pascal, bar, technical atmosphere (at), physical atmosphere (atm), millimeter of mercury, meter of water, pounds-force per sq. inch, kilogram force per sq. meter.
- Consumption: m3/s, m3/min, m3/h, l/s, l/min, l/h, US gal/day, US gal/h, US gal/min, US gal/s, imp. gallons/day, imp. gal/h, imp. gal/min, imp. gal/s, cu. ft/min, cu. ft/s, bbl/h, pounds of water/min, tons of water (meter)/day.
- Strength, weight: newton, dyne, kilogram-force, kilopond, gram-force, pond, ton-force.
- Power: watt, kilowatt, megawatt, kilogram-force-meter per second, erg per second, horsepower (metric), horsepower (English).
- Number of information: bit, byte (B), Kibibyte (KiB), Mebibyte (MiB), Gibibyte (GiB), Tebibyte (TiB).
- Time: millennium, century, decade, five-year plan, year, half year, quarter, month, decade, week, day, hour, minute, second, millisecond, microsecond, nanosecond.
- Caloric content of products: kcal based on the weight of the product indicated in grams.
Please use a dot and not a comma to separate tenths!
The converter of units of measurement of physical quantities allows you to convert most of the main units of measurement of physical quantities into each other. To convert, first select the value you would like to convert. Then select the original unit of measure and the unit of measure to which you want to convert. Now, if you enter the value of the unit of measure, its value in the required unit of measure will automatically appear in the "Result" field.
Converter Features
Converter of units of measurement of physical quantities allows you to convert units of measurement of the following physical quantities into each other: length, mass, temperature, volume, area, speed, time, pressure, energy and work, angular measures.
Units
Length: millimeter, centimeter, decimeter, meter, kilometer, foot, inch, league, nautical mile, microinch, mile, yard.
Weight: microgram, milligram, centigram, decigram, gram, decagram, hectogram, kilogram, centner, ton, pound, ounce, drachma, grain, centner (England), centner (US), ton (England), ton (US).
Temperature: Celsius (ºC), Fahrenheit (ºF), Rankine (ºRa), Réaumur, Kelvin.
Volume: cubic micrometer, cubic millimeter, cubic centimeter, cubic decimeter, cubic meter, cubic decameter, cubic kilometer, microliter, milliliter, centiliter, decaliter, hectoliter, liter, kiloliter, megaliter, acrofoot, acrofoot (US), barrel (England), barrel (US dry), barrel (US liquid), barrel (US oil), board fct, bucket (England), bucket (US), bushel (England), bushel (US dry), cord (firewood), cord foot (timber) ), cubic cubit (Egypt), cubic foot, cubic inch, cubic mile, cubic yard, drachma, quint, gallon (England), gallon (US dry), gallon (US liquid), hogshead (England), hogshead (US) , ounce (England liquid), ounce (US liquid), pint (England), pint (US dry), pint (US liquid), quart (England), quart (US dry), quart (US liquid), cubic yard.
Area: square millimeter (mm2, mm2), square centimeter (cm2, cm2), square meter (m2, m2), square kilometer (km2, km2), hectare (ha), decare, ar (weave, a, league), barn ( b, b), township, square mile, homestead, acre, rood, square rod, square yard (yd2), square foot (ft2), square inch (in2), square verst, square arshin.
Speed: kilometers per second (km/s, km/s), meters per second (m/s, m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), meters per minute, miles per second, miles per hour (mph), foot per second, foot per minute, knot, nautical mile per hour, speed of light in a vacuum.
Time: century, year, month, week, day, hour, minute, second.
Pressure: bar, kilopascal (kPa, kPa), hectopascal (hPa, hPa), megapascal (mPa, mPa), millibar, pascal (Pa, Pa), kilogram force per square meter (kgf/m2), newton per square meter (n/ m2), pounds per square inch (psi), pounds per square foot, inch of mercury, millimeter of mercury, centimeter of mercury, physical atmosphere (atm, atm), technical atmosphere (at).
Energy, work: megajoule (mJ, mJ), kilojoule (kJ, kJ), joule (J, J), kilocalorie (kcal), calorie (cal), kilowatt/hour (kW*h, kWh), watt/hour (W* h, W * h), electron volt (eV), kilogram of TNT.
Angle measure: circle (circle), sextant, radian (rad), degree (deg), hail (grad), minute ("), second ("), rhumb.
