Types of cables for wiring. Electrical cable and wire: differences, types, applications
Find out the main types of cables and wires used for installation in a private house or apartment. When buying, installing, operating and repairing, careful information about them is necessary.
Purpose
It is used for transmission and distribution of electric current, operating voltage - 660-1000 V, frequency - 50 Hz.
The number of cores can vary from 1 to 5. The cross section is from 1.5 to 240 mm2. In domestic conditions, a cable with a cross section of 1.5-6 mm2 is used, in the construction of a private house - a cable with a cross section of up to 16 mm2. The cores can be either single or multi-wire. There are no restrictions - you can also put a cable with a cross section of 10 mm2 in the apartment.
Power cables
Among the most popular types of cable products in recent times are cables. VVG and its modifications.
VVG denoted power cable with insulation TPG from PVC, shell (cambric) of PVC, copper core material, not having external protection.
VVG it is used in a wide temperature range: from -50 to + 50 "C. Withstands humidity up to 98% at temperatures up to +40 °C. The cable is strong enough to break and bend, resistant to aggressive chemicals. When installing, remember that each cable or wire has a certain bending radius. This means that for a 90 °C rotation in the case of VVG the bending radius must be at least 10 cable diameters. In the case of a flat cable or wire, the width of the plane is considered.
The outer shell is usually black, although white can sometimes be found. Does not spread fire. Insulation TPG marked in different colors: blue, yellow-green, brown, white with a blue stripe, red and black. The cable is packaged in coils of 100 and 200 m. Sometimes there are other sizes.
Sectional VVG cable
Varieties VVG:AVVG- the same characteristics, only aluminum is used instead of a copper core. Conductor, insulation made of PVC-plastic compound, sheath made of PVC- plastic compound.
VVGng - cambric with increased incombustibility
VVGp- the most common variety, the cable section is not round, but flat.
VVGz- space between insulation TPG and cambric filled with bundles of PVC or rubber compound.
NYM does not have a Russian decoding of the letter designation. This is an insulated copper power cable. TPG PVC, outer shell made of non-combustible PVC. Between the insulation layers there is a filler in the form of coated rubber, which gives the cable increased strength and heat resistance. Stranded conductors, always copper.
NYM cable
1 - copper core; 2 - PVC sheath; 3 - longitudinal non-combustible sealing; 4- PVC insulation
The number of cores is from 2 to 5, the cross section is from 1.5 to 16 mm2. Designed for lighting and power networks with a voltage of 660 V. It has high moisture and heat resistance. Can be used for laying outdoors. Operating temperature range - from -40 to +70 "C.
Disadvantage: does not withstand sunlight well, so the cable must be covered. Compared with VVG of any kind is more resistant and easy to use. However, it happens only with a round section (it is inconvenient to lay it in plaster or concrete) and is much more expensive VVG. Bending radius - 4 diameters of the cable section.
wires
The most popular wire brands PBPP (PUNP) And PBPPg (PUGNP). Pronounce letter combination PBPPg difficult, so it is often called PUNP or PUGNP.
PBPP (PUNP) refers to the installation, or assembly. Flat wire, with copper single-wire conductors, covered with insulation made of PVC, the outer shell is also from PVC.
The number of cores is 2 or 3, the cross section is from 1.5 to 6 mm2. It is used when laying stationary lighting systems, as well as for mounting sockets, although it is preferable to use it specifically for lighting. Rated voltage - up to 250 V, frequency - 50 Hz. Temperature range of operation - from -15 to +50 "C. Bending radius - not less than 10 diameters.
PBPPg (PUGNP) differs from PUNP veins - they are multi-wire. That is why the letter "g" is added to the name of the wire - flexible.
All other characteristics correspond PUNP, only the minimum bending radius is 6. A distinctive property is flexibility, therefore PUGNP lay in places where the wiring makes frequent bends, or to connect to the network of household appliances. Wires of these brands are sold in coils of 100 and 200 m. The color is usually white, black is less common.
To variety PUNP applies wire with aluminum conductors APUFP. It has exactly the same characteristics as PUNP, adjusted for the core material. The only difference is APUFP cannot be multiwire, and therefore flexible.
Note
General wire brands PUNP, PUGNP and APUNP perfectly proved to be exactly as household wires. In half the cases, the master has to deal with them. However, it should be remembered that these brands of wires are highly specialized, and you should not use them instead of power cables (such as NYM or VVG).
Attention!
The popularity of wires PUNP And PUGNP based primarily on price. However, there is a catch in this. The fact is that recently a discrepancy has been noticed between the declared wire cross-section and the actual one. After checking, it turned out that the wire marked PUGNP 3 × 1.5, in fact 3 x 1 - that is, the actual cross section of the core is smaller. The same applies to isolation. When buying wires of this brand, it is necessary to measure the cross section of the cores and the thickness of the insulation.
400 Hz. The wire is resistant to aggressive chemical environments, non-flammable, has a wide temperature range of operation - from -50 to +70 "C. Moisture resistance - 100% at a temperature of +35 "C. The bending radius during laying is at least 10 diameters of the wire section. Resistant to mechanical damage and vibration.
APPV has the same characteristics as PPV, except for the core material - it is aluminum.
AR- aluminum single-core wire with insulation made of PVC. The wire is round, single-wire with a cross section of 2.5 to 16 mm2 and stranded - from 25 to 95 mm2.
The wire is used in almost all types of installation of stationary lighting and power systems. It is laid in voids, pipes, steel and plastic trays. Widely used in the installation of switchboards. Chemically resistant, operating temperature - from -50 to +70 "C. Moisture resistance - 100% at a temperature of +35 "C. Bending radius - not less than 10 diameters. Resistant to mechanical damage and vibration.
Appearance and characteristics PV 1 coincide with everything AR, except for the core material: instead of aluminum - copper. The core cross section starts from 0.75 mm2.
In addition, the core becomes multi-wire not from 25, but from 16 mm2. More flexible than AR.
Wire specifications PV 3 match the properties AR And PV 1. Scope - installation of sections of lighting and power circuits where frequent bending of wires is necessary: in switchboards, when installing a large number of electrical devices.
It is also used for laying electrical circuits in cars. Bending radius - not less than 6 wire diameters.
Note
Wire marks AR, MF 1 and MF 3 They have a wide variety of insulation colors, so they are very convenient to use for mounting various types of switchboards.
PVA- stranded copper wire with PVC insulation and sheath. The sheath penetrates into the space between the cores, giving the wire a round shape and density.
The core is multi-wire, their total number ranges from 2 to 5, the cross section is from 0.75 to 16 mm2. Rated voltage - up to 380 V, frequency - 50 Hz. The core insulation is color-coded, the sheath is white.
The wire is used when connecting various electrical devices, from household appliances to garden tools. Due to its flexibility and lightness, it is also used for lighting and even mounting sockets. PVA is a household wire used for the manufacture of extension cords, cords for any kind of equipment and repair of electrical networks. It is non-combustible (does not spread combustion with a single gasket), heat-resistant: temperature range - from -40 to +40 ° C (PVA U option) and from -25 to +40 "C. Due to its design, it is resistant to bending and mechanical wear. PVA can withstand at least 3000 kinks.
SHVVP- copper or copper-tinned flat wire. Core insulation and PVC sheath
Lived multi-wire, increased flexibility. The number of cores is 2 or 3, the cross section is from 0.5 to 0.75 mm2. Voltage - up to 380 V, frequency - 50 Hz. It is used as a cord for connecting lighting fixtures and household appliances of low power, such as soldering irons, mixers, coffee grinders and radio-electronic devices.
Note
SHVVP- the wire is exclusively for domestic use, it is not used for wiring lighting or sockets.
Cables for information transmission
In addition to electricity, cables transmit information signals. Recently, many new types of information conductors have appeared. If 10-15 years ago there were only telephone and antenna cables, now, with the development of computer technology, there are much more types of information conductors. Most of them are too specialized and are of interest only to narrowly specialized specialists. For a home master, it is enough to know and be able to use only a few types. We will consider them.
Antenna cables
Today, the most commonly used RG-6, RG-59, RG-58 or Russian analogues of the series RK 75.
RG-6- a coaxial cable for the transmission of high-frequency signals for electronic equipment, television or radio.
Consisting of a central 1 mm2 copper core, surrounding foamed polyethylene insulation, aluminum foil shield, tinned copper braid outer conductor and sheath PVC. Widely used to transmit cable and satellite TV signals. It has many technical characteristics regarding the frequency of the transmitting signal, resistance, shielding, etc. For example, the designation in the cable name RK 75 means that the resistance of the conductor is 75 ohms.
This cable is ideal for transmitting a video signal from an antenna or camcorder to a receiver (TV) and distributing the video signal to multiple sources.
Each conductor is insulated PVC or propylene. The outer shell is also PVC. The cable can be optionally equipped with a moisture-proof polypropylene sheath. There is a breaking thread in the twisted pair design. With its help, the outer sheath is easily removed from the cable, opening access to the conductive cores.
RG cables have many varieties and differ from each other in some characteristics, such as conductor resistance, resistance to temperature and shock loads, signal attenuation time, screen type, etc.
Computer cables (twisted pair)
Used to build computer networks. The cable with which computers connect to the Internet or to each other is just a twisted pair cable (Fig. 4.44 and 4.45). Consists of one or more pairs of wires intertwined in pairs, which is done in order to improve.
Twisted pair cable with a connector for connecting to a computer, protected by a PVC sheath
Depending on the type of cable, various protection options are possible: UTP, or unprotected, without a common shield for pairs of wires.
Coaxial cable with ferrule
FTP, or foil, with an aluminum foil screen; STP, or protected, with an overall copper mesh shield, in addition, each twisted pair is surrounded by a separate shield.
Tip RJ-45 to connect to a computer S/FTP, or foil, shielded with a common foil shield, in addition, each pair is additionally enclosed in a shield. In addition, twisted pairs are categorized according to the number of pairs combined in one cable. The most common type used for computer networks is the category CAT5e. It consists of 4 pairs of wires of different colors. Data transfer rate - up to 1 Gb / s when using all pairs.
You can see such a cable used as a category telephone wire. CAT1 or CAT2, that is, consisting of 1 or 2 pairs of wires.
Telephone cables and wires
TPPep: 1 - vein; 2- polyethylene insulation; 3 - core; 4 - fastening winding; 5 - belt insulation; 6-screen
Telephone conductors are divided into 2 main types. The former are intended for laying several (up to 400) subscriber lines. The second type is used for wiring in a single apartment or house.
TPPep- the main type of cable for laying a line designed for a large number of subscribers.
The cable consists of two wires twisted in pairs. TPG made of soft copper wire, cross section 0.4 or 0.5 mm2, covered with polyethylene insulation. In some types of cable, the pairs are grouped into groups of 5 or 10 pairs. The outer shell is also polyethylene or vinyl. The letters "e" and "and" in the name indicate a film screen. There are varieties of cable armored with tapes, or filled, in which the space between the sheath and the cores is occupied by a hydrophobic sealant.
In a word, this is a cable for conducting telephone communications in an apartment building, it is intended for laying in almost all conditions: underground, in cable channels or by air.
To conduct a telephone line to an individual subscriber and wiring indoors, the following two types of telephone wires are used.
TRV - one- or two-pair telephone distribution wire.
This is a flat wire with a divided base, a copper core, single-wire, with a cross section of 0.4 or 0.5 mm2. Number of cores - 2 or 4. Insulation made of PVC. Designed for conducting telephone lines indoors.
It is operated at temperatures from -10 to +40 °C. Humidity should not exceed 80% at a temperature of +30 °C.
TRP- according to the characteristics coincides with TRV. The only difference is the isolation TRP it is made of polyethylene.
Possessing increased resistance to the influence of the external environment. These places include baths, stoves and cellars. In general, wherever it is too hot, humid or cold, and besides, there is a possibility of mechanical damage. It is clear that PVA or VVG in such places it is impossible to install, not to mention PUNP or SHVVP.
RKGM - power mounting single-core wire of increased heat resistance, flexible.
Copper conductor, multi-wire, section from 0.75 to 120 mm2. Silicone rubber insulation, fiberglass sheath impregnated with heat-resistant enamel or varnish.
This wire is designed for rated voltage up to 660 V and frequency up to 400 Hz. Resistant to vibration, high humidity (up to 100% at a temperature of +35 °C), heat-resistant (operating temperature range from 60 to +180 °C). In addition, the wire is protected from the harmful effects of varnishes, solvents and fungal mold. An ideal conductor for rooms with high temperatures (boiler rooms and stoves), suitable for electrical installation in baths, saunas, oven connections.
PNSV - heating single-core wire. TPZh single-wire steel, blued or galvanized steel.
Core cross section - 1.2; 1.4; 2 and 3 mm2. PVC or polyethylene insulation. Rated voltage up to 380 V, frequency 50 Hz. The wire is heat-resistant: operating temperature range - from -50 to +80 °С, resistant to alkalis and moisture resistant (tolerates immersion in water). It is used as a heating element: in domestic conditions, with the help of PNSV, warm floors are mounted.
Runway - single-core copper wire.
The core is multi-wire, enclosed in polyethylene insulation, the sheath is also made of polyethylene or PVC.
The cross section of the core is from 1.2 to 25 mm2. Rated voltage - 380 or 660 V, frequency 50 Hz. The wire is resistant to pressure changes. Operating temperature range - from -40 to +80 °С. It is used for engines of artesian wells immersed in water under high pressure conditions.
LED cable
LED cable is a very interesting power option. Additional wires with LEDs of different colors connected in series are placed under the transparent outer shell along the power TPGs. They are located at a distance of 2 cm from each other, they burn with a constant sufficiently strong light.
Such a cable performs not only decorative functions, although it can be used to create entire light patterns. In addition to aesthetic purposes, it is very convenient for attaching to portable electrical mechanisms. Most often, the LED cable is used to connect stage equipment.
It is useful in that when it breaks, it is not necessary to look for the place of damage: the diodes in this area will stop glowing. In addition to power conductors, there are computer luminous cables.
With the help of such conductors, you can create very interesting design solutions.
Electroluminescent cable
In addition to LED cables, there are electroluminescent ones. They glow evenly along the entire length. With the help of such cables, you can create luminous inscriptions and even whole paintings.
It's a great alternative to the flexible neon tubes that these kind of designer jewelry is usually made from. In addition, the electroluminescent cable is cheaper than neon tubes and is not limited in length.
It is used for conducting lines indoors and in telephone sets. Highly flexible wire.
PRDP- a flat wire with a separating base and single-wire copper conductors with polyethylene insulation and sheath. There is a modification FRP, the shell of which is made of PVC.
Special types of cables and wires
For the installation of electrical systems in places where the conditions are very different from the usual, special cables are used.
Compared with TRV the wire is more resistant to the external environment and can be laid outside buildings.
STLP- telephone flat cord with copper stranded conductors.
Polyethylene core insulation. Isolated TPG sheathed in PVC. The number of cores is 2 or 4, the cross section is from 0.08 to 0.12 mm2.
The cables used to build the infrastructure of computer networks are produced in a wide range of varieties. Among the most popular are coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic. What is the specificity of each of them? What are the features of the installation of the most common - twisted pair?
Cable types: coaxial
Among the earliest historical types of cable used in network connections is coaxial. In terms of thickness, it roughly corresponds to a power supply for a computer, designed to work with a 220 V outlet.
The structure of the coaxial structure is as follows: in the very middle there is a metal conductor, it is shrouded in thick, most often plastic insulation. On top of it - a braid of copper or aluminum. The outer layer is an insulating sheath.
The connection of the network cable of the type in question can be carried out by:
BNC connector;
BNC terminator;
BNC-T connector;
BNC barrel connector.
Let's consider their specifics in more detail.
The BNC connector is intended to be placed at the ends of the cable, used to connect with T- or barrel connectors. The BNC terminator is used as an isolating barrier that prevents the signal from traveling along the cable. The correct functioning of the network without this element in some cases is not feasible. coaxial cable involves the use of two terminators, one of which requires grounding. The BNC-T connector is used to connect the PC to the main backbone. It has three slots in its structure. The first is connected to the computer connector, with the help of the other two, different ends of the trunk are connected. Another type of coaxial cable connector is the BNC barrel. It is used to connect different ends of the backbone, or to increase the radius of a computer network.
Among the useful features of coaxial designs is that there are no problems with deciding how to connect two network cables of this type. It is enough to ensure reliable contact of the conductive cores, of course, subject to the technology of pairing the insulation and the screen grid. However, coaxial cable is quite sensitive to electromagnetic interference. Therefore, in the practice of building computer networks, it is now rarely used. However, it is indispensable in terms of organizing the infrastructure for transmitting television signals - from dishes or cable providers.
twisted pair
Probably the most common computer network cables today are called "twisted pair". Why exactly this name? The fact is that in the structure of this type of cable there are paired conductors. They are made from copper. The standard cable of the type in question includes 8 cores (in total, therefore, 4 pairs), but there are also samples with four conductors. The so-called pinout of a network cable of this type (correlation of each core with a particular function) involves the use of insulation of a certain color on each conductor.

The outer insulation of the twisted pair is made of PVC, which provides sufficient protection of the conductive elements from electromagnetic interference. There is a considered type - FTP and STP. In the first, the foil performing the corresponding function is located on top of all the cores, in the second - on each of the conductors. There is an unshielded modification of twisted pair - UTP. As a rule, foil cables are more expensive. But it makes sense to use them only if there is a need for high-quality data transmission over a relatively long distance. For home networks, an unshielded version of twisted pair is quite suitable.
There are several classes of the corresponding type of structures, each of them is designated as CAT with a number from 1 to 7. The higher the corresponding indicator, the better the materials that provide signal transmission. Modern network cables for a computer to communicate via the Ethernet protocol in home networks assume that the elements comply with the CAT5 class. In connections where twisted pair is used, connectors are used that will correctly be classified as 8P8C, but there is also an unofficial name for them - RJ-45. It can be noted that cables that correspond to at least CAT5 and CAT6 classes can transmit data at speeds close to the maximum for the type of structure under consideration - up to 1 Gbps.
Optical fiber
Perhaps the most modern and fastest network cables for a computer are fiber optic. In their structure there are light-conducting elements made of glass, which are protected by durable plastic insulation. Among the key advantages that these network cables for a computer have is high immunity to interference. It is also possible to transmit data via optical fiber over a distance of about 100 km. The connection of cables of this type with devices can be carried out using various types of connectors. Among the most common are SC, FC, F-3000.
What does this high-tech network cable for a computer look like? A photo of the fiber optic construction is below.

The intensity of the practical use of optical fiber is limited by the rather high cost of the equipment required to transmit data through it. However, recently many Russian providers are actively using this network cable for the Internet. According to IT experts, with the expectation that the corresponding investments will pay off in the future.
The evolution of cable infrastructure
On the example of the three types of cables noted, we can trace some evolution in terms of building the infrastructure of computer networks. So, initially, when transmitting data via the Ethernet standard, it was coaxial structures that were involved. At the same time, the maximum distance at which a signal could be sent from one device to another did not exceed 500 meters. The maximum over a coaxial cable was about 10 Mbps. The use of twisted pair made it possible to significantly increase the dynamics of file exchange in computer networks - up to 1 Gbit / s. It also became possible to transmit data in duplex mode (one device could both receive signals and send them). With the advent of fiber optics, the IT industry has been able to transfer files at speeds of 30-40 Gbps or more. Largely due to this technology, computer networks successfully connect countries and continents.

Of course, when working with a PC, many other types of cables used in the installation of computer networks are used. Theoretically, for such purposes, you can use, for example, a USB cable, although this will not be very effective, in particular, due to the fact that, within the USB standard, data can be transmitted over a short distance - about 20 m.
How to connect twisted pair
Twisted pair, as we noted above, is today the most common type of cable in the design of computer networks. However, its practical use is characterized by some nuances. In particular, they reflect such an aspect as the pinout of the network cable, which we mentioned above. It is important to know how to properly position the cores in the area where they come into contact with the RJ-45 connector. The procedure by which the twisted pair is connected to the corresponding element is called crimping, since during its implementation a special tool is used that involves a force effect on the structure.
The nuances of crimping
During this procedure, the connectors are securely fixed at the ends of the twisted pair. The number of contacts in them corresponds to the number of cores - in both cases there are 8 such elements. There are several schemes within which twisted pair crimping can be carried out.
Next, we will look at the relevant specifics. But first, the person who works with the cable needs to properly pick up the connectors. They should be held so that the metal contacts are on top.

The plastic latch should point towards the crimper. On the left in this case there will be the 1st contact, on the right - the 8th. Numbering is an extremely important nuance of working with twisted pair. So, what crimping schemes are used by network infrastructure specialists?
First, there is a network cable diagram called EIA/TIA-568A. It assumes the location of the cores in relation to the metal contacts of the connector in the following order:
For 1 contact: white-green;
For the 2nd: green;
For the 3rd: white-orange;
For the 4th: blue;
For the 5th: white and blue;
For the 6th: orange;
For the 7th: white-brown;
For the 8th: brown.

There is another scheme - EIA / TIA-568B. It assumes the location of the veins in the following order:
For 1 contact: white-orange;
For the 2nd: orange;
For the 3rd: white-green;
For the 4th: blue;
For the 5th: white and blue;
For the 6th: green;
For the 7th: white-brown;
For the 8th: brown.

How to connect a network cable to a connector, you now know. But it is useful to study the specifics regarding the various schemes for connecting a twisted pair to certain devices.
Crimp and connection type
So, when connecting a PC to a router or switch, use the direct connection method. If there is a need to organize the exchange of files between two computers without using a router, then you can use the cross connection method. The difference between the marked schemes is small. With a direct connection method, the cable must be crimped according to the same pinout. When crossed, one end is according to the 568A scheme, the other is according to 568B.
High tech economy
Twisted pair is characterized by one interesting feature. With a direct connection scheme, the device can be used not 4 pairs of conductors, but 2. That is, using one cable, it is permissible to connect 2 computers to the network at the same time. Thus, you can save on cable or make a connection if it really needs to be done, but there are no extra meters of twisted pair at hand. True, in this case, the maximum data exchange rate will not be 1 Gb / s, but 10 times less. But for organizing homework in most situations, it is acceptable.
How to distribute the veins in this case? In relation to the contacts on the connectors for connection:
1 contact: white-orange core;
2nd: orange;
3rd: white-green;
6th: green.
That is, 4, 5, 7 and 8 cores are not used in this scheme. In turn, on the connectors for connecting a second computer:
1 contact: white-brown core;
2nd: brown;
3rd: white-blue;
6th: blue.
It can be noted that when implementing a cross connection scheme, it is always necessary to use all 8 conductors in a twisted pair. Also, if the user needs to implement data transfer between devices at a speed of 1 Gb / s, the pinout will need to be done according to a special scheme. Let's consider its features.
Cross connection at gigabit speed
The first cable connector should be crimped according to diagram 568B. The second assumes the following comparison of cores and contacts on the connector:
1 contact: white-green core;
2nd: green;
3rd: white-orange;
4th: white-brown;
5th: brown;
6th: orange;
7th: blue;
8th: white and blue.
The circuit is quite similar to the 568A, but the position of the blue and brown pairs of conductors has been changed.
Compliance with the marked rules for correlating the color of cores and contacts on the 8P8C connector is the most important factor in ensuring the functionality of the network infrastructure. The person designing it must be careful when installing the appropriate elements. It happens that the computer does not see the network cable - this is often due to incorrect crimping of the twisted pair.
How to crimp the cable

Let's look at some technical details. The main device that is involved in this case is a crimper. It looks like pliers, but it is adapted to work with the appropriate type of computer cables.
The design of the crimper requires the presence of special knives designed to cut the structure. Also, sometimes crimpers are equipped with a small device for stripping twisted pair insulation. In the central part of the tool there are special sockets adapted to the thickness of the cable structure.
The optimal algorithm for the actions of a person who compresses a twisted pair cable can be as follows.
- First of all, it is necessary to cut a section of cable of suitable length - thus, its exact measurements will be required.
- After that, the outer insulation should be removed - approximately in a section of 3 cm at the end of the cable. The main thing at the same time is not to accidentally damage the insulation of the cores.
- Then you need to arrange the conductors in relation to the above connection diagrams to the connector. Then evenly trim the ends of the strands so that the length of each of them outside the outer layer of insulation is about 12 mm.
- Next, you need to put the connector on the cable so that the cores remain in the order that corresponds to the connection diagram, and each of them enters the desired channel. You should move the wires until you feel the resistance of the plastic wall of the connector.
- After proper placement of the cores inside the connector, the PVC sheath must be positioned inside the connector housing. If this does not work out, you may need to pull out the cores and shorten them a little.
As soon as all structural elements are located correctly, you can crimp the cable by inserting the connector into a special socket on the crimper and gently pressing the tool handle until it stops.
Large apartment repairs necessarily include the replacement of electrical wiring. There are two main reasons for this action.
The first is the age of this very wiring. As a rule, overhaul or any major repairs are carried out in 15-20 years after the delivery of the apartment. During this time, even a properly made home electrical network ages and wears out. So, it potentially becomes a source of danger for the inhabitants of housing.
The second reason is the redevelopment and extensive renovation of individual premises with the addition of new electrical appliances. Inserts and other connections of new wiring with the old one are highly undesirable. Due to a mismatch in the characteristics of the cable or the materials in it.
So, the question - whether to change the wiring, is considered resolved, it remains to deal with its practical implementation. And you need to start with the choice of cable.
Cable for electrical wiring in the apartment - 300 brands and 5000 varieties
Which side to start from? A person who is far from electrical installation will grab his head. And there is something to grab. Because there are not just a lot of cables and wires, they literally cannot be counted, like Donov Pedro in Brazil. Even professional electricians sometimes "drown" and get confused in the abundance of manufacturers and products.
The choice of wire for electrical wiring in an apartment is not only a matter of the cost of repairs. Much more important is the point that the wiring should ensure the “delivery” of electricity to any corner of the apartment and be safe, that is, not “bite” with current. And also be fire resistant and reliable.
Attention! The key to reliable electrical wiring is finding the right electrician. A specially trained master should deal with electricians and choose a cable for wiring in an apartment! Who has a permit for electrical work and practical experience.
We will briefly talk about cables and wires, their cross-section, marking, materials and types. We will explain what is suitable for home wiring and what cannot be used. So that you are aware of what your electrician is doing and why.
Characteristics of wires and cables to pay attention to when choosing
We will immediately stipulate that we are talking about a household power cable or wire with a voltage of 220/380 V for transmitting electric current in a home network. We do not consider all other types like heating, television, computer and others now.
The general list of characteristics looks like this:
- core material;
- design;
- section;
- thickness of core insulation;
- shell thickness;
- marking;
- lived coloring;
- package;
- certificate;
- product condition.
1. Material and design
According to the composition of the vein, cable products are divided into copper and aluminum. Copper products are more reliable, resistance is lower, current indicators are higher, heating is less when compared with aluminum of equal cross section. In addition, copper oxidizes less, is more ductile, which means that the cable lasts longer without loss of properties and characteristics.
Attention! It is forbidden to do wiring in an apartment with an aluminum cable in accordance with the requirements of the PUE (rules for electrical installations).
By design single-core (single-wire) and multi-core (multi-wire) cables and wires are produced. Single-core varieties are more rigid and inflexible, especially with a large conductor cross section.
Answering the question “which wire to use for wiring under plaster”, we can say that theoretically a single-core single-wire copper cable is also suitable. Plaster will create additional protection for such a conductor. But in fact, no one is laying a home electrical network with a single-wire wire.
Stranded single-core cable is softer and more ductile. It tolerates kinks and turns well and is suitable for both open wiring and hidden under plaster. It is the three-core single-wire that is now used for laying in apartments.
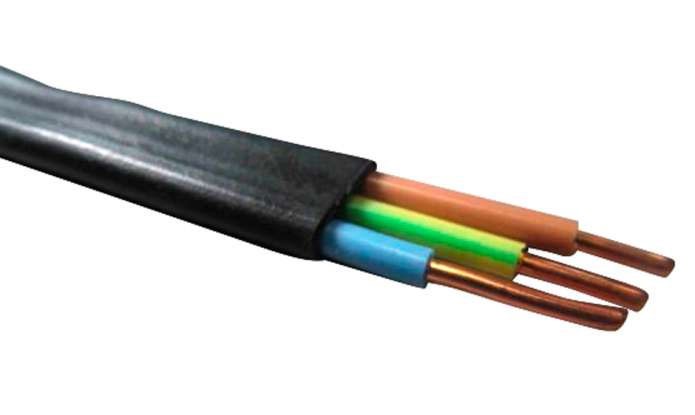
Attention! Do not confuse cables where each strand consists of a single conductor with wires where the strand is made of several conductors. Multi-wire cable products are prohibited for fixed laying in an apartment due to a high fire hazard. More about them in the block"what wires can not be used for electrical wiring in the apartment"

2. Cable cross section for wiring in the apartment
It is measured in "squares", that is, square millimeters and shows the throughput. For a copper cable, one “square” passes 8-10 Amperes of current, for an aluminum cable only 5 A. For safe operation, the conductor should be selected with a margin of bandwidth, which ensures that the wire is heated within the permissible value, or, more simply, so that the load does not “float” insulation. In addition, with hidden wiring, it must be borne in mind that it is less cooled, which means that the section margin should compensate for this.
Attention! Do not confuse the cross section of the cable with its diameter, these are two big differences! The diameter can be measured with a ruler, or better with a caliper. And then substitute it into the formula and calculate the cross-sectional area.

Also remember that the choice of cable for wiring in the apartment always comes with rounding up. If the calculation results in 2.3 "squares", a cable of two and a half is selected, and not two "squares".
Ideally, the cross section should match the marking on the cable tag, but in fact it often differs downwards. Small discrepancies are acceptable because the cable is certified by resistance, not core cross-section. If the differences are significant, it is a marriage. An experienced electrician will see it visually, and you can measure the diameter of the core and calculate the cross section for interest or help a friend who decides to buy a cable for residential wiring on his own.
Some electricians advise taking a cable with a rating higher than the calculated one. For example, 4 "squares", instead of 2.5, to cover the "lack" of the section, if any. But, then you will have to calculate the protection of the wiring accordingly and install the correct machines and RCDs.
Advice! We recommend for electrical wiring in the apartment the cross section of copper wires from 1.5 to 2.5 square meters. mm. Let two and a half "squares" into sockets and one and a half - for lighting.
3. Thickness of core insulation
Each core in a multi-core or single-core cable is insulated with conventional or low-flammability PVC compound, polymers and cross-linked polyethylene are also used. The thickness of the insulation is regulated by GOSTs and it should be sufficient. For household cables (rated voltage up to 660V) with a cross section of 1.5 and 2.5 mm 2, the thickness of the insulating layer according to the standard is 0.6 mm. Deviation is allowed, but the insulation should not be thinner than 0.44 mm.
Simply put, there is a gap in thickness where the insulation must “fit in” so that the wiring serves reliably and there are no problems during installation. Whether the manufacturer violated the technology - you can’t determine without a micrometer if you don’t fiddle with cables every day. Therefore, if there is no experienced electrician nearby, you need to buy only in trusted stores and cables of famous brands.
4. Shell thickness
The sheath covers the cable over the insulated cores, fixes them and protects them. It is made, like the core insulation, of PVC compound or polymer, but has a greater thickness. For multi-core cables, the thickness is 1.8 mm, for single-core cables - 1.4 mm. Smaller deviations are also possible, but insignificant.
The insulating shell is a mandatory element. For any residential wiring cable, even with a minimum power, double insulation is “registered”. That is, first on the core, and then on top of it. This ensures the safety of people and protects the conductor itself from damage.
5. Marking
This is an inscription on the cable sheath for wiring in an apartment. It contains all the information you need to make a selection. The inscription is printed or squeezed out during the manufacture of cable products. It should be clear, contrasting, well readable.
The labeling states:
- The brand of the product (cable or wire), in which the main properties and characteristics are encrypted.
- Manufacturer's name.
- Year of issue.
- The number of lived
- Section.
- Voltage rating.
The inscription is applied along the entire length of the conductor at small intervals.
On the price tag and in the catalogs of online stores, they usually do not indicate the year of issue and the manufacturer and write the marking in the form VVGng(ozh)-0.66 kV 3x1.5 or VVG, VVGng cable 3x1.5.
Deciphered as a three-core copper cable with a core cross section of 1.5 "square" (3x1.5), single-wire core (OJ). Insulation and sheath made of PVC compound (VV), flexible cable (G), non-combustible (ng). Rated voltage 660 volts.
Remember! The letter designation of the cable brand begins with the material of the core, for aluminum the letter A is always put, for copper — the letter is not indicated, therefore all cables of the VVG brands of all modifications have a copper conductor.
6. Coloring of cores
You need to know about the coloring that it is either solid color, or a strip is applied on the sheath along the entire cable with a width of about a millimeter. This is the standard. Everything else, in the form of smudges, spots, stripes across - from the evil one. And he says that incomprehensible people made the cable in some basement.
According to the colors of the veins, there is a table that any experienced electrician knows. It is written there what shade the main conductors are indicated - phase, zero, grounding. This was done for ease of installation, in order to see where which conductor to connect. Phase and working conductors may differ in color, but the “earth” is always “painted” in yellow-green color.

7. Packing
Standard for all types is a bay or a drum. Coils go for sale in stores, they are wound on drums for wholesalers, builders and other large buyers. In any case, a label with a description is attached to the cable.
The content of the tag repeats the information of the inscription on the shell with some additions. It states:
- manufacturer's name or trade mark
- brand (designation) of products
- GOST or TU
- Release date
- number of segments with their length
- drum number
- conductor weight
- mark of conformity
- OTC mark.
If you came to buy a cable for wiring in an apartment with a whole bay of 100 m, you will receive a tag along with it. But if a piece is cut off for you, then the label will not be given away, you can just look at it.
8. Certificate
It is necessary to confirm that the cable is of high quality. Typically, products have 2 documents - a certificate of conformity, which is responsible for the suitability of the cable as an electrical installation material, and a fire safety certificate. You can ask the seller to review them. Documents must be filled out indicating GOSTs for the cable and have a valid deadline, for example, until the end of the current year. As a rule, the documentation indicates TU (technical specifications) according to GOST and for cable products this is tantamount to compliance with GOST.
9. Condition
This is the appearance of the power wire. Pay attention to how the cable looks, because behind the bruises, strong kinks, and compression, there is an internal defect. The veins can be broken and even closed to each other. It is clear that it is impossible to lay such material, therefore, do not be too lazy to inspect the cable in the store, even before paying for an independent purchase.
What cable is needed for wiring in the apartment
We have already said that the wiring in the apartment "requires" 2 cable sections.
For sockets, you need to take a cross section of 2.5 mm 2, because the included load can reach 3-4 kilowatts. A cable of two and a half "squares" is just designed for a maximum power of up to 5.9 kilowatts and a current of up to 27 amperes. This does not mean that you need to "load" the cable line to the limit. The choice always comes with a margin of the planned load by a third. Moreover, the cable lying under the plaster cools less and this is also taken into account when selecting.
For the lighting circuit, a cross section of 1.5 mm 2 is used. The load here is much less, but even if you decide to arrange illumination in the apartment, the current and power reserve will be more than enough.
Important information! Since modern electrical safety rules require grounding household electrical appliances and installing special sockets, a three-core cable is used for installation. In which, there is a working phase conductor, zero working and protective zero.
Which cable does the online store recommend for hidden wiring in a house or apartment
Recall that the marking contains the main characteristics of cable products. The letter designations indicate the materials of the cores, insulation, sheaths and flexibility, the digital designations indicate the number of conductive cores and their cross section.
VVG cable
The most common domestic cable for electrical installation in an apartment. It has single-core copper conductors, insulation and sheath made of PVC compound, it is used in rooms with normal and high humidity. Designed for voltage up to 660 volts. Refers to flexible unarmoured power wires. It can include from 1 to 5 cores, with a cross section from one and a half to 240 "squares". The shape of the conductor is round, flat or triangular.
VVG cables are available in several modifications:
- VVG - the main type with vinyl insulation and sheath;
- VVGng - non-combustible power wire, self-extinguishing core insulation, that is, combustion does not spread;
- VVGng-LS - also has self-extinguishing non-combustible core insulation (ng) and a sheath with low smoke emission;
- VVGng FR-LS - in addition to incombustibility and low smoke, this type of cable received additional fire protection from mica tape.
All brands with the prefix ng can be mounted in bundles, that is, lay several cable lines in one corrugation, pipe or pit.
| For sockets | For switches |
| VVGng 3x2.5 | VVGNG 3x1.5 |
| VVGng-LS 3x2.5 | VVGng-LS 3x1.5 |
Conventional VVG is cheaper, but not suitable for bundled gaskets and the jacket is less fire resistant and fuming. And the VVGng FR-LS brand is professional and is used in conditions of increased fire hazard in enterprises and is much more expensive.
NYM cable
European standard copper cable developed in Germany. It is produced at Russian factories and complies with EU and GOST standards. It is similar in design to the VVGng cable, rated voltage is 660 V. A single-wire stranded NYM cable with a cross section of 1.5-10 mm2 and a multi-wire cable with a cross section of 16 mm2 or more are produced. Number of cores 1-5, PVC insulation and sheath, incombustibility is ensured by a rubber filler between the core insulation and the cable sheath.
Note! In stores you can find cheap cables marked NUM. This "typo" says that you have a copy with reduced performance. By buying it, you risk getting low-quality products. We advise you to refrain from dubious savings on security.
VVGng and NYM cables have similar characteristics and advantages of use:
- Quality performance. Cores, insulation, sheath comply with GOST and this makes the cable reliable.
- Convenient installation and easy cutting. The round cable is easy to install due to the absence of twists, it is easier to seal it during input.
- High fire resistance and safety. Compliance with standards ensures safe operation of the cable under load, and special insulation allows it to be laid in bundles, without the risk of ignition from mutual heating.
- Self-extinguishing and low smoke. The sheath material is self-extinguishing and slows down combustion. It also provides low smoke without dangerous halogens. If the protection works with a delay, then the damage from fire will be minimal.
- Large selection of options in stamps at a price for any budget.
Which wire is not suitable for wiring in an apartment
And one more important point. We understand that for most people "wire" and "cable" are synonymous. In fact, these are different types of cable products. The main difference is that the cable always has a very strong two-layer insulation, with the first layer over the conductive cores and the second one covering the entire bundle. Even if there is only one core in the cable, the insulation is always double. Wire is a weaker construction with light insulation.
Note! Making wiring in an apartment with a wire, even stranded or stranded, is a very bad idea.
The main trouble with wires is their poor resistance to prolonged heating under constant load and high flammability. Therefore, they do not meet the requirements of the PUE for wiring in residential premises.
PVC wire
| PVA |
This is a connecting copper wire with vinyl insulation and sheath. Used to connect household electrical appliances to the home network, for the manufacture of extension cords. The number of conductors is 2-6, the core structure is multi-wire, the cross section is 0.75-10 mm2. Designed for a voltage rating of 380 V.
Attention! No need to take the PVA wire for wiring on the advice of friends or from savings.
- Firstly, PVS have a multi-wire core design. And this means that all the ends for the connection must be tinned and must be soldered. This takes a lot of time and requires high quality core processing and a lot of experience from an electrician.
- Secondly, the multi-wire core construction is a factor of increased fire hazard. Such a wire heats up more, which means that the insulation wears out faster, which is dangerous and can result in a short circuit.
- Thirdly, the PVA wire cannot be laid in a bundle, like a cable. Only with the distance between the threads. That is, ditch the walls for each line separately.
So, the savings are very doubtful and symbolic. The low price of the wire will be "eaten" by the high cost of installation. And the quality of the wiring leaves much to be desired.
Wire SHVVP and PVVP
| SHVVP, PVVP |
Mounting cords or cables with single and stranded copper conductors. Used to connect electrical equipment and household appliances. They have a short service life, the stranded type requires processing of the ends and soldering during installation. They are not suitable for fixed wiring due to the lack of non-combustible insulation and poor performance.
Wire PUNP
Attention! PUNP has been banned for wiring since 2007 due to its unreliability.
Although there are "craftsmen" among both customers and unfortunate electricians who use it. Motivating this by the fact that "it is he who stands in all the old apartments."
But the "citizens" forget that since the days of the USSR, the equipment of home electrical equipment has changed a lot and its power has increased. Therefore, PUNP was banned - it is low-power, with poor insulation and does not hold modern loads.
The online store site offers only high-quality cable for electrical wiring in an apartment or house. A complete list of brands and types in the section:
Come and choose your cable!
Also, ask any questions. Funny and naive in the first place! They are the most correct! Because it's better to make electricians laugh than firefighters, agree?
We always answer questions and talk about all the intricacies of installation. We quickly select a complete set for the device of apartment wiring from cable to sockets and switches. We take into account your wishes and budget.
Call, ask! Phones
Content:
Electricity is very convenient for its consumers, including the fact that it is easily transmitted through wires, cords and cables. They form the basis of the electrical grids on which modern civilization rests. For this reason, the efficiency of electrical conductors is of great importance with far-reaching consequences. Their failure leads to disconnection of the electrical circuit with this emergency element for at least tens of minutes. In this case, disruptions in power supply can be fraught with significant losses throughout the infrastructure.
The main design features of the wires
Like any product, the wire has a certain design. In electrical engineering, conductors are necessarily combined with insulators. As a result, the wires can be either without insulation (bare) or with an insulating coating.

The conductor part is called the "vein". In fact, this is one or more high-quality metal wires with minimal resistance.

The most common are copper and aluminum conductors. These metals are the most accessible for mass use. However, the best veins are obtained from silver. For this reason, usually for a minimum resistance, the copper core is covered with a layer of silver. The high cost limits its use for the manufacture of conductor products. Copper and aluminum are soft and ductile materials.
If a wire with copper or aluminum strands experiences a mechanical tensile load, it elongates relatively quickly. To prevent this from happening, a steel core is introduced into its composition. In some cases, the wire has to be made entirely of steel wires. Usually these are especially long spans of power lines. The fact that wires are used for this is beyond doubt. But what then is a cord or a cable?
Cords and cables
- Cord is a piece of flexible stranded insulated wire, which is used for detachable connection of electricity consumers.

During operation, the cord is subjected to multiple bends. They are known to cause cracks and breakage when repeated in the same place. Therefore, the properties of the insulation and the thickness of the wires determine the life of the cord. The woven structure is best counteracted by the destructive effect of bending. It, like the stranded conductive part of the wire, consists of thin threads. But not from a conductor, but from an insulator - fiberglass, cotton or lavsan.
The insulating coating of the cord is selected according to the characteristics of the electrical appliance. For example, any electric iron is connected to the mains only with a cord whose outer layer is made of woven cotton or fiberglass. Polymeric materials may melt if accidentally contacted with a heated iron. The consequence of this is likely to be a short circuit or electric shock.

- A cable is a structure with at least two conductive cores and several layers of insulation, each of which performs its own function. For certain purposes, one or more layers of insulation are replaced by a metal layer, for example, for strength.
In some cases, in a cable with two conductors, only one of them is used to transfer the load current. For example, in a coaxial cable used at high frequencies, the outer core can be used as a shield.

The role of the insulating layer
The insulation used in wires, cords and cables performs a protective function. It safely separates the conductive wires and the person coming into contact with these products from each other. But the insulation properties depend on the operating conditions. Their violation can lead to a violation of the insulating layer. The consequence of this sooner or later will be either a short circuit or an electric shock. A short circuit results in a high temperature zone.
If there is no disconnection of the electrical circuit with a fault, this zone can move along the core, melting it and destroying the insulation. The most critical in terms of reliability are the junctions of the cores in the wire segments. These places are always securely isolated in one way or another. The most convenient and common of these is the use of insulating tape.

A more reliable, but at the same time technically complex way of insulating wires is an insulating tube with thermal shrinkage (cambric). It must correspond to the diameter of the connected wires. You also need a fairly efficient heat source for its temperature deformation. In strong winds or in a room with a high explosion hazard, such a source cannot be used. But if everything is done properly, the tube fits snugly and securely to the wires. Better than duct tape.


Variety of wires
There are many different wires for one purpose or another. For their systematization, a certain marking is used. That is, each wire corresponds to a particular brand. The manufacturer supplies pieces of wire, cable or cord that are either coiled or wound on a spool. At the same time, a label is placed indicating the brand and other necessary data.

The data given on the label is necessary for product identification. Its preliminary selection is made according to special directories and other sources. They contain tables with a list of information to compare the technical capabilities of the wires with the operating conditions of a particular user.

- When choosing a wire, it is necessary to know the limits of voltage and current changes in the designed electrical network or electrical circuit. If the selected wire does not meet these limits, either an unjustified increase in the cost of the wire or an unacceptable reliability of the end result will result.
Marking
The brand of the wire is formed as an alphanumeric designation. First, the letters indicate the purpose of the wire (W - cord):


Then the numbers corresponding to the number of cores and their cross section are indicated. It is the last in the designation and is indicated in square millimeters. In general, the above can be shown in the image:

For example, Rubber Wire 2-core with a core diameter of 1.5 sq. mm:

Three main groups of wires
Wires are used both indoors and out. Bare wires are used exclusively in the open air, mainly for power lines. Coated wires are the most widely used. Most of all, different brands of wires are in conditional groups, referred to as
- installation (i.e. designed for open and hidden wiring);

- assembly (i.e. for the installation of electrical equipment);

- winding (for the manufacture of windings of electrical machines and devices with electromagnetic coils).


Installation
Installation wires are produced in a wide range of insulated wire cross-sections, which can be from one to four. The maximum cross section reaches 500 square meters. mm, and the minimum starts from 0.5 sq. mm. The material is both copper and aluminum. The number of wires - from one to several tens. The most widely used wires are PVC (polyvinylchloride) and PE (polyethylene) insulated wires. The reason for this is the cheapness of such insulation. But there are brands of installation wires coated with special varnishes, as well as with silk and rubber insulation.

Mounting
For mounting wires, it is characteristic that their cores are made only of copper. The installation process involves a large number of wire bends. Aluminum conductors do not tolerate this well due to brittleness, which manifests itself during repeated bending. But one more feature of aluminum cores lies in the fact that their soldering is difficult and accessible mainly to specialists. And during installation, the need to perform this procedure cannot be completely excluded. The insulating coating of some brands of mounting wires, due to their adaptation for soldering, is made two-layer. The layer in contact with the core is made of a thread with which the core is wrapped. The thread can be fiberglass, nylon or lavsan. It prevents melting during soldering of the outer insulating layer of PVC or PE. The cross section of the wires in the cores can be in the range of 0.05–6 sq. mm.
- Most brands of mounting wires begin with the letter M.

Winding
Winding wires are mainly single-wire and are used for the manufacture of various electromagnetic and resistive winding elements. Since in electromagnetic devices it is important to obtain the smallest distance between the turns, the core is covered with a special varnish insulation of minimum thickness. Licensees are an exception. These wires are used to make high frequency coils. Therefore, the licendrate wire is stranded and in multilayer insulation. At the same time, the wires lived the thinnest in comparison with other brands of wires.

In addition to coils wound with copper and aluminum wire, resistors are produced, the wire of which is made of other metals. They are made of nichrome, constantan and manganin and are used in both electrical circuits and electric heaters.
- Most brands of winding wires begin with the letter P.


Conclusion
The suitability for use of any piece of wire is checked with a tester (multimeter) and inspection of the condition of the insulating layer. The device in the resistance measurement mode checks the absence of a break in the core, which is not visible under the insulation layer. The insulation must not be damaged by cuts or punctures. There should be no scratches on the varnish layer.
The correct choice of wire is one of the main conditions for the efficient operation of electrical circuits and networks.
Today, few people imagine their life without the use of electrical appliances. However, electricity is not only the key to a comfortable life, but also a source of danger. When thinking about electrifying your own home or about repairs that involve changing wiring, you need to carefully consider the issue of fire safety.
In addition, it will be important to choose the best wires for electrical wiring, taking into account specific conditions. The nuances of choice and varieties will be discussed below.

Varieties
Consider the types of wires and their purpose for internal and external (street) conduction of the electrical network. The material for the manufacture are copper and aluminum.

Today, preference is given to wires with copper conductors, since this metal has much less resistance. Copper wire is able to give more power and pass more current than aluminum, despite the same cross section.









In addition, the service life of the copper product is longer. However, aluminum is a cheaper metal, so relatively recently it has been widely used in the arrangement of wiring in residential buildings.

The number of veins also serves as the basis for the selection of varieties. Allocate single-core and multi-core wires. The former are rigid and do not bend well, the main direction of their use is the creation of simple hidden wiring.

The latter are able to bend repeatedly, have a high degree of softness. They are used as cords for connecting a wide variety of household appliances, to create extension cords. Suitable for exposed wiring. The main safety requirement for stranded wires is the presence of a double braid.

It is important to remember that the connection of different metals by twisting is strictly prohibited. Oxidation will occur, or heating and loss of contact. It is correct to do the wiring with only one type of wire (in terms of the material of manufacture).
As for the main types of wire insulation, there are several of them: rubber, PVC (the most popular option), paper (very rarely used) and fluoroplastic (the most reliable).

Hidden wiring
Marking electrical wires allows you to understand their characteristics. The abbreviation may contain letters indicating the material and numbers indicating the cross section and number of cores.
Marking of non-armored aluminum wire will be AVVG (VVG). In the absence of the letter "A", we can conclude that we have a copper wire. Hidden wiring in a dry living space or office can be made from wires of the AVVG brand.






The letter "G" means the absence of protective insulation, literally "bare" wire. Non-combustible modifications are designated as VVGng. Reduced smoke emission VVGng-LS.
You can also use SHVVP - a flat copper wire of a stranded type. The cross section of this variety is not more than 0.75 mm2.

outdoor wiring
Wooden houses, as well as retro-style interiors, involve outdoor wiring. The type of wire here depends entirely on the material of the walls.

Only wires of non-combustible brands should be used, for example, the already mentioned VVGng. Perhaps the design of the premises will make the color of the walls and wires inadequate to each other. In this case, you can use the cable channel.

street mounting
An underground electrical wire can be connected to the building, but a prerequisite for this is the use of an armored cable. The designation is as follows - AVBBSHV (VBBShV).


Reservation is carried out due to a special steel tape, which is located on top of the second layer of insulation and has its own protective rubber braid. Thus, a high degree of protection against mechanical influences and groundwater is achieved.
The armored wire is able to conduct electricity to the house for a long time and reliably. For wall mounting, wiring uses varieties of the AVVG brand of different sections. Wires are not afraid of precipitation and the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation.






In conditions of high humidity
If the room is operated in conditions of high humidity, for example, if it is a bathhouse, basement or barn, then a special wire is required to create an electrical network.
The best option would be a heat-resistant cable with protective silicone insulation. Among these, the PVKV and RKGM brands stand out. The main requirement for arranging the network is high-quality grounding not only of the wiring itself, but of all devices.
Dimensions and calculation of the wire section
There are many types of wire sections, a specific brand is chosen taking into account the device that will be connected using this wire. It is extremely important to correctly calculate the cross section.

The action plan should be as follows. First you need to calculate the sum of the capacities of all consumers inside the house and outside it (street lighting, for example). The resulting value will allow you to select the main cable leading from the power line through the meter to the house.

Then the total power for each room or individual area is calculated. The wires from the main switchboard must match the value obtained. The wiring for each section is carried out depending on the specific consumer, whether it is a simple light bulb or a TV.

In general, you can find out the required wire cross-section, based on the power of the consuming device, from a special table. It is easy to find on the net or in any good reference book on the subject of electricians. When making calculations, rounding up is carried out to provide some margin in case of unforeseen circumstances.






How to make a choice
The question of which wires to choose should be decided by an electrician. But if you have some experience and basic knowledge, you can make the right choice yourself. The main thing is that the cross section of the purchased wires fully corresponds to the power consumption. Installation of open wiring involves a combination of wire color and wall material.

There are wires, the operation of which, for reasons of fire safety, is not recommended. Among them: PUNP, PUVP, PBPP and PUGP. Outwardly, they differ little from less dangerous counterparts, so you need to be extremely careful, but it is better to entrust the matter to a specialist.

It will not be superfluous to check the certificates for products from the manufacturer. Conscientious sellers must have documentation without fail.


Be guided not only by viewing a photo of wires from a catalog or scraps at an exhibition stand. Check the markings on the bay itself. Then there will be much more guarantees for the purchase of the necessary products. If any designations are missing, it is better to refuse to purchase such a product.

The electrification of the premises, carried out with careful preliminary calculations and without saving on materials, gives a durable and safe result. The excellent quality of the wires, the required cross section and the observance of elementary safety rules during installation and operation will allow you to achieve a high level of comfort in your home.

Photo of wires of different types

















